中断-底半部机制内部调用关系
前言
前面已经了解了底半部机制tasklet,工作队列,软中断,threaded_irq如何使用,这篇文章中将继续了解各种机制内部的调用关系。
软中断
初始化
软中断类型
//软中断的类型
enum
{
HI_SOFTIRQ=0, /* 最高优先级软中断 */
TIMER_SOFTIRQ, /* Timer定时器软中断 */
NET_TX_SOFTIRQ, /* 发送网络数据包软中断 */
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, /* 接收网络数据包软中断 */
BLOCK_SOFTIRQ, /* 块设备软中断 */
BLOCK_IOPOLL_SOFTIRQ,/* 支持IO轮询的块设备软中断 */
TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, /* tasklet软中断 */
SCHED_SOFTIRQ, /* 进程调度及负载均衡的软中断 */
HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ,//高精度定时器(已经放弃)
RCU_SOFTIRQ, //RCU相关的软中断
/* Preferable RCU should always be the last softirq */
NR_SOFTIRQS
};
#define SOFTIRQ_STOP_IDLE_MASK (~(1 << RCU_SOFTIRQ))
/* map softirq index to softirq name. update 'softirq_to_name' in
* kernel/softirq.c when adding a new softirq.
*/
/* 软中断描述符表,实际上就是一个全局的数组 */
extern const char * const softirq_to_name[NR_SOFTIRQS];
/* softirq mask and active fields moved to irq_cpustat_t in
* asm/hardirq.h to get better cache usage. KAO
*/
/* 软件中断描述符,只包含一个handler函数指针 */
struct softirq_action
{
void (*action)(struct softirq_action *);
};
asmlinkage void do_softirq(void);
asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void);
#ifdef __ARCH_HAS_DO_SOFTIRQ
void do_softirq_own_stack(void);
#else
static inline void do_softirq_own_stack(void)
{
__do_softirq();
}
#endif
extern void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *));
extern void softirq_init(void);
extern void __raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr);
extern void raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr);
extern void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr);
/* 内核为每个CPU都创建了一个软中断处理内核线程 */
DECLARE_PER_CPU(struct task_struct *, ksoftirqd);

softirq_vec[]数组,类比硬件中断描述符表irq_desc[],通过软中断号可以找到对应的handler进行处理,比如图中的tasklet_action就是一个实际的handler函数;
软中断可以在不同的CPU上并行运行,在同一个CPU上只能串行执行;
每个CPU维护irq_cpustat_t状态结构,当某个软中断需要进行处理时,会将该结构体中的__softirq_pending字段或上1UL << XXX_SOFTIRQ;
软中断注册
软中断处理流程中,通过open_softirq接口来注册:
void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *))
{
softirq_vec[nr].action = action;//将软中断描述符表中对应描述符的handler函数指针指向对应的函数
}
软中断执行->中断处理后
软中断执行的入口是invoke_softirq:
static inline void invoke_softirq(void)
{
if (!force_irqthreads) {
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_IRQ_EXIT_ON_IRQ_STACK
/*
* We can safely execute softirq on the current stack if
* it is the irq stack, because it should be near empty
* at this stage.
*/
__do_softirq();//中断未强制线程化
#else
/*
* Otherwise, irq_exit() is called on the task stack that can
* be potentially deep already. So call softirq in its own stack
* to prevent from any overrun.
