题目梗概
任务:从键盘接收一串电文字符,输出对应的哈夫曼编码。同时,能翻译由哈夫曼编码生成的代码串,输出对应的电文字符串。
①构造一棵哈夫曼树;
②实现哈夫曼编码,并用哈夫曼编码生成的代码串进行译码;
③程序中字符和权值是可变的,实现程序的灵活性。
设计思路
对于不理解哈夫曼编码的同学可以看看这篇博客
为了完成题设要求我们分成了三个阶段:
创建哈夫曼树
对哈夫曼树进的叶子节点行编码
读取代码串进行译码
代码解析
结构体部分
结构体这块有哈夫曼树的结构、输入的数据结构、编码存储结构三大结构体。(其实个人感觉结构体这块写的并不好😢)
typedef struct Node
{
int weight;
char data;
int parent;
int Lchild;
int Rchild;
}Node;
typedef struct
{
int number;
char s;
}Data;
typedef struct
{
char code[30];
int cnt;
}codetype;
节点
通过比较大小得出两节点的父节点,并将两节点的父节点设置为该节点,该节点的左右孩子分别为当前最小值与次小值。最后可以链接成哈夫曼树。
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
HT[i].parent = -1;
HT[i].Lchild = -1;
HT[i].Rchild = -1;
HT[i].data = d[i].s;
HT[i].weight = d[i].number;
}
for(int i = n; i < 2*n-1; i++)
{
HT[i].data = '#';
HT[i].parent = -1;
HT[i].Lchild = -1;
HT[i].Rchild = -1;
HT[i].weight = -1;
}
for(int i=n; i<2*n-1; i++)
{
int min = 99999;//最小值
int cmin = 99999;//次小值
int m = 0; c = 0;//记录最小值和次小值的下标
for (int j = 0; j<i; j++)
{
if (HT[j].parent == -1)
if (HT[j].weight<min)
{
c = m;
cmin = min;
min = HT[j].weight;
m = j;
}
else if (HT[j].weight<cmin)
{
cmin = HT[j].weight;
c = j;
}
}
HT[i].weight = min + cmin;//hfmTree[m].weight+hfmTree[c].weight;
HT[i].Lchild = m;
HT[i].Rchild = c;
HT[m].parent = i;
HT[c].parent = i;
HT[i].parent = -1;//新结点的双亲没有为-1
编码
编码的过程则是在我们构建的哈夫曼树上通过叶节点像树的根节点溯源的过程。只要当前节点的父节点不为-1(即父节点之上还有父节点的父节点)就进行判断,如若为父节点的左子树则填入’0’反之为’1’。但是我们这样溯源到根节点字符的编码是与真实相反的,这个时候就需要在填入的时候就反转(或者在输出的时候反向输出也可行)。
void code(Node *HT, codetype *codeFile, int n)
{
int i, p, c;
codetype S;
for (i = 0; i<n; i++)//对N的字符进行编码
{
c = i;
p = HT[c].parent;
S.cnt = n;//把cnt的值初始化为N,后续再用数组(S->code[])存字符的编码时,倒着存
S.code[n] = '\0';
while (p != -1)
{
if (HT[p].Lchild == c)
S.code[--S.cnt] = '0';
else//否则存‘1’
S.code[--S.cnt] = '1';
c = p;
p = HT[c].parent;
}
codeFile[i] = S;//第i个字符的编码存入codeFile
}
}
///编码结束进行译码
译码
译码与编码的思想是一致的,本质上是编码的逆运算。
void Decode(Node *HT, int n)
{
int m = 2*n-1, i, j=m-1;
printf("请输入要译码的Huffman编码:\n");
char str[100];
scanf("%s", &str);
char C;
int len = strlen(str);
for(i = 0; i<len; i++)
{
C = str[i];
if(C == '0')
j = HT[j].Lchild;
else
j = HT[j].Rchild;
if(HT[j].Lchild == -1)
{
printf("%c", HT[j].data);
j = m -1;
}
}
}
完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct Node
{
int weight;
char data;
int parent;
int Lchild;
int Rchild;
}Node;
typedef struct
{
int number;
char s;
}Data;
typedef struct
{
char code[30];
int cnt;
}codetype;
char c;
int num = 0;
int n = 0;
Data d[100];
void creat_huffman();
void output(Node *HT);
void code(Node *HT, codetype *codeFile, int n);
void Decode(Node *HT, int n);
int main()
{
creat_huffman();
Node *HT = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)*(2*n-1));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
