seq2seq模型——机器翻译
1 任务目标
1.1 案例简介
seq2seq是神经机器翻译的主流框架,如今的商用机器翻译系统大多都基于其构建,在本案例中,我们将使用由NIST提供的中英文本数据训练一个简单的中英翻译系统,在实践中学习seq2seq的具体细节,以及了解机器翻译的基本技术。
1.2 seq2seq模型
从根本上讲,机器翻译需要将输入序列(源语言中的单词)映射到输出序列(目标语言中的单词)。正如我们在课堂上讨论的那样,递归神经网络(RNN)可有效处理此类顺序数据。机器翻译中的一个重要难题是输入和输出序列之间没有一对一的对应关系。即,序列通常具有不同的长度,并且单词对应可以是不平凡的(例如,彼此直接翻译的单词可能不会以相同的顺序出现)。
为了解决这个问题,我们将使用一种更灵活的架构,称为seq2seq模型。该模型由编码器和解码器两部分组成,它们都是RNN。编码器将源语言中的单词序列作为输入,并输出RNN层的最终隐藏状态。解码器与之类似,除了它还具有一个附加的全连接层(带有softmax激活),用于定义翻译中下一个单词的概率分布。以此方式,解码器本质上用作目标语言的神经语言模型。关键区别在于,解码器将编码器的输出用作其初始隐藏状态,而不是零向量。
1.3 数据和代码
本案例使用了一个小规模的中英平行语料数据,并提供了一个简单的seq2seq模型实现,包括数据的预处理、模型的训练、以及简单的评测。
1.4 评分要求
分数由两部分组成,各占50%。第一部分得分为对于简单seq2seq模型的改进,并撰写实验报告,改进方式多样,下一小节会给出一些可能的改进方向。第二分部得分为测试数据的评测结果,我们将给出一个中文测试数据集(test.txt),其中每一行为一句中文文本,需要同学提交模型做出的对应翻译结果,助教将对于大家的提交结果统一机器评测,并给出分数。
1.5 改进方向
-
初级改进:
-
将RNN模型替换成GRU或者LSTM
-
使用双向的encoder获得更好的源语言表示
-
对于现有超参数进行调优,这里建议划分出一个开发集,在开发集上进行grid search,并且在报告中汇报开发集结果
-
引入更多的训练语料(如果尝试复杂模型,更多的训练数据将非常关键)
-
-
进阶改进:
-
使用注意力机制(注意力机制是一个很重要的NMT技术,建议大家优先进行这方面的尝试,具体有许多种变体,可以参考这个综述)
-
在Encoder部分,使用了字级别的中文输入,可以考虑加入分词的结果,并且将Encoder的词向量替换为预训练过的词向量,获得更好的性能
-
-
复杂改进:
-
使用beam search的技术来帮助更好的解码,对于beam-width进行调优
-
将RNN替换为Transformer模型,以及最新的改进变体
-
1.6 参考
[1] ml/NLPTrainingCamp/seq2seq at 8dfefc2f41e3cee96efb9e81a3cba97ec3cb0f29 · hotbaby/ml (github.com)
2 seq2seq 基本实现
2.1 seq2seq 基本原理
Seq2Seq(Sequence-to-Sequence,序列到序列)是一种处理序列数据的机器学习模型,尤其在自然语言处理(NLP)领域中非常流行。
Seq2Seq模型的架构通常由两个基本组件组成:编码器(Encoder)和解码器(Decoder)。

- 编码器(Encoder):负责学习源语言的表示。编码器的任务是读取输入序列(例如,一句话或一段文本),并将其转换成一个固定大小的内部表示,通常称为“上下文向量”(Context Vector)。这个向量旨在捕捉输入序列的主要信息,以便解码器可以生成输出序列。
- 解码器(Decoder):解码器可以看作一个条件语言模型,它基于编码器学到的表示产生目标语言。解码器的任务是使用编码器生成的上下文向量来生成输出序列。解码器通常是一个循环神经网络(RNN),它可以逐步生成输出序列的每个元素。
2.2 代码实现
项目中已给出可以运行的完整代码,但是测试下来发现某些中文字符无法预测,经过修改后,以下是代码实现的详细介绍。
-
读取数据
我们将读取目录下的
cn-eng.txt文件,其中每一行是一个平行句对,例子如下我們試試看! Let's try something.-
对于单词进行编号
定义了一个
Lang类,用于处理文本分词,这里除了引入了三个特殊的Token:SOS, "Start of sentence”,标识句子开始EOS, “End of sentence”,表示句子结束UNK, “Unknown Token”,标识未登录词
SOS_token = 0 EOS_token = 1 UNK_token = 2 class Lang: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name # 语言名称 self.word2index = {} # 词到索引的映射 self.word2count = {} # 词到出现次数的映射 self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS", 2: "UNK"} # 索引到词的映射 self.n_words = 3 # 单词的数量 # 索引句子中的单词 def index_words(self, sentence): if self.name == 'cn': for word in sentence: self.index_word(word) else: for word in sentence.split(' '): self.index_word(word) # 索引单个单词 def index_word(self, word): if word not in self.word2index: self.word2index[word] = self.n_words self.word2count[word] = 1 self.index2word[self.n_words] = word self.n_words += 1 else: self.word2count[word] += 1 -
文本预处理
丢弃除了中文、字母和常用标点之外的符号。
# Turn a Unicode string to plain ASCII, thanks to http://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427 def unicode_to_ascii(s): return ''.join( c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s) if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn' ) # Lowercase, trim, and remove non-letter characters def normalize_string(s): s = unicode_to_ascii(s.lower().strip()) s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s) s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z\u4e00-\u9fa5.!?,。?]+", r" ", s) return s读取平行语料,并进行清理。
def read_langs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False): print("Reading lines...") # Read the file and split into lines lines = open('%s-%s.txt' % (lang1, lang2)).read().strip().split('\n') # Split every line into pairs and normalize pairs = [[normalize_string(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines] # Reverse pairs, make Lang instances if reverse: pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs] input_lang = Lang(lang2) output_lang = Lang(lang1) else: input_lang = Lang(lang1) output_lang = Lang(lang2) return input_lang, output_lang, pairs -
过滤句子
样例为了加快训练,只保留了不长于10个单词的句对,真正实验中将更多数据考虑进来可能获得更好的效果。
MAX_LENGTH = 10 def filter_pair(p): return len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH def filter_pairs(pairs): return [pair for pair in pairs if filter_pair(pair)]处理数据的全过程:
-
读取数据,每一行分别处理,将其转换成句对
-
对于文本进行处理,过滤无用符号
-
根据已有文本对于单词进行编号,构建符号到编号的映射