*/
do_softirq_own_stack();
#endif
} else {//中断线程化
wakeup_softirqd();//唤醒内核线程来处理软中断
}
}
invoke_softirq函数中,根据中断处理是否线程化进行分类处理,如果中断已经进行了强制线程化处理(中断强制线程化,需要在启动的时候传入参数threadirqs),那么直接通过wakeup_softirqd唤醒内核线程来执行,否则的话则调用__do_softirq函数来处理;
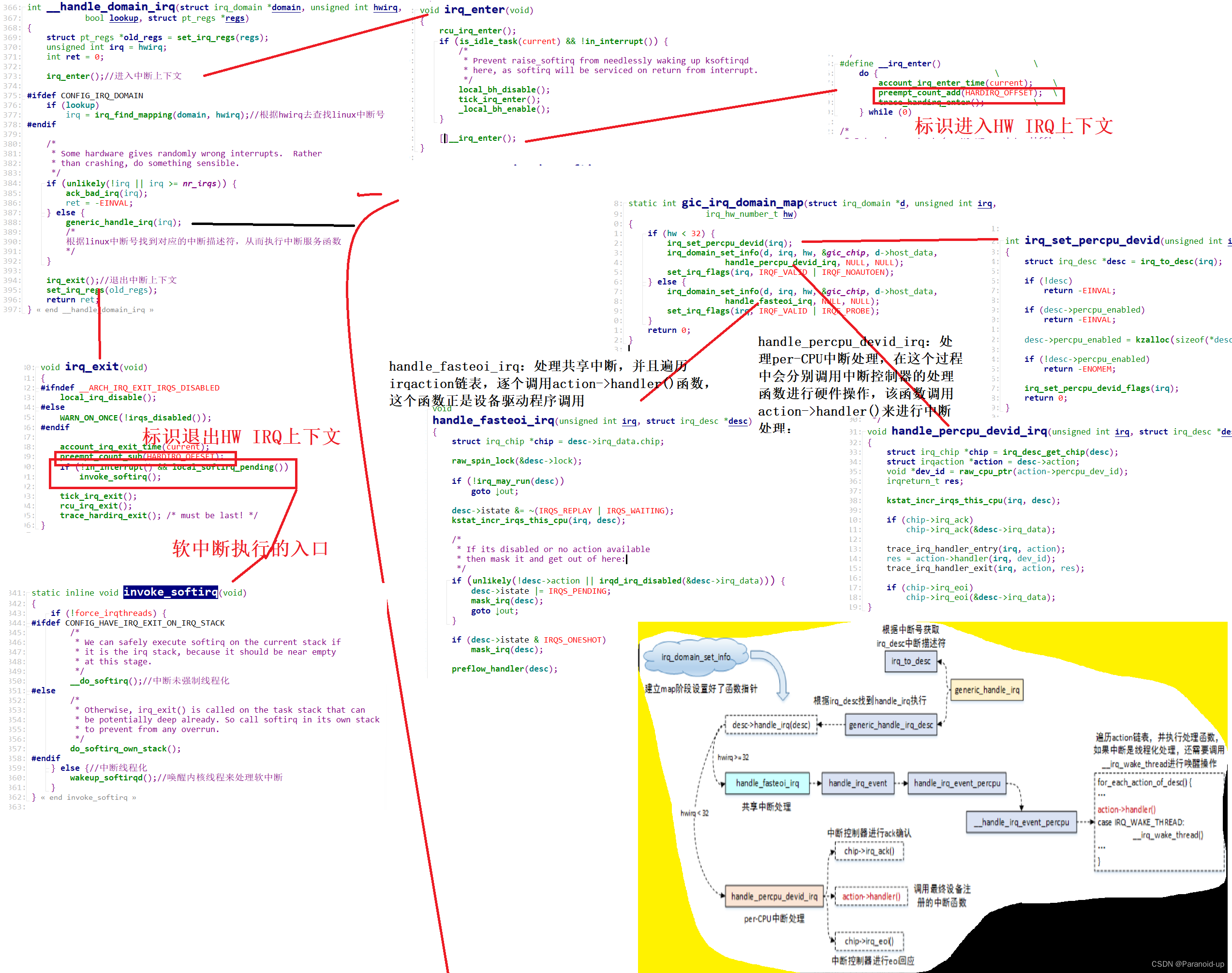
在接收到中断信号后,处理器进行异常模式切换,并跳转到异常向量表处进行执行,关键的流程为:
el0_irq->irq_handler->handle_arch_irq(gic->handle_irq)->handle_domain_irq->__handle_domain_irq;
在__handle_domain_irq函数中,irq_enter和irq_exit分别用于来标识进入和离开硬件中断上下文处理,这个从preempt_count_add/preempt_count_sub来操作HARDIRQ_OFFSET可以看出来,这也对应到了上文中的Context描述图;
在离开硬件中断上下文后,如果!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending为真,则进行软中断处理。这个条件有两个含义:1)!in_interrupt()表明不能处在中断上下文中,这个范围包括in_nmi、in_irq、in_softirq(Bottom-half disable)、in_serving_softirq,凡是处于这几种状态下,软中断都不会被执行;2)local_softirq_pending不为0,表明有软中断处理请求;

invoke_softirq函数中,根据中断处理是否线程化进行分类处理,如果中断已经进行了强制线程化处理(中断强制线程化,需要在启动的时候传入参数threadirqs),那么直接通过wakeup_softirqd唤醒内核线程来执行,否则的话则调用__do_softirq函数来处理;
Linux内核会为每个CPU都创建一个内核线程ksoftirqd,通过smpboot_register_percpu_thread函数来完成,其中当内核线程运行时,在满足条件的情况下会执行run_ksoftirqd函数,如果此时有软中断处理请求,调用__do_softirq来进行处理;
核心处理
asmlinkage __visible void __do_softirq(void)
{
unsigned long end = jiffies + MAX_SOFTIRQ_TIME;//软中断处理时间小于两毫秒;
unsigned long old_flags = current->flags;
int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART;//跳转到restart循环的次数不大于10次;
struct softirq_action *h;
bool in_hardirq;
__u32 pending;
int softirq_bit;
/*
* Mask out PF_MEMALLOC s current task context is borrowed for the
* softirq. A softirq handled such as network RX might set PF_MEMALLOC
* again if the socket is related to swap
*/
current->flags &= ~PF_MEMALLOC;
pending = local_softirq_pending();//读取__softirq_pending字段,用于判断是否有处理请求
//可以类比于设备驱动中的状态寄存器,用于判断是否有软中断处理请求
account_irq_enter_time(current);
__local_bh_disable_ip(_RET_IP_, SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);//关闭button-half
in_hardirq = lockdep_softirq_start();
restart:
/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */
set_softirq_pending(0);//将__softirq_pending字段清零
local_irq_enable();//关闭本地中断
h = softirq_vec;
while ((softirq_bit = ffs(pending))) {//软中断处理