HT[i].parent = -1;
HT[i].Lchild = -1;
HT[i].Rchild = -1;
HT[i].data = d[i].s;
HT[i].weight = d[i].number;
}
for(int i = n; i < 2*n-1; i++)
{
HT[i].data = '#';
HT[i].parent = -1;
HT[i].Lchild = -1;
HT[i].Rchild = -1;
HT[i].weight = -1;
}
// for(int i = 0; i < 2*n-1; i++)
// {
// printf("---%d---\n", HT[i].weight);
// }
for(int i=n; i<2*n-1; i++)
{
int min = 99999;//最小值
int cmin = 99999;//次小值
int m = 0; c = 0;//记录最小值和次小值的下标
for (int j = 0; j<i; j++)
{
if (HT[j].parent == -1)
if (HT[j].weight<min)
{
c = m;
cmin = min;
min = HT[j].weight;
m = j;
}
else if (HT[j].weight<cmin)
{
cmin = HT[j].weight;
c = j;
}
}
HT[i].weight = min + cmin;//hfmTree[m].weight+hfmTree[c].weight;
//hfmTree[i].CH = ' ';//方便整体输出加个字符空格
HT[i].Lchild = m;
HT[i].Rchild = c;
HT[m].parent = i;
HT[c].parent = i;
HT[i].parent = -1;//新结点的双亲没有为-1
}
// for(int i = 0; i < 2*n-1; i++)
// {
// printf("---%d---\n", HT[i].weight);
// }
output(HT);
printf("各字符编码如下:\n");
codetype *codeFile;
codeFile = (codetype *)malloc(sizeof(codetype)*n);
code(HT, codeFile, n);
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("%c字符的编码: ", HT[i].data);
printf("%s", codeFile[i].code + codeFile[i].cnt);
printf("\n");
}
Decode(HT, n);
}
void creat_huffman()
{
Node *p;
p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p ->parent = NULL;
int count[100] = {};
while((c = getchar()) != '\n') ///读取输入的字符
{
num++;
count[c-65]++;
}
for(int i=0; i<100; i++)
{
if(count[i] != 0)
{
d[n].number = count[i];
d[n].s = char(i+65);
n++;
}
}
}
/Huffman树构建完成
///打印哈夫曼树的结构
void output(Node *HT)
{
printf("Huffman Tree List:\n");
printf("Number\tData\tWeight\tParent\tLchild\tRchild\n");
for(int i=0; i<2*n-1; i++)
{
printf("%d\t%c\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n", i,HT[i].data, HT[i].weight,HT[i].parent, HT[i].Lchild, HT[i].Rchild);
}
}
///对节点进行编码
void code(Node *HT, codetype *codeFile, int n)
{
int i, p, c;
codetype S;
for (i = 0; i<n; i++)//对N的字符进行编码
{
c = i;
p = HT[c].parent;
S.cnt = n;//把cnt的值初始化为N,后续再用数组(S->code[])存字符的编码时,倒着存
S.code[n] = '\0';
while (p != -1)
{
if (HT[p].Lchild == c)
S.code[--S.cnt] = '0';
else//否则存‘1’
S.code[--S.cnt] = '1';
c = p;
p = HT[c].parent;
}
codeFile[i] = S;//第i个字符的编码存入codeFile
}
}
///编码结束进行译码
void Decode(Node *HT, int n)
{
int m = 2*n-1, i, j=m-1;
printf("请输入要译码的Huffman编码:\n");
char str[100];
scanf("%s", &str);
char C;
int len = strlen(str);
for(i = 0; i<len; i++)
{
C = str[i];
if(C == '0')
j = HT[j].Lchild;
else
j = HT[j].Rchild;
if(HT[j].Lchild == -1)
{
printf("%c", HT[j].data);
j = m -1;
}
}
}
运行结果
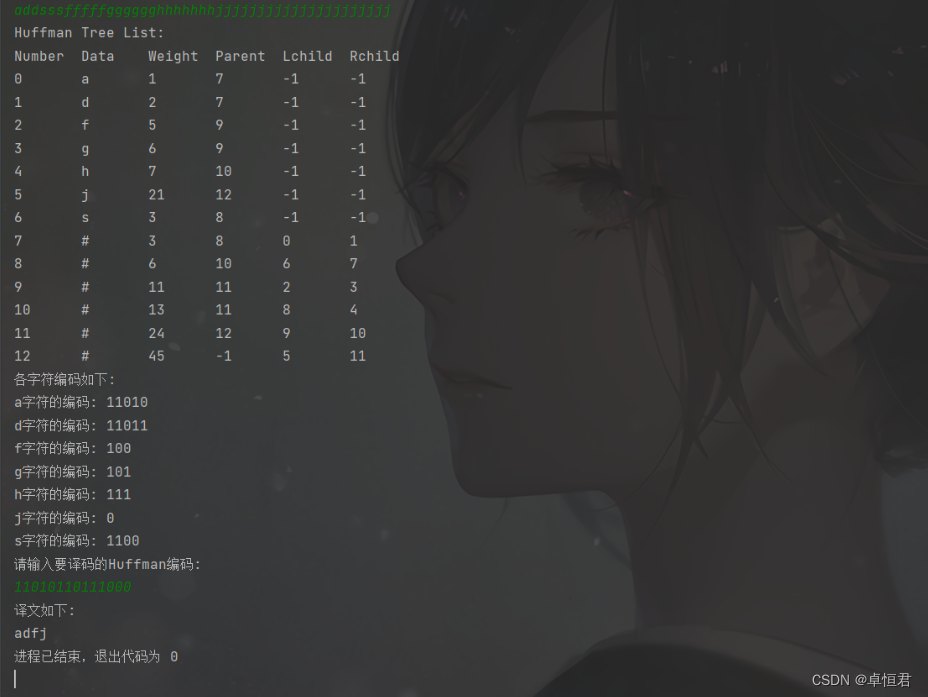
最后,期待大家在评论区在留言区留下问题或宝贵的改进建议。




















 2147
2147











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








