之后的学习工作要围绕Message、Packet、Flits展开,此帖主要是学习Packet类。
Packet
代码 /src/mem/packet.hh
class Packet : public Printable, public Extensible<Packet>
{
public:
MemCmd cmd; // 包内要求内存对象执行的命令
const PacketId id; // 包 ID
RequestPtr req; // 指向原本请求的指针
typedef uint32_t FlagsType;
typedef gem5::Flags<FlagsType> Flags;
typedef MemCmd::Command Command;
uint32_t headerDelay; // 从看到包到发送报头的额外延迟。这个延迟是用来传递交叉转发延迟到相邻的对象(例如缓存),实际上使数据包等待。
uint32_t snoopDelay; // 在向内存系统发送请求之前,跟踪由向上窥探引起的额外延迟。这被相干交叉条用来解释额外的请求延迟。
uint32_t payloadDelay; // 从看到数据包到负载结束的额外流水线延迟。这包括报头延迟。与报头延迟类似,这是用来弥补交叉条不会使包等待的事实。
SenderState *senderState; // 此数据包的发送者状态。
private:
enum : FlagsType {}
Flags flags; // 标志位
PacketDataPtr data; // 指向被传输数据的指针
Addr addr;
bool _isSecure;
unsigned size; // 请求的大小
std::vector<bool> bytesValid;
uint8_t _qosValue;
HtmCacheFailure htmReturnReason;
uint64_t htmTransactionUid;FlagsType
描述了 Packet 对象内具体状态信息,包括侦听、拷贝、应答、共享、有效位等:
enum : FlagsType
{
// Flags to transfer across when copying a packet
COPY_FLAGS = 0x000000FF,
// Flags that are used to create reponse packets
RESPONDER_FLAGS = 0x00000009,
// Does this packet have sharers (which means it should not be
// considered writable) or not. See setHasSharers below.
HAS_SHARERS = 0x00000001,
// Special control flags
/// Special timing-mode atomic snoop for multi-level coherence.
EXPRESS_SNOOP = 0x00000002,
/// Allow a responding cache to inform the cache hierarchy
/// that it had a writable copy before responding. See
/// setResponderHadWritable below.
RESPONDER_HAD_WRITABLE = 0x00000004,
// Snoop co-ordination flag to indicate that a cache is
// responding to a snoop. See setCacheResponding below.
CACHE_RESPONDING = 0x00000008,
// The writeback/writeclean should be propagated further
// downstream by the receiver
WRITE_THROUGH = 0x00000010,
// Response co-ordination flag for cache maintenance
// operations
SATISFIED = 0x00000020,
// hardware transactional memory
// Indicates that this packet/request has returned from the
// cache hierarchy in a failed transaction. The core is
// notified like this.
FAILS_TRANSACTION = 0x00000040,
// Indicates that this packet/request originates in the CPU executing
// in transactional mode, i.e. in a transaction.
FROM_TRANSACTION = 0x00000080,
/// Are the 'addr' and 'size' fields valid?
VALID_ADDR = 0x00000100,
VALID_SIZE = 0x00000200,
/// Is the data pointer set to a value that shouldn't be freed
/// when the packet is destroyed?
STATIC_DATA = 0x00001000,
/// The data pointer points to a value that should be freed when
/// the packet is destroyed. The pointer is assumed to be pointing
/// to an array, and delete [] is consequently called
DYNAMIC_DATA = 0x00002000,
/// suppress the error if this packet encounters a functional
/// access failure.