//循环读取状态位,直到处理完每一个软中断请求
unsigned int vec_nr;
int prev_count;
h += softirq_bit - 1;
vec_nr = h - softirq_vec;
prev_count = preempt_count();
kstat_incr_softirqs_this_cpu(vec_nr);
trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);
h->action(h);
trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);
if (unlikely(prev_count != preempt_count())) {
pr_err("huh, entered softirq %u %s %p with preempt_count %08x, exited with %08x?\n",
vec_nr, softirq_to_name[vec_nr], h->action,
prev_count, preempt_count());
preempt_count_set(prev_count);
}
h++;
pending >>= softirq_bit;
}
/*
跳出while循环之后,再一次判断是否又有新的软中断请求到来(由于它可能被中断打断
,也就意味着可能有新的请求到来),有新的请求到来,则有三个条件判断,满足的话跳
转到restart处执行,否则调用wakeup_sotfirqd来唤醒内核线程来处理:
*/
rcu_bh_qs();
local_irq_disable();//打开本地中断
pending = local_softirq_pending();//判断是否有新的请求到来
if (pending) {
if (time_before(jiffies, end) && !need_resched() &&
--max_restart)
/*
time_before(jiffies, MAX_SOFTIRQ_TIME),软中断处理时间小于两毫秒;
!need_resched,当前没有进程调度的请求
*/
goto restart;//跳转到restart
wakeup_softirqd();//唤醒内核线程来处理
}
lockdep_softirq_end(in_hardirq);
account_irq_exit_time(current);
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);//打开button_half
WARN_ON_ONCE(in_interrupt());
tsk_restore_flags(current, old_flags, PF_MEMALLOC);
}
local_softirq_pending函数用于读取__softirq_pending字段,可以类比于设备驱动中的状态寄存器,用于判断是否有软中断处理请求;
软中断处理时会关闭Bottom-half,处理完后再打开;
软中断处理时,会打开本地中断,处理完后关闭本地中断
time_before(jiffies, MAX_SOFTIRQ_TIME),软中断处理时间小于两毫秒;
!need_resched,当前没有进程调度的请求;
max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART,跳转到restart循环的次数不大于10次;
这三个条件的判断,是基于延迟和公平的考虑,既要保证软中断尽快处理,又不能让软中断处理一直占据系统。
软中断的触发
软中断的触发通过raise_softirq接口:
void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);//关闭本地中断
raise_softirq_irqoff(nr);
local_irq_restore(flags);//打开本地中断
}
inline void raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr)
{
__raise_softirq_irqoff(nr);
/*
* If we're in an interrupt or softirq, we're done
* (this also catches softirq-disabled code). We will
* actually run the softirq once we return from
* the irq or softirq.
*
* Otherwise we wake up ksoftirqd to make sure we
* schedule the softirq soon.