def prepare_data(lang1_name, lang2_name, reverse=False): input_lang, output_lang, pairs = read_langs(lang1_name, lang2_name, reverse) print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs)) pairs = filter_pairs(pairs) print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs)) print("Indexing words...") for pair in pairs: input_lang.index_words(pair[0]) output_lang.index_words(pair[1]) return input_lang, output_lang, pairs input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepare_data('cn', 'eng', False) # Print an example pair print(random.choice(pairs)) -
-
-
将文本数据转换为张量
为了训练,我们需要将句子变成神经网络可以理解的东西(数字)。每个句子将被分解成单词,然后变成张量,其中每个单词都被索引替换(来自之前的Lang索引)。在创建这些张量时,我们还将附加EOS令牌以表示该句子已结束。

此处添加
UNK_token以免出现未标识的中文字符。# Return a list of indexes, one for each word in the sentence def indexes_from_sentence(lang, sentence): """ 根据词表,将句子转化成索引列表。 :reutrn list,e.g. [1, 2, 3, 4] """ if lang.name == 'cn': return [lang.word2index[word] if word in lang.word2index else UNK_token for word in sentence ] else: return [lang.word2index[word] if word in lang.word2index else UNK_token for word in sentence.split(' ')] def variable_from_sentence(lang, sentence): """ 将句子转换成Tensor. :return Tensor, shape(n, 1) """ indexes = indexes_from_sentence(lang, sentence) indexes.append(EOS_token) var = torch.LongTensor(indexes).view(-1, 1) if USE_CUDA: var = var.cuda() return var def variables_from_pair(pair): """ 将平行语料对转化成Tensors. :return (input_tensor, output_tensor) """ input_variable = variable_from_sentence(input_lang, pair[0]) target_variable = variable_from_sentence(output_lang, pair[1]) return (input_variable, target_variable) -
组件模型
介绍训练需要的组件。
-
编码器
采用 RNN 架构的编码器,将输入序列(如一句话或一段文本)转换成一个固定大小的内部表示,即上下文向量。
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, n_layers=1): super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) self.rnn = nn.RNN(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers) def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden): # Note: we run this all at once (over the whole input sequence) seq_len = len(word_inputs) embedded = self.embedding(word_inputs).view(seq_len, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.rnn(embedded, hidden) return output, hidden def init_hidden(self): hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers, 1, self.hidden_size) if USE_CUDA: hidden = hidden.cuda() return hidden -
解码器
采用 RNN 架构的解码器,使用编码器的上下文向量和先前生成的单词来生成目标序列,一步一个单词。
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, dropout_p=0.1): super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__() # Keep parameters for reference self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.dropout_p = dropout_p # Define layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) self.rnn = nn.RNN(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) def forward(self, word_input, last_hidden): # Note: we run this one step at a time word_embedded = self.embedding(word_input).view(1, 1, -1) # S=1 x B x N rnn_output, hidden = self.rnn(word_embedded, last_hidden) rnn_output = rnn_output.squeeze(0) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(rnn_output)) return output, hidden
-
2.3 模型训练
本次实验采用在本地训练,具体训练过程及结果如下。
-
一次训练迭代
为了训练,我们首先通过编码器逐字运行输入语句,并跟踪每个输出和最新的隐藏状态。接下来,为解码器提供解码器的最后一个隐藏状态作为其第一隐藏状态,并向其提供
<SOS>作为其第一输入。从那里开始,我们迭代地预测来自解码器的下一个单词。-
Teacher Forcing
"Teacher Forcing"指的是每次都基于完全准确的上文进行解码,这样训练模型收敛很快,但是会造成实际场景和训练场景有较大差别,因为实际场景上文也都是模型预测的,可能不准确,具体细节可参考论文。
观察Teacher Forcing的网络的输出,我们可以看到该网络语法连贯,但是偏离正确的翻译。可以将其为学会了如何听老师的指示,而未学习如何独自冒险。
-
Scheduled Sampling
解决强迫教师问题的方法称为“计划抽样”(Scheduled Sampling),它在训练时仅在使用目标值和预测值之间进行切换。我们将在训练时随机选择,有时我们将使用真实目标作为输入(忽略解码器的输出),有时我们将使用解码器的输出。
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5 clip = 5.0 def train(input_variable, target_variable, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): # Zero gradients of both optimizers encoder_optimizer.zero_grad() decoder_optimizer.zero_grad() loss = 0 # Added onto for each word # Get size of input and target sentences input_length = input_variable.size()[0] target_length = target_variable.size()[0] # Run words through encoder encoder_hidden = encoder.init_hidden() encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_variable, encoder_hidden) # Prepare input and output variables decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[SOS_token]]) decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # Use