LRU :最近最少使用,缓存淘汰法
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
//链表中的每一个结点
typedef struct DoubleNode {
struct DoubleNode* prve;
struct DoubleNode* next;
int data;
}DNode;
//定义链表总体
typedef struct ListHead {
DNode* head;
DNode* tail;
int size;
}DHead;
//链表初始化
void dlist_init(DHead* dlist) {
dlist->size = 0;
dlist->head = NULL;
dlist->tail = NULL;
return;
}
//删除链表
void dlist_destory(DHead* dlist) {
DNode* pNode = NULL;
while (dlist->size > 0) {
pNode = dlist->head;
dlist->head = dlist->head->next;
free(pNode);
dlist->size--;
}
memset(dlist, 0, sizeof(DHead));
return;
}
//插入头结点
int dlist_insert_head(DHead* dlist, DNode* pNode, int data) {
/*不懂*/
if (pNode == NULL) { //当传递一个数据时
pNode = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
if (pNode == NULL) {
return -1;
}
}
pNode->data = data;
pNode->next = NULL;
pNode->prve = NULL;
if (dlist->size == 0) {
dlist->head = pNode;
dlist->tail = pNode;
}
else {
pNode->next = dlist->head;
dlist->head->prve = pNode;
dlist->head = pNode;
}
dlist->size++;
return 0;
}
//移除尾结点,并返回反删除结点
DNode * dlist_remove_tail(DHead* dlist) {
DNode* pNode = NULL;
if (dlist->size == 0) {
return NULL;
}
pNode = dlist->tail; //注意注意,不要忘了赋值
if (dlist->size > 1) {
pNode = dlist->tail;
dlist->tail = dlist->tail->prve;
dlist->tail->next = NULL;
}
else {
dlist->head = NULL;
dlist->tail = NULL;
}
dlist->size--;
return pNode;
}
//删除制定结点
void dlist_remove_node(DHead* dlist, DNode* pNode) {
if ((dlist == NULL) || (pNode == NULL)) {
return;
}
if (pNode == dlist->head) {
dlist->head = pNode->next;
dlist->head->prve = NULL;
}
else if (pNode == dlist->tail) {
dlist->tail = pNode->prve;
dlist->tail->next = NULL;
}
else {
pNode->prve->next = pNode->next;
pNode->next->prve = pNode->prve;
}
//free(pNode);
pNode->next = NULL;
pNode->prve = NULL;
dlist->size--;
/*不懂*/
if (dlist->size == 0) {
memset(dlist, 0, sizeof(DHead));
}
return;
}
//根据值查找结点,并返回结点
DNode* dlist_search(DHead* dlist, int data) {
DNode* pNode = dlist->head;
while (pNode != NULL) {
if (pNode->data == data) {
return pNode;
}
pNode = pNode->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//显示链表中的数据
void dlist_dump(DHead* dlist) {
int no = 0;
DNode* pNode = dlist->head;
while (pNode != NULL) {
printf("[%d] = %d\n", no++, pNode->data);
pNode = pNode->next;
}
return;
}
//LRU(最近最少使用)缓存淘汰法
void Lru_dlist(DHead* dlist, int data) {
DNode* pNode = NULL; //要将pNode赋值为空
pNode = dlist_search(dlist, data); //不然不会执行else if
if (pNode != NULL) {
dlist_remove_node(dlist,pNode);
}
else if (dlist->size >= 4) {
pNode = dlist_remove_tail(dlist);
}
dlist_insert_head(dlist, pNode,data);
return;
}
int main() {
DHead dlist = { 0 };
DNode* pNode = NULL;
dlist_init(&dlist);
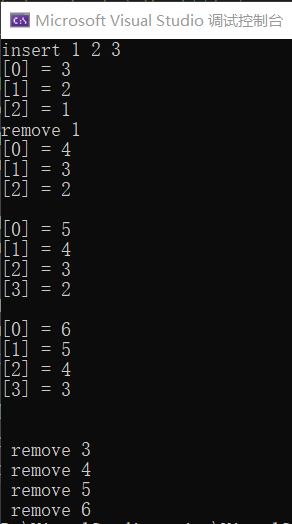
printf("\rinsert 1 2 3\n");
//为什么上面的 dlist_insert_head DHead 部分没有用&
//为什么 NULL 可以当作DNode来使用
dlist_insert_head(&dlist, pNode, 1);
dlist_insert_head(&dlist, pNode, 2);
dlist_insert_head(&dlist, pNode, 3);
dlist_dump(&dlist);
pNode = dlist_remove_tail(&dlist); //不可以和if换顺序*_*
if (pNode != NULL) { //不然pNode没有赋值
printf("\rremove %d \n", pNode->data);
}
/*for (int i = 4; i < 8; i++) { //写入死循环了*_* , 为啥
dlist_insert_head(&dlist, pNode, i);
}
dlist_dump(&dlist);*/
dlist_insert_head(&dlist, pNode, 4);
dlist_dump(&dlist);
printf("\n");
Lru_dlist(&dlist, 5);
dlist_dump(&dlist);
printf("\n");
Lru_dlist(&dlist, 6);
dlist_dump(&dlist);
printf("\n");
while (dlist.size > 0) {
pNode = dlist_remove_tail(&dlist);
if (pNode != NULL) {
printf("\r\n remove %d ", pNode->data);
free(pNode);
}
}
return 0;
}
开心的一天又结束了,开心今天下午给同学将了一下午代码,发现我的代码能力又提高了,再接再厉。接下来就是链表的反转等等了。虽然看不懂,但终会弄懂的,刚把得^-^





















 212
212











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