*/
if (!in_interrupt())//如果不在中断上下文中,那么唤醒内核线程来处理软中断
wakeup_softirqd();
}
raise_softirq_irqoff函数中,最终会调用到or_softirq_pending,该函数会去读取本地CPU的irq_stat中__softirq_pending字段,然后将对应的软中断号给置位,表明有该软中断的处理请求
void __raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr)
{
trace_softirq_raise(nr);
or_softirq_pending(1UL << nr);//将__softirq_pending字段的比特位置位,请求软中断处理
}
raise_softirq_irqoff函数中,最终会调用到or_softirq_pending,该函数会去读取本地CPU的irq_stat中__softirq_pending字段,然后将对应的软中断号给置位,表明有该软中断的处理请求
软中断执行->Bottom-half Enable后
void __local_bh_enable_ip(unsigned long ip, unsigned int cnt)
{
WARN_ON_ONCE(in_irq() || irqs_disabled());
/*
如果已经关闭了中断调用__local_bh_enable_ip就会警告
原因:关中断比关Bottom-half级别更高,已经关了中断就
没必要在管Bottom-half了
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
local_irq_disable();
#endif
/*
* Are softirqs going to be turned on now:
*/
if (softirq_count() == SOFTIRQ_DISABLE_OFFSET)
trace_softirqs_on(ip);
/*
* Keep preemption disabled until we are done with
* softirq processing:
*/
preempt_count_sub(cnt - 1);
/*
preempt_count_sub与preempt_count_add配对使用(用于操作thread_info->preempt_count
字段,加与减的值是一致的),先减去cnt-1,
preempt_count不为0,禁止了抢占
*/
if (unlikely(!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending())) {
/*软中断处理
并发处理时,可能已经把Bottom-half进行关闭了,如果此时中断来
了后,软中断不会被处理,在进程上下文中打开Bottom-half时,这
时候就会检查是否有软中断处理请求了
* Run softirq if any pending. And do it in its own stack
* as we may be calling this deep in a task call stack already.
*/
do_softirq();
}
preempt_count_dec();//preempt_count再减去1,刚好总共减去cnt值
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
local_irq_enable();
#endif
preempt_check_resched();//检查是否有调度请求
}
tasklet
tasklet是软中断的一种类型,但是软中断类型内核中都是静态分配,不支持动态分配,而tasklet支持动态和静态分配,也就是驱动程序中能比较方便的进行扩展;软中断可以在多个CPU上并行运行,因此需要考虑可重入问题,而tasklet会绑定在某个CPU上运行,运行完后再解绑,不要求重入问题,当然它的性能也就会下降一些。
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))//测试并设置tasklet的状态
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
void __tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);//关闭本地中断
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;//将tasklet添加到本地CPU的tasklet_vec中
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);//触发软中断执行
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
tasklet本质上是一种软中断
工作队列
Workqueue工作队列是利用内核线程来异步执行工作任务的通用机制;Workqueue工作队列可以用作中断处理的Bottom-half机制,利用进程上下文来执行中断处理中耗时的任务,因此它允许睡眠,而Softirq和Tasklet在处理任务时不能睡眠;
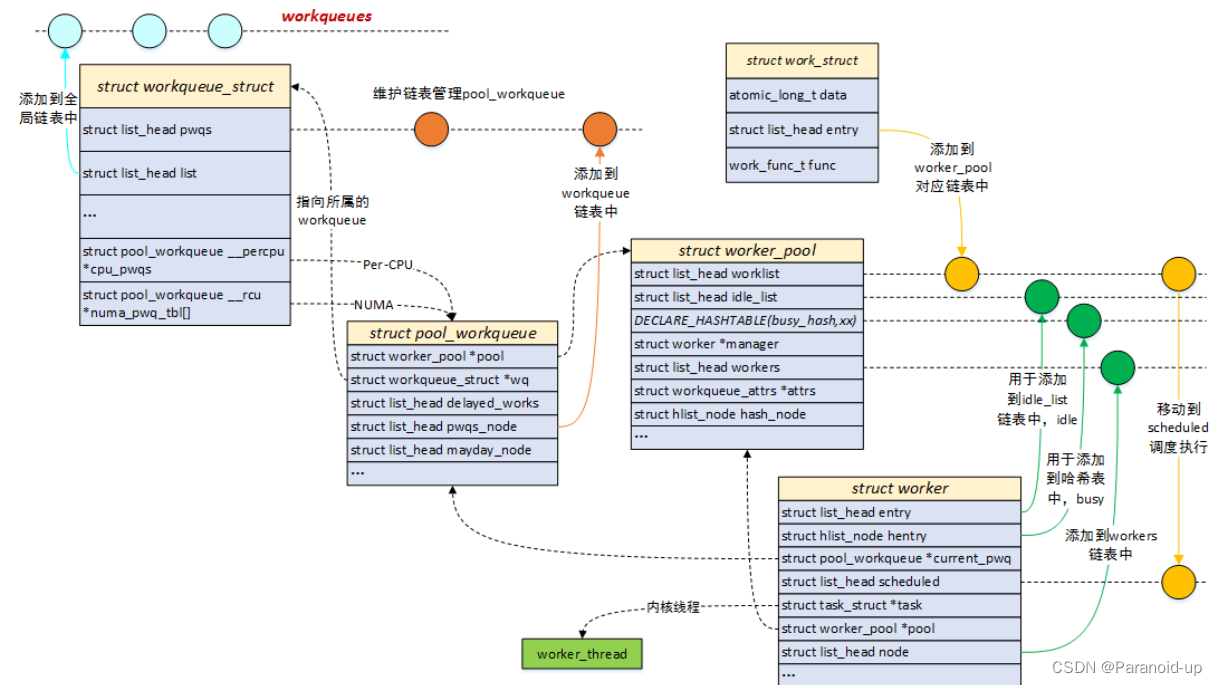
struct work_struct {
atomic_long_t data;//低比特存放状态位,高比特存放worker_pool的ID或者pool_workqueue的指针
struct list_head entry;//用于添加到其他队列上
work_func_t func;//工作任务的处理函数,在内核线程中回调
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};
驱动程序要通过工作队列实现延迟操作时,需要生成一个struct work_struct对象(工作节点),然后通过queue-work函数将其提交给工作队列。
struct workqueue_struct {
struct list_head pwqs; /*维护链表管理pool_workqueue