last hidden state from encoder to start decoder if USE_CUDA: decoder_input = decoder_input.cuda() # Choose whether to use teacher forcing use_teacher_forcing = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio if use_teacher_forcing: # Teacher forcing: Use the ground-truth target as the next input for di in range(target_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden) loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_variable[di]) decoder_input = target_variable[di] # Next target is next input else: # Without teacher forcing: use network's own prediction as the next input for di in range(target_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden) loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_variable[di]) # Get most likely word index (highest value) from output topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1) ni = topi[0][0] decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[ni]]) # Chosen word is next input if USE_CUDA: decoder_input = decoder_input.cuda() # Stop at end of sentence (not necessary when using known targets) if ni == EOS_token: break # Backpropagation loss.backward() torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm(encoder.parameters(), clip) torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm(decoder.parameters(), clip) encoder_optimizer.step() decoder_optimizer.step() return loss.item() / target_length下面是用于辅助输出训练情况的函数。
def as_minutes(s): m = math.floor(s / 60) s -= m * 60 return '%dm %ds' % (m, s) def time_since(since, percent): now = time.time() s = now - since es = s / (percent) rs = es - s return '%s (- %s)' % (as_minutes(s), as_minutes(rs)) -
-
进行训练
-
模型初始化
定义隐藏层大小和层数,初始化模型、优化器,定义损失函数。
hidden_size = 500 n_layers = 2 dropout_p = 0.05 # Initialize models encoder = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size, n_layers) decoder = DecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, n_layers, dropout_p=dropout_p) # Move models to GPU if USE_CUDA: encoder.cuda() decoder.cuda() # Initialize optimizers and criterion learning_rate = 0.0001 encoder_optimizer = optim.Adam(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) decoder_optimizer = optim.Adam(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) criterion = nn.NLLLoss()以下设置变量用于绘制图标和跟踪进度:
# Configuring training n_epochs = 50000 plot_every = 200 print_every = 1000 # Keep track of time elapsed and running averages start = time.time() plot_losses = [] print_loss_total = 0 # Reset every print_every plot_loss_total = 0 # Reset every plot_every -
实际训练
要进行实际训练,我们会多次调用训练函数,并在进行过程中打印中间信息。
# Begin! for epoch in range(1, n_epochs + 1): # Get training data for this cycle training_pair = variables_from_pair(random.choice(pairs)) input_variable = training_pair[0] target_variable = training_pair[1] # Run the train function loss = train(input_variable, target_variable, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion) # Keep track of loss print_loss_total += loss plot_loss_total += loss if epoch == 0: continue if epoch % print_every == 0: print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every print_loss_total = 0 print_summary = '%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (time_since(start, epoch / n_epochs), epoch, epoch / n_epochs * 100, print_loss_avg) print(print_summary) if epoch % plot_every == 0: plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg) plot_loss_total = 0
-
-
训练结果
运行训练代码,进行如下打印。
0m 13s (- 11m 23s) (1000 2%) 5.0433 0m 27s (- 11m 7s) (2000 4%) 4.6816 0m 41s (- 10m 46s) (3000 6%) 4.4992 ... 11m 17s (- 0m 28s) (48000 96%) 4.0000 11m 31s (- 0m 14s) (49000 98%) 3.9631 11m 45s (- 0m 0s) (50000 100%) 3.9057绘制训练 loss 曲线,结果如下。

可以看出,训练最终得到的loss值在3.9左右波动,结果并不是很好。
2.4 模型测试
-
测试代码
该代码用于评估一个给定的输入句子,并生成对应输出的翻译序列。