SUPPRESS_FUNC_ERROR = 0x00008000,
// Signal block present to squash prefetch and cache evict packets
// through express snoop flag
BLOCK_CACHED = 0x00010000
};| 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| COPY_FLAGS | Flags to transfer across when copying a packet |
| RESPONDER_FLAGS | used to create reponse packets |
| HAS_SHARERS | packet have sharers (which means it should not be considered writable) or not. |
| EXPRESS_SNOOP | Special timing-mode atomic snoop for multi-level coherence. |
| RESPONDER_HAD_WRITABLE | Allow a responding cache to inform the cache hierarchy that it had a writable copy before responding. |
| CACHE_RESPONDING | Snoop co-ordination flag to indicate that a cache is responding to a snoop. |
| WRITE_THROUGH | The writeback/writeclean |
| SATISFIED | Response co-ordination flag for cache maintenance |
| FAILS_TRANSACTION | Indicates that this packet/request has returned from the cache hierarchy in a failed transaction. |
| FROM_TRANSACTION | Indicates that this packet/request originates in the CPU executing in transactional mode |
| VALID_ADDR | addr valid fields |
| VALID_SIZE | size valid fields |
| STATIC_DATA | The data pointers to a value that shouldn’t be freed when the packet is destroyed. |
| DYNAMIC_DATA | The data pointers to a value that should be freed when the packet is destroyed. |
| SUPPRESS_FUNC_ERROR | suppress the error if this packet encounters a functional access failure. |
| BLOCK_CACHED | Signal block present to squash prefetch and cache evict packets through express snoop flag |
Memcmd(目前不晓得作用)
MemCmd 类定义了与命令相关的属性和其他数据。MemCmd 类中有所有关于cache/memory 的操作和属性。关于cache的命令操作,可分为以下几大类:
- 无效
- 读取
- 预取
- 写入
- 清除
- 升级
- 同步
这些命令操作也会配上数据包的属性,且命令与数据通常有固定搭配,不完全举例如下:
| 命令 | 属性字符 | 应答命令 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| InvalidCmd | - | InvalidCmd(即不应答) | 无效命令 | |
| ReadReq | IsRead, IsRequest, NeedsResponse | ReadResp | 由非缓存代理(例如 CPU 或设备)发出的读取,对对齐没有限制 | |
| ReadResp | IsRead, IsResponse, HasData | InvalidCmd | 从 requester 到 responder 的数据流 | |
| ReadRespWithInvalidate | IsRead, IsResponse, HasData, IsInvalidate | InvalidCmd | 是否是要升级的数据 | |
| WriteReq | IsWrite, NeedsWritable, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, HasData | WriteResp | ||
| WriteResp | IsWrite, IsResponse | InvalidCmd | ||
| WriteCompleteResp | IsWrite, IsResponse | InvalidCmd | ||
| WritebackDirty | IsWrite, IsRequest, IsEviction, HasData, FromCache | InvalidCmd | ||
| WritebackClean | IsWrite, IsRequest, IsEviction, HasData, FromCache | InvalidCmd | ||
| WriteClean | IsWrite, IsRequest, HasData, FromCache | InvalidCmd | ||
| CleanEvict | IsRequest, IsEviction, FromCache | InvalidCmd | ||
| SoftPFReq | IsRead, IsRequest, IsSWPrefetch, NeedsResponse | SoftPFResp | ||
| SoftPFExReq | IsRead, NeedsWritable, IsInvalidate, IsRequest, IsSWPrefetch, NeedsResponse | SoftPFResp | ||
| HardPFReq | IsRead, IsRequest, IsHWPrefetch, NeedsResponse, FromCache | HardPFResp | ||