WR: all pwqs of this wq */
struct list_head list; /*添加到全局链表中
PR: list of all workqueues */
struct mutex mutex; /* protects this wq */
int work_color; /* WQ: current work color */
int flush_color; /* WQ: current flush color */
atomic_t nr_pwqs_to_flush; /* flush in progress */
struct wq_flusher *first_flusher; /* WQ: first flusher */
struct list_head flusher_queue; /* WQ: flush waiters */
struct list_head flusher_overflow; /* WQ: flush overflow list */
struct list_head maydays; /* rescue状态下的pool_workqueue添加到本链表中MD: pwqs requesting rescue */
struct worker *rescuer; /* rescuer内核线程,用于处理内存紧张时创建工作线程失败的情况I: rescue worker */
int nr_drainers; /* WQ: drain in progress */
int saved_max_active; /* WQ: saved pwq max_active */
struct workqueue_attrs *unbound_attrs; /* WQ: only for unbound wqs */
struct pool_workqueue *dfl_pwq; /* WQ: only for unbound wqs */
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
struct wq_device *wq_dev; /* I: for sysfs interface */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
char name[WQ_NAME_LEN]; /* I: workqueue name */
/*
* Destruction of workqueue_struct is sched-RCU protected to allow
* walking the workqueues list without grabbing wq_pool_mutex.
* This is used to dump all workqueues from sysrq.
*/
struct rcu_head rcu;
/* hot fields used during command issue, aligned to cacheline */
unsigned int flags ____cacheline_aligned; /*Per-CPU都创建pool_workqueueWQ: WQ_* flags */
struct pool_workqueue __percpu *cpu_pwqs; /* I: per-cpu pwqs */
struct pool_workqueue __rcu *numa_pwq_tbl[]; /*Per-Node创建pool_workqueue FR: unbound pwqs indexed by node */
};
struct worker {
/* on idle list while idle, on busy hash table while busy */
union {
struct list_head entry; /*用于添加到worker_pool的空闲链表中 L: while idle */
struct hlist_node hentry; /* 用于添加到worker_pool的忙碌列表中L: while busy */
};
struct work_struct *current_work; /*当前正在处理的work L: work being processed */
work_func_t current_func; /* 当前正在执行的work回调函数L: current_work's fn */
struct pool_workqueue *current_pwq; /*指向当前work所属的pool_workqueue L: current_work's pwq */
bool desc_valid; /* ->desc is valid */
struct list_head scheduled; /* 所有被调度执行的work都将添加到该链表中L: scheduled works */
/* 64 bytes boundary on 64bit, 32 on 32bit */
struct task_struct *task; /*指向内核线程 I: worker task */
struct worker_pool *pool; /*该worker所属的worker_pool I: the associated pool */
/* L: for rescuers */
struct list_head node; /*添加到worker_pool->workers链表中 A: anchored at pool->workers */
/* A: runs through worker->node */
unsigned long last_active; /* L: last active timestamp */
unsigned int flags; /* X: flags */
int id; /* I: worker id */
/*
* Opaque string set with work_set_desc(). Printed out with task
* dump for debugging - WARN, BUG