max_length指定了输出序列的最大长度,解码器循环max_length次,或直到生成结束符号<EOS>。def evaluate(sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): input_variable = variable_from_sentence(input_lang, sentence) input_length = input_variable.size()[0] # Run through encoder encoder_hidden = encoder.init_hidden() encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_variable, encoder_hidden) # Create starting vectors for decoder decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[SOS_token]]) # SOS if USE_CUDA: decoder_input = decoder_input.cuda() decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden decoded_words = [] decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length) # Run through decoder for di in range(max_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden) # Choose top word from output topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1) ni = topi[0][0] if ni == EOS_token: decoded_words.append('<EOS>') break else: decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[ni.item()]) # Next input is chosen word decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[ni]]) if USE_CUDA: decoder_input = decoder_input.cuda() return decoded_words -
预测测试集数据
测试集数据
test.txt是 9688 行的中文文本,编写以下代码,使用evaluate翻译test.txt为英文。def predict(filepath): """预测""" with open('test.txt') as f: sentences = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()] output_sentences = [] for sentence in sentences: output_sentence = ' '.join(evaluate(sentence)) output_sentences.append(output_sentence.strip('<EOS>')) with open(filepath, 'w') as f: f.write('\n'.join(output_sentences))翻译结果前10行结果如下。
Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? where is the ? ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she is a to . . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this is is a the . . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this is is a the . . . 我不能幫你了。 i m t you . . . 我不能幫你了。 i m t you . . . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom is mary to . . . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 my father is a the . . . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 this is is a the . . . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he is a to . . . . 可以看出,翻译效果很差。只会用一些基本词汇拼接,无法组成一个由完整意思的句子。
3 seq2seq 改进
根据 1.5 改进方向 来对 seq2seq 进行改进。
3.1 使用LSTM替换RNN
-
LSTM介绍
LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)是一种特殊的RNN,由Sepp Hochreiter和Jürgen Schmidhuber在1997年提出。LSTM设计了一种复杂的门控机制来解决传统RNN的梯度消失问题,这使得LSTM能够学习到长距离的依赖关系:
- 遗忘门(Forget Gate):这个门决定在当前状态下应该丢弃多少之前的信息。它基于当前输入和先前的隐藏状态来计算一个遗忘门的激活值。
- 输入门:这个门与遗忘门相对,它决定在当前状态下应该记住多少新的信息。输入门会更新单元状态,这是模型中的一个内部状态,可以看作是长期记忆。
- 单元状态(Cell State):LSTM有一个额外的状态,称为单元状态,它通过遗忘门和输入门的控制来更新。
- 隐藏状态:LSTM的隐藏状态是基于当前的单元状态和先前的隐藏状态计算得到的,它用作模型的输出。
LSTM的这种结构使其能够在序列数据中捕捉长期依赖关系,这在许多自然语言处理任务中非常有用,如机器翻译、文本摘要和情感分析。
-
代码改进
将编码器、解码器的RNN替换为LSTM架构,并采用
jieba进行中文分词。-
编码器
class EncoderLSTM(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, n_layers=1): super(EncoderLSTM, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) self.lstm = nn.LSTM(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers) def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden): # 注意:我们一次性处理整个输入序列 seq_len = len(word_inputs) embedded = self.embedding(word_inputs).view(seq_len, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.lstm(embedded, hidden) return output, hidden def init_hidden(self): # 初始化隐藏状态和细胞状态 hidden = (torch.zeros(self.n_layers, 1, self.hidden_size), torch.zeros(self.n_layers, 1, self.hidden_size)) if USE_CUDA: hidden = (hidden[0].cuda(), hidden[1].cuda()) return hidden -
解码器
class DecoderLSTM(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, dropout_p=0.1): super(DecoderLSTM, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) self.rnn = nn.LSTM(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) def forward(self, word_input, last_hidden): word_embedded = self.embedding(word_input).view(1, 1, -1) rnn_output, hidden = self.rnn(word_embedded, last_hidden) rnn_output = rnn_output.squeeze(0) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(rnn_output), dim=1) return output, hidden -
使用
jieba进行中文分词相比于将中文逐个字进行分词,选择使用
jieba对中文按词汇短语分词,更容易让模型学习中文。def index_words(self, sentence): if self.name == 'cn': words = list(jieba.cut(sentence)) if SEGMENTATION else sentence for word in words: self.index_word(word) else: words = sentence.split(' ') for word in words: self.index_word(word)
-
-
模型训练
模型仍然训练50000轮次,结果如下。
Epoch 1000/50000, 0m 21s (- 17m 35s), 5.2286 Epoch 2000/50000, 0m 43s (- 17m 21s), 4.8161 Epoch 3000/50000, 1m 5s (- 16m 59s), 4.6575 ... Epoch 48000/50000, 18m 0s (- 0m 45s), 3.4405 Epoch 49000/50000, 18m 23s (- 0m 22s), 3.4779 Epoch 50000/50000, 18m 45s (- 0m 0s), 3.4605Loss曲线如下图所示。