| SoftPFResp | IsRead, IsResponse, IsHWPrefetch, HasData | InvalidCmd | ||
| HardPFResp | IsRead, IsResponse, IsHWPrefetch, HasData | InvalidCmd | ||
| WriteLineReq | IsWrite, NeedsWritable, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, HasData | WriteResp | ||
| UpgradeReq | IsInvalidate, NeedsWritable, IsUpgrade, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, FromCache | UpgradeResp | ||
| SCUpgradeReq | IsInvalidate, NeedsWritable, IsUpgrade, IsLlsc, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, FromCache | UpgradeResp | IsUpgrade, IsResponse | InvalidCmd |
| SCUpgradeFailReq | sRead, NeedsWritable, IsInvalidate, IsLlsc, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, FromCache | UpgradeFailResp | ||
| UpgradeFailResp | IsRead, IsResponse, HasData | InvalidCmd | ||
| ReadExReq | IsRead, NeedsWritable, IsInvalidate, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, FromCache | ReadExResp | ||
| ReadExResp | IsRead, IsResponse, HasData | InvalidCmd | ||
| ReadCleanReq | IsRead, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, FromCache | ReadResp | ||
| ReadSharedReq | IsRead, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, FromCache | ReadResp | ||
| LoadLockedReq | IsRead, IsLlsc, IsRequest, NeedsResponse | |||
| StoreCondReq | sWrite, NeedsWritable, IsLlsc, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, HasData | |||
| StoreCondFailReq | IsWrite, NeedsWritable, IsLlsc, IsRequest, NeedsResponse, HasData | |||
| StoreCondResp | IsWrite, IsLlsc, IsResponse | |||
| SwapReq | IsRead, IsWrite, NeedsWritable, IsRequest, HasData, NeedsResponse | |||
| SwapResp | IsRead, IsWrite, IsResponse, HasData | |||
| MemFenceReq | ||||
| MemSyncReq | ||||
| MemSyncResp | ||||
| MemFenceResp | ||||
| CleanSharedReq | ||||
| CleanSharedResp | ||||
| CleanInvalidReq | ||||
| CleanInvalidResp |
MSHR
MSHR(Miss Status and handling Register) 在"Dead Flit Attack on NoC by Hardware Trojan and its Impact Analysis"中有体现。保存并处理缓存丢失所需的所有信息,包括要请求的目标列表。
指向 SenderState 类的指针会在应答 Packet 的函数中被返回,如此,SimObject 对象可以迅速查看 Packet 中的状态位,并进行相应的处理(见src/mem/packet.hh::findNextSenderState() 函数)。 SenderState 类以链表的形式相串起来:
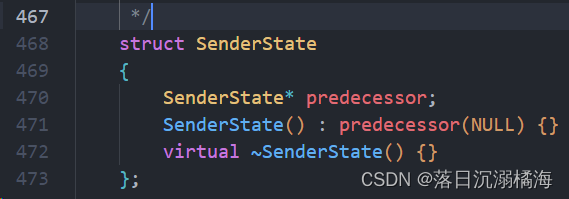
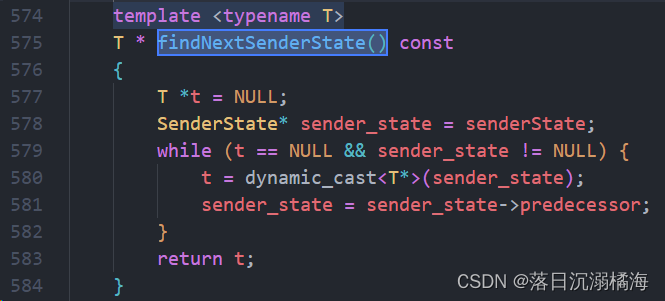
在响应该 Packet 时,会返回一个 SenderState* 类型的指针,以便 SimObject 对象可以快速查找处理它所需的状态。要遍历发送者组成的链表,返回第一个符合类型T的实例,需使用 findNextSenderState() 函数:
有时,为处理特殊发送设备的状态,程序员也可以从该类中派生出相对应的子类。由于多个 SimObject 对象都可以从自己的视角出发来添加新的 SenderState,只要在响应返回时,能恢复之前的 SenderState 对象即可。因此,在修改 Packet 类中的 SenderState 字段之前,应该始终维护 SenderState 链表。
Packet功能
- 地址:getAddr()
- 请求或包的大小:getSize()
- 指向 Packet 中数据的指针。在不同层次结构中,数据可能是不同的,因此在设计上它位于 Packet 对象,而不是 request:
- 用
dataStatic()dataDynamic()函数设置的数据,在 Packet 对象被 free 时,其内的数据分别应:不被 free、 delete [] data 、 free。 - 用
allocate()函数分配空间时,数据会在 Packet 被释放时 free - 通过
getPtr()获得指针 - 使用
get()函数获取,set()函数设置
- 用
- 状态:Success, BadAddress, Not Acknowleged, and Unknown.
