一、备忘录模式的介绍
1、定义
备忘录模式是指在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样,以后就可以将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
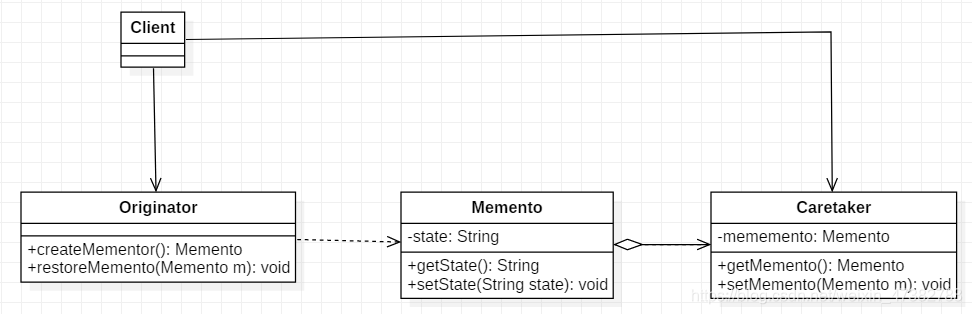
备忘录模式的角色划分:
- 发起人角色(Originator):该角色记录当前时刻的内部状态,负责定义哪些属于备份范围的状态,负责创建和恢复备忘数据。
- 备忘录角色(Memento):该角色负责存储发起人角色的内部状态,在需要时提供发起人需要的内部状态数据。
- 负责人角色(Caretaker):该角色对备忘录角色进行管理、保存和提供备忘录。
备忘录模式的类图如下:
2、使用场景
- 需要保存和恢复数据的相关状态场景。
- 提供一个可回滚的操作。
- 需要监控副本的场景。例如:监控一个对象的属性,但是监控又不应该作为系统的主业务来调用,它只能是边缘调用,即使出现监控不准、错误报警也影响不大,因此,一般做法是备份一个主线程中的对象,然后由分析程序来分析。
- 数据库连接的事务管理使用的就是备忘录模式。
3、优缺点
(1)优点
- 它提供了一种状态恢复的实现机制,使得用户可以方便地回到一个特定的历史步骤,当新的状态无效或者存在问题时,可以使用暂时存储起来的备忘录将状态复原。
- 备忘录实现了对信息的封装,一个备忘录对象是一种原发器对象状态的表示,不会被其他代码所改动。备忘录保存了原发器的状态,采用列表、堆栈等集合来存储备忘录对象可以实现多次撤销操作。
(2)缺点
- 资源消耗过大,如果需要保存的原发器类的成员变量太多,就不可避免需要占用大量的存储空间,每保存一次对象的状态都需要消耗一定的系统资源。
二、备忘录模式的实现
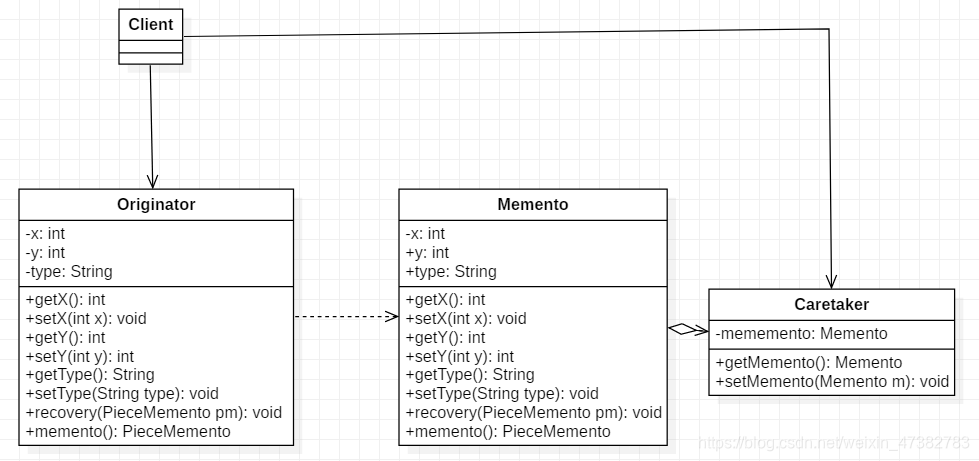
场景描述:棋类游戏中的悔棋过程。其类图如下:
实现如下:
/**
* 棋子类:发起人角色
*/
public class Piece {
//下棋的位置
private int x;
private int y;
//棋子的类型
private String type;
public Piece(int x, int y, String type) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.type = type;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
/**
* 悔棋操作
* @param pm
*/
public void recovery(PieceMemento pm){
this.x = pm.getX();
this.y = pm.getY();
this.type = pm.getType();
}
/**
* 备忘操作
* @return
*/
public PieceMemento memento(){
return new PieceMemento(this);
}
}
/**
* 备忘录角色
*/
public class PieceMemento {
//棋子的位置
private int x;
private int y;
//棋子的类型
private String type;
public PieceMemento(Piece p) {
this.x = p.getX();
this.y = p.getY();
this.type = p.getType();
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
/**
* 负责人角色
*/
public class Caretaker {
//备忘录对象
private PieceMemento pieceMemento;
public PieceMemento getPieceMemento() {
return pieceMemento;
}
public void setPieceMemento(PieceMemento pieceMemento) {
this.pieceMemento = pieceMemento;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Caretaker caretaker = new Caretaker();
Piece piece = new Piece(0, 1, "黑棋");
caretaker.setPieceMemento(piece.memento());
System.out.println(piece.getType() + "的位置: " + piece.getX() + " : " + piece.getY());
piece.setX(4);
piece.setY(5);
piece.setType("白棋");
System.out.println(piece.getType() + "的位置: " + piece.getX() + " : " + piece.getY());
piece.recovery(caretaker.getPieceMemento());
System.out.println(piece.getType() + "要悔棋,新的位置: " + piece.getX() + " : " + piece.getY());
}
}





















 2687
2687











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