可以看到,loss最终下降到3.4左右,相比于基础版本的3.8左右的loss值有明显下降。
-
模型测试
-
文本测试
使用
evaluate()预测test.txt文件,翻译中文文本,结果前10行结果如下。Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? why can t we me to ? ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she asked her her her . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 no one are not to . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 no one are not to . . 我不能幫你了。 i can t you you . . 我不能幫你了。 i can t you you . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom is not a good good . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 i bought a a a of my . . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 this is not not this this . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he can speak speak speak . . 可以看出,翻译效果仍然并不是很好。
-
BLEU测试
随机选取100条数据,生成
cn-eng-test.txt作为验证集。def sample_test_dataset(size=100): with open('cn-eng-test.txt', 'w+') as f: f.write('\n'.join(['\t'.join(pair) for pair in random.sample(pairs, k=size)])) sample_test_dataset()通过
torchtext.data.metrics库的bleu_score来计算BLEU值。import collections from torchtext.data.metrics import bleu_score # 读取测试数据集 with open('cn-eng-test.txt') as f: lines = f.read().strip().split('\n') test_pairs = [[normalize_string(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines] test_pairs_dict = collections.defaultdict(lambda : []) for pair in test_pairs: test_pairs_dict[pair[0]].append(pair[1].split(' ')) def evaluate_bleu_score(): candicates = [] references = [] for i, pair in enumerate(test_pairs_dict.items(), start=1): candicate = evaluate(pair[0]) if candicate[-1] == '<EOS>': candicate.pop(-1) candicates.append(candicate) references.append(pair[1]) score = bleu_score(candicates, references) return score print('test dataset bleu score: %s' % evaluate_bleu_score())最终得到的 BLEU 值如下:
test dataset bleu score: 0.045502024475269916
-
3.2 使用GRU替换RNN
-
GRU介绍
**GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit)**是一种使用门控机制来控制信息流的RNN,它由Kyunghyun Cho等人在2014年提出。GRU的核心思想是通过引入两个门(update gate和reset gate)来控制信息的遗忘和记忆:
- 更新门(Update Gate):这个门决定在当前状态下应该保留多少之前的信息。它基于当前输入和先前的隐藏状态来计算一个更新门的激活值。
- 重置门(Reset Gate):这个门决定在当前状态下应该忽略多少之前的信息。它允许模型在处理当前输入时“重置”或“忘记”之前的一些信息。
- 隐藏状态:GRU的隐藏状态同时用作输出状态,这意味着它的输出是隐藏状态的直接输出。
GRU的结构简化了LSTM,因为它没有单独的单元状态,只有隐藏状态。这使得GRU在某些情况下比LSTM更快、更简单,但也可能导致它无法捕捉比LSTM更长的依赖关系。
-
代码改进
-
将编码器、解码器的RNN替换为GRU架构。
class EncoderGRU(nn.Module): """GRU 编码器""" def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, n_layers=1, bidirectional=False): super(EncoderGRU, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.bidirectional = bidirectional self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 用GRU替换RNN # self.rnn = nn.RNN(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers) self.rnn = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional=bidirectional) def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden): # Note: we run this all at once (over the whole input sequence) seq_len = len(word_inputs) embedded = self.embedding(word_inputs).view(seq_len, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.rnn(embedded, hidden) return output, hidden def init_hidden(self): num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers*num_directions, 1, self.hidden_size) if USE_CUDA: hidden = hidden.cuda() return hiddenclass DecoderGRU(nn.Module): """GRU 解码器""" def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, dropout_p=0.1, bidirectional=False): super(DecoderGRU, self).__init__() # Keep parameters for reference self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.bidirectional = bidirectional # Define layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) # 使用GRU替换RNN # self.rnn = nn.RNN(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.rnn = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p, bidirectional=bidirectional) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) def forward(self, word_input, last_hidden): # Note: we run this one step at a time word_embedded = self.embedding(word_input).view(1, 1, -1) # S=1 x B x N rnn_output, hidden = self.rnn(word_embedded, last_hidden) rnn_output = rnn_output.squeeze(0) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(rnn_output)) return output, hidden -
