什么是线程?
线程是程序中执行的线程。(来自JDK8API)
程序一旦跑起来,就变成了进程,而线程是进程的最小单位。
创建方式一: 继承Thread类
Thread 类:直接继承于Object ,它是实现了Runnabble 接口的。
最基本的创建使用方式:
// 方式一 :1. 继承Thread
public class TestThread extends Thread {
// 2. 重写Run方法
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
// main线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3.创建线程对象
TestThread t1 = new TestThread();
// 4.调用start()方法开启线程 线程开启后不一定马上执行。具体由cpu调度
t1.start();
}
}
测试是否同时执行:
// 方式一 :1. 继承Thread
public class TestThread extends Thread {
// 2. 重写Run方法
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我是run - 我在看书。--");
// 休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// main线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3.创建线程对象
TestThread t1 = new TestThread();
// 4.调用start()方法开启线程
t1.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我是main - 我在看代码。 --");
// 休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
输出结果相互交叉,从而得知,这两个线程是同时执行的。

继承Thread类的案例:
使用CommonsIO工具实现多线程下载
maven 依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-io/commons-io -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
</dependency>
package com.java.Thread;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
// 实现多线程下载图片
public class ThreadDemo extends Thread {
private String url;
private String path;
public ThreadDemo(String url, String path) {
this.url = url;
this.path = path;
}
// 线程体
@Override
public void run() {
WebDownloader webDownloader = new WebDownloader();
webDownloader.downloaderImg(url, path);
System.out.println("图片" + path + "下载完成");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ThreadDemo t1 = new ThreadDemo(
"https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3323791702,320789907&fm=26&gp=0.jpg",
"1.jpg");
ThreadDemo t2 = new ThreadDemo(
"https://ss2.bdstatic.com/70cFvnSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=1779655133,2327716287&fm=26&gp=0.jpg",
"2.jpg");
ThreadDemo t3 = new ThreadDemo(
"https://ss0.bdstatic.com/70cFuHSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2938289910,1021943104&fm=26&gp=0.jpg",
"3.jpg");
// 三个线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
// 下载器
class WebDownloader {
public void downloaderImg(String url, String path) {
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(path));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exception in WebDownloader - downloaderImg");
}
}
}
运行结果:

创建方式二:实现Runnable接口
public class TestRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我是run - 我在看书。--");
// 休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建线程对象
TestRunnable runnable = new TestRunnable();
// 作为参数传入Thread
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable);
// 开启线程
thread1.start();
// main 线程
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我是main - 我在写代码。--");
// 休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
小结:

创建方式三:实现Callable接口

package com.java.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
// 创建线程对象
TestCallable testCallable = new TestCallable();
// 创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 提交执行
Future<Boolean> r1 = ser.submit(testCallable);
Future<Boolean> r2 = ser.submit(testCallable);
Future<Boolean> r3 = ser.submit(testCallable);
// 获取结果
Boolean boolean1 = r1.get();
Boolean boolean2 = r1.get();
Boolean boolean3 = r1.get();
// 关闭服务
ser.shutdown();
}
}
初识并发问题
多个线程操作同一对象的情况下。线程不安全的问题
package com.java.Thread;
// 多个线程同时操作同一个对象
// 买火车票的例子
public class RunnableDemo implements Runnable {
private int total = 10; // 票数
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (total <= 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到了第" + total-- + "票");
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RunnableDemo runnableDemo = new RunnableDemo();
// 多个线程 同时卖票
new Thread(runnableDemo, "小明").start();
new Thread(runnableDemo, "小红").start();
new Thread(runnableDemo, "黄牛党").start();
}
}

静态代理
线程 就是静态代理实现的
package com.java.proxy;
public class StaticProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
You you = new You();
new ProxyRole(you).start();
}
}
interface ProxyInter {
public void start();
}
// 真实对象
class You implements ProxyInter {
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("You");
}
}
// 代理对象
class ProxyRole implements ProxyInter {
private You you;
public ProxyRole(You you) {
this.you = you;
}
@Override
public void start() {
before();
you.start();
after();
}
private void after() {
System.out.println("之后");
}
private void before() {
System.out.println("之前");
}
}
常用方法
sleep:

// 模拟计时
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(LocalDateTime.now()));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
tenDown();
}
yield:

Join: 合并线程 等待这个线程执行完后,再执行其他线程,可以理解为插队。
class Test2 implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Test2 test2 = new Test2();
Thread thread = new Thread(test2);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (i == 200) {
thread.join(); // 执行到这里的时候。会把run执行到结束,然后再继续执行main
}
System.out.println("main 线程" + i);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("run" + i);
}
}
}
执行结果

Thread.state:

package com.java;
public class ThreadState {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("///");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) { // 只要线程不终止就一直输出
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
线程优先级
线程优先级并不是绝对的
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---> " + "Priority" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
Priority priority = new Priority();
Thread t1 = new Thread(priority);
Thread t2 = new Thread(priority);
Thread t3 = new Thread(priority);
Thread t4 = new Thread(priority);
Thread t5 = new Thread(priority);
t1.setPriority(7);
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(4);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(5);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(3);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(10);
t5.start();
}
}
class Priority implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out
.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + "Priority" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
守护线程

// 测试守护线程
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true); // 设置为守护线程 。 默认为false 表示是用户线程
thread.start(); // 守护线程启动
new Thread(you).start(); // 用户线程
}
}
class God implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("IIIIIIIIIII");
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) {
System.out.println("Happy one day");
}
System.out.println("goodBy world");
}
}
由此可以看到。当守护线程开启后,守护线程会一直在允许,直到用户线程结束。
线程同步


线程不安全的例子:
// 线程不安全的List
public class UnSafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
arrayList.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(arrayList.size()); // 期待值为1000 因为上面add了1000次
}
}
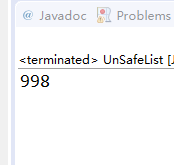
原因是,多条线程同时操作时 添加到了list的同一个位置,然后被覆盖了。造成了线程不安全。

买票 案例:
package com.java;
public class BuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Buy buy = new Buy();
Thread t1 = new Thread(buy, "小明");
Thread t2 = new Thread(buy, "小红");
Thread t3 = new Thread(buy, "黄牛党");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
class Buy implements Runnable {
private int total = 10; // 总票数
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
buy();
}
System.out.println("以售罄!");
}
// synchronized 同步方法,默认锁的是this
private synchronized void buy() {
if (total <= 0) {
flag = false;
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了第" + total-- + "票");
}
}
同步块


JDK 自带 线程安全List
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
死锁

死锁: 多个线程互相抱着对方的需要的资源,从而形成僵持。
死锁案例:
package com.java;
// 测试死锁
public class TestLock {
/**
* 场景: 有一个口红 和 一个镜子 有个女孩需要化妆
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup makeup = new Makeup(0, "小红");
Makeup makeup2 = new Makeup(1, "小白");
makeup.start();
makeup2.start();
}
}
// 口红
class Lipstick {
}
// 镜子
class Mirror {
}
class Makeup extends Thread {
// 用static 保证 镜子和口红只有一份
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice; // 选择
String girlName; // 使用化妆品的人
public Makeup(int choice, String girlName) {
this.choice = choice;
this.girlName = girlName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 化妆
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if (choice == 0) {
synchronized (lipstick) { // 一开始进来 拿到口红
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红");
Thread.sleep(1000); // 后想获得镜子
synchronized (mirror) {
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子");
}
}
} else {
synchronized (mirror) { // 一开始进来 拿到镜子
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子");
Thread.sleep(2000); // 后想获得口红
synchronized (lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红");
}
}
}
}
}

lock

package com.java;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
// 使用Lock
public class TestLock2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
tick tick = new tick();
new Thread(tick).start();
new Thread(tick).start();
new Thread(tick).start();
}
}
class tick implements Runnable {
int total = 10;
// 定义lock 锁
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
lock.lock(); // 加锁
if (total <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在卖票" + "当前第" + total-- + "张");
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
线程池


Executors.newCacheThreadPool():可缓存线程池,先查看池中有没有以前建立的线程,如果有,就直接使用。如果没有,就建一个新的线程加入池中,缓存型池子通常用于执行一些生存期很短的异步型任务
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int n):创建一个可重用固定个数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程。
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(int n):创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor():创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。






















 9万+
9万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