- List of command attributes 需要对 Packet 施加的命令和属性,由 MemCmd 维护。注意:状态字段和命令属性中的数据有一些重叠。这在很大程度上是为了使包在打包时可以很容易地重新初始化,或者在原子访问或函数访问时很容易重用。
- Pointer to SenderState 携带特定的发送设备的状态。在包的响应中返回一个指向该状态的指针,以便发送方可以快速查找处理它所需的状态。
- Pointer to CoherenceState 用于保存 Coherence 一致性相关的状态。
- Pointer to request 指向请求的指针
Func trySatisfyFunctional::
const Addr func_start = getAddr();
const Addr func_end = getAddr() + getSize() - 1;
const Addr val_start = addr;
const Addr val_end = val_start + size - 1;这一段代码首先获取当前功能块的起始地址 `func_start`、结束地址 `func_end`,以及请求的起始地址 `val_start` 和结束地址 `val_end`。这些地址都是相对于数据块的地址。这些变量都是用于后续的比较和计算,例如判断请求是否与功能块相交,计算 overlap 区域的大小等。
`getAddr()` 函数是 `Packet` 类的一个成员函数,用于获取当前功能块的地址。`getSize()` 函数也是 `Packet` 类的一个成员函数,用于获取当前功能块的大小。
Request
Request 对象封装了 CPU 或 I/O 设备发出的原始请求。Request 的参数在整个事务中是持久的。因此对于一给定的 Request,其字段最多只需写入一次。但也有一些构造函数和 update 方法允许在不同时间(或根本不)写入对象的某些字段。用户可通过 accessor() 函数获取 Request 字段的读取权限,同时也可验证正在读取的字段中的数据是否有效。注意,Request 中的字段通常不适用于真实系统中的设备,通常用于统计或调试,不能作为真实的系统架构。Request 对象包括:
- Virtual Address 虚拟地址。当该请求直接表示为物理地址时该字段无效(如 DMA I/O 设备发出的请求)
- Physical Address 物理地址
- Data Size 数据大小
- Time the request was created 创建时间
- The ID of the CPU/thread that caused this request. 创建该请求的 CPU 或线程 ID
- The PC that caused this request 产生该请求的指令 PC 值。若不是由 CPU 发送的,那么该字段无效
Request 类
class Request {
private:
// The physical address of the request.
Addr _paddr = 0;
// The virtual address of the request.
Addr _vaddr = MaxAddr;
// The size of the request. Always valid as long as vir/phy address fields is valid.
unsigned _size = 0;
/** Byte-enable mask for writes. */
std::vector<bool> _byteEnable;
// The requestor ID which is unique in the system for all ports
// that are capable of issuing a transaction
RequestorID _requestorId = invldRequestorId;
/** Flag structure for the request. */
Flags _flags;
/** Flags that control how downstream cache system maintains coherence*/
CacheCoherenceFlags _cacheCoherenceFlags;
/** Private flags for field validity checking. */
PrivateFlags privateFlags;
// The time this request was started. Used to calculate latencies.
Tick _time = MaxTick;
// The task id associated with this request
uint32_t _taskId = context_switch_task_id::Unknown;
/**
* The stream ID uniquely identifies a device behind the
* SMMU/IOMMU Each transaction arriving at the SMMU/IOMMU is
* associated with exactly one stream ID.
*/
uint32_t _streamId = 0;
/**
* The substream ID identifies an "execution context" within a
* device behind an SMMU/IOMMU. It's intended to map 1-to-1 to
* PCIe PASID (Process Address Space ID). The presence of a
* substream ID is optional.
*/
uint32_t _substreamId = 0;
/**
* Extra data for the request, such as the return value of
* store conditional or the compare value for a CAS. */
uint64_t _extraData = 0;
/** The context ID (for statistics, locks, and wakeups). */
ContextID _contextId = InvalidContextID;
/** program counter of initiating access; for tracing/debugging */
Addr _pc = MaxAddr;
/** Sequence number of the instruction that creates the request */
InstSeqNum _reqInstSeqNum = 0;
/** A pointer to an atomic operation */
AtomicOpFunctorPtr atomicOpFunctor = nullptr;
LocalAccessor _localAccessor;
/** The instruction count at the time this request is created */
Counter _instCount = 0;
};
Request(Addr vaddr, unsigned size, Flags flags,
RequestorID id, Addr pc, ContextID cid,
AtomicOpFunctorPtr atomic_op=nullptr)
{
setVirt(vaddr, size, flags, id, pc, std::move(atomic_op));
setContext(cid);
_byteEnable = std::vector<bool>(size, true);
}
void
setVirt(Addr vaddr, unsigned size, Flags flags, RequestorID id, Addr pc,
AtomicOpFunctorPtr amo_op=nullptr)
{
_vaddr = vaddr;
_size = size;
_requestorId = id;
_pc = pc;
_time = curTick();
_flags.clear(~STICKY_FLAGS);
_flags.set(flags);
privateFlags.clear(~STICKY_PRIVATE_FLAGS);
privateFlags.set(VALID_VADDR|VALID_SIZE|VALID_PC);
depth = 0;
accessDelta = 0;
translateDelta = 0;
atomicOpFunctor = std::move(amo_op);
_localAccessor = nullptr;
}
void
setContext(ContextID context_id)
{
_contextId = context_id;
privateFlags.set(VALID_CONTEXT_ID);
}
}





















 2005
2005











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