使用
jieba进行中文分词相比于将中文逐个字进行分词,选择使用
jieba对中文按词汇短语分词,更容易让模型学习中文。def index_words(self, sentence): if self.name == 'cn': words = list(jieba.cut(sentence)) if SEGMENTATION else sentence for word in words: self.index_word(word) else: words = sentence.split(' ') for word in words: self.index_word(word)
-
-
模型训练
模型仍然训练50000轮次,结果如下。
Epoch 1000/50000, 0m 21s (- 17m 25s), 5.0521 Epoch 2000/50000, 0m 54s (- 21m 56s), 4.6759 Epoch 3000/50000, 1m 25s (- 22m 21s), 4.5540 ... Epoch 48000/50000, 17m 53s (- 0m 44s), 3.2733 Epoch 49000/50000, 18m 15s (- 0m 22s), 3.2901 Epoch 50000/50000, 18m 37s (- 0m 0s), 3.1813Loss曲线如下图所示。

可以看到,loss最终下降到3.0左右,相比于基础版本的3.8左右的loss值有明显下降,也比训练相同轮次 LSTM改进后 的 loss 值更低。
-
模型测试
-
文本测试
使用
evaluate()预测test.txt文件,翻译中文文本,结果前10行结果如下。Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? why is he speak english ? ? ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she made me her her . . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this can t be in this . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this can t be in this . . 我不能幫你了。 i can t you you . . 我不能幫你了。 i m t you you . . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom is not a good . . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 i ll take the the the . . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 this is not not this . . . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he can speak speak speak speak english . 可以看出,虽然也没有翻译出很完整,但是相比于基础代码有所提升,能够贴近正确翻译。
-
BLEU 测试
通过
torchtext.data.metrics库的bleu_score来计算BLEU值,最终得到的 BLEU 值如下:test dataset bleu score: 0.06819677298621382相比于 LSTM 改进后的结果,BLEU值更高。
-
3.3 使用双向的 encoder 获得更好的源语言表示
本小节分别实现了双向的 LSTM 和双向的 GRU 来提升模型能力。
-
双向LSTM
-
代码设计
**编码器:**将
nn.LSTM的bidirectional参数置为True,将init_hidden的n_layers翻倍。class BioEncoderLSTM(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, n_layers=1): super(BioEncoderLSTM, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 设置双向LSTM self.lstm = nn.LSTM(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional=True) def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden): seq_len = len(word_inputs) embedded = self.embedding(word_inputs).view(seq_len, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.lstm(embedded, hidden) return output, hidden def init_hidden(self): # 对于双向LSTM,num_directions 应该是2 num_directions = 2 hidden = (torch.zeros(self.n_layers * num_directions, 1, self.hidden_size), torch.zeros(self.n_layers * num_directions, 1, self.hidden_size)) if USE_CUDA: hidden = (hidden[0].cuda(), hidden[1].cuda()) return hidden**解码器:**与单向的解码器相同。
class DecoderLSTM(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, dropout_p=0.1): super(DecoderLSTM, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, self.hidden_size) self.rnn = nn.LSTM(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, output_size) def forward(self, word_input, last_hidden): word_embedded = self.embedding(word_input).view(1, 1, -1) rnn_output, hidden = self.rnn(word_embedded, last_hidden) rnn_output = rnn_output.squeeze(0) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(rnn_output), dim=1) return output, hidden -
模型训练
因为是双向,解码器
n_layers变成2倍。# Initialize models encoder = BioEncoderLSTM(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size, n_layers) decoder = DecoderLSTM(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, n_layers*2, dropout_p=dropout_p)训练过程如下:
Epoch 1000/50000, 0m 30s (- 25m 3s), 5.4492 Epoch 2000/50000, 1m 1s (- 24m 37s), 4.9193 Epoch 3000/50000, 1m 33s (- 24m 20s), 4.7066 ... Epoch 48000/50000, 36m 30s (- 1m 31s), 3.5253 Epoch 49000/50000, 37m 1s (- 0m 45s), 3.4787 Epoch 50000/50000, 37m 32s (- 0m 0s), 3.4415训练得到的loss曲线如下:
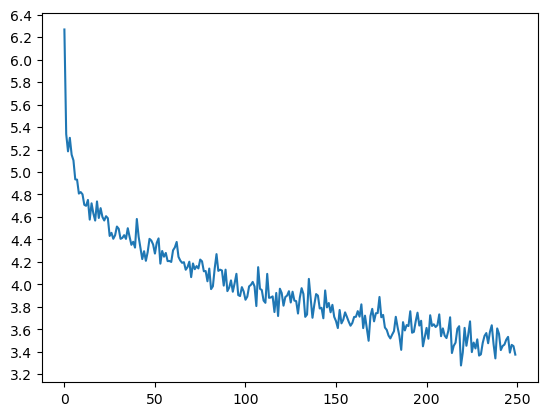
可以看到 loss 值降低到 3.4 左右,相比单向的编码器区别不大。
-
模型测试
通过
predict来测试test.txt文件,前十条数据翻译如下。Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? why do i think that is ? ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she asked her her her her . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 the is is t t . . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 the is is t t . . . . 我不能幫你了。 i can t you you you . 我不能幫你了。 i can t you you you . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom is t a good good . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 i can i i to to to . . . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 the boy is is to . . . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he can speak english english english . 可以看到,翻译的结果也并没有很准确。
BLEU值测试如下:
test dataset bleu score: 0.05062519386410713BLEU值相比于单向的编码器有所增加。
-
-
双向GRU
-
代码设计
**编码器:**将
nn.LSTM的bidirectional参数置为True,将init_hidden的n_layers翻倍。class BioEncoderGRU(nn.Module): """GRU 编码器""" def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, n_layers=1, bidirectional=False): super(BioEncoderGRU, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.bidirectional = bidirectional self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 用GRU替换RNN # self.rnn = nn.RNN(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers) self.rnn = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional=bidirectional) def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden): # Note: we run this all at once (over the whole input sequence) seq_len = len(word_inputs) embedded = self.embedding(word_inputs).view(seq_len, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.rnn(embedded, hidden) return output, hidden def init_hidden(self): num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers*num_directions, 1, self.hidden_size) if USE_CUDA: hidden = hidden.cuda() return hidden**解码器:**与单向的解码器相同。
class DecoderGRU(nn.Module): """GRU 解码器""" def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, dropout_p=0.1): super(DecoderGRU, self).__init__() # Keep parameters for reference self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.dropout_p = dropout_p # Define layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) # 使用GRU替换RNN # self.rnn = nn.RNN(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.rnn = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) def forward(self, word_input, last_hidden): # Note: we run this one step at a time word_embedded = self.embedding(word_input).view(1, 1, -1) # S=1 x B x N rnn_output, hidden = self.rnn(word_embedded, last_hidden) rnn_output = rnn_output.squeeze(0) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(rnn_output)) return output, hidden -
模型训练
训练过程如下:
Epoch 1000/50000, 0m 39s (- 31m 55s), 4.8897 Epoch 2000/50000, 1m 18s (- 31m 31s), 4.5166 Epoch 3000/50000, 1m 58s (- 30m 59s), 4.3445 ... Epoch 48000/50000, 32m 16s (- 1m 20s), 2.4504 Epoch 49000/50000, 32m 57s (- 0m 40s), 2.4343 Epoch 50000/50000, 33m 37s (- 0m 0s), 2.4332训练得到的loss曲线如下:

可以看到,loss值下降到2.2左右,相比单向编码器有着明显下降。
-
模型测试
通过
predict来测试test.txt文件,前十条数据翻译如下。Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? why don t i have a english ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she made me angry at the . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this isn t a little . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this isn t a little . . 我不能幫你了。 i can t help you . 我不能幫你了。 i can t help you . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom isn t a good . . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 i can speak spanish spanish in english . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 this problem is not so . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he can t speak speak speak french . 可以看到,翻译的准确性有很大的提升。
BLEU值测试如下:
test dataset bleu score: 0.2297259837529158BLEU值与单向编码器,双向的LSTM相比,也有着显著的提升。
-
3.4 使用注意力机制提升模型能力
-
注意力机制
本小节实现了一个简单的注意力机制,允许解码器根据解码器的隐藏状态动态地聚焦于编码器输出的不同部分,并以此生成一个聚合的、加权的编码器表示,这个表示随后可以用于解码器的下一步输入。

-
代码设计
注意力机制类:采用简单的注意力机制。
class Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size): super(Attention, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size def forward(self, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs): attn_weights = F.softmax(torch.matmul(torch.squeeze(encoder_outputs), torch.squeeze(decoder_hidden).view(-1, 1))) attn_weights = attn_weights.expand(encoder_outputs.shape[0], -1) attn_output = torch.sum(attn_weights * torch.squeeze(encoder_outputs), dim=0) return attn_output.view(1, 1, -1)编码器:采用单向GRU。
class EncoderGRU(nn.Module): """GRU 编码器""" def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, n_layers=1, bidirectional=False): super(EncoderGRU, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.bidirectional = bidirectional self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 用GRU替换RNN self.rnn = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers) def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden): # Note: we run this all at once (over the whole input sequence) seq_len = len(word_inputs) embedded = self.embedding(word_inputs).view(seq_len, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.rnn(embedded, hidden) return output, hidden def init_hidden(self): num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers*num_directions, 1, self.hidden_size) if USE_CUDA: hidden = hidden.cuda() return hidden解码器:采用注意力机制的解码器。
class DecoderGRU(nn.Module): """注意力机制解码器""" def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, dropout_p=0.1): super(DecoderGRU, self).__init__() # Keep parameters for reference self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.n_layers = n_layers self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.attention = Attention(hidden_size) # Define layers self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) # 使用GRU替换RNN self.rnn = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout=dropout_p) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size*2, output_size) def forward(self, word_input, last_hidden, encoder_outputs): # Note: we run this one step at a time word_embedded = self.embedding(word_input).view(1, 1, -1) # S=1 x B x N rnn_output, hidden = self.rnn(word_embedded, last_hidden) rnn_output = rnn_output.squeeze(0) # attention weighted encoder output attn_weighted_encoder_output = self.attention(hidden, encoder_outputs) attn_weighted_encoder_output = attn_weighted_encoder_output.squeeze(0) concat_output = torch.cat([rnn_output, attn_weighted_encoder_output], dim=1) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(concat_output)) return output, hidden -
模型训练
本次实验采用150000 epoch 的训练轮次,训练过程如下:
Epoch 1000/150000, 0m 22s (- 56m 33s), 4.8073 Epoch 2000/150000, 0m 46s (- 57m 43s), 4.3964 Epoch 3000/150000, 1m 10s (- 57m 15s), 4.2832 ... Epoch 148000/150000, 77m 34s (- 1m 2s), 1.7956 Epoch 149000/150000, 77m 58s (- 0m 31s), 1.8039 Epoch 150000/150000, 78m 23s (- 0m 0s), 1.7942loss曲线如下:

经过长时间的训练,loss最终降低到了1.6左右。
-
模型验证
通过
predict来测试test.txt文件,前十条数据翻译如下。Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? why should i always been english ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she let me by her sit . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 the does not take the . . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 the does not take the . . 我不能幫你了。 i couldn t help you . 我不能幫你了。 i couldn t help you . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom isn t a good . . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 i like this meeting and may . . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 this question is not . . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he can speak english can speak english english . 可以看到翻译效果有所提升。
BLEU值测试如下:
test dataset bleu score: 0.3370101494002167BLEU值经过长时间训练,也有所提高。
4 总结
可以看到,通过多种改进方式,有效提升了模型能力,最终采用了训练 150000 epoch 轮次的双向GRU编码器,训练结果最好。
-
模型训练
训练过程如下:
Epoch 1000/150000, 0m 38s (- 96m 7s), 4.9300 Epoch 2000/150000, 1m 18s (- 97m 7s), 4.5659 Epoch 3000/150000, 1m 58s (- 96m 43s), 4.3506 ... Epoch 148000/150000, 100m 45s (- 1m 21s), 1.4097 Epoch 149000/150000, 101m 26s (- 0m 40s), 1.4008 Epoch 150000/150000, 102m 7s (- 0m 0s), 1.4062loss曲线如下:

-
模型验证
通过
predict来测试test.txt文件,前十条数据翻译如下。Original Translation 為什麼我一直學不好英語? why don t i have any english english ? 她讓我坐在她的身邊。 she asked her on her side . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this bottle has not gone to . 這瓶酸奶不含乳糖。 this bottle has not gone to this 我不能幫你了。 i m not help you . 我不能幫你了。 i m not help you . 湯姆不是一個好司機。 tom isn t a good driver . 我會普通話、西南官話、吳語和西班牙語。 i m getting spanish and my brother . 這個問題沒有那麼簡單。 this question is not that . . 他不會說英語也不會說法語。 he can t speak english and french . 可以看出,这组的翻译结果最好。
BLEU值测试如下:
test dataset bleu score: 0.5388663729613064BLEU值也是整体训练结果最高的。



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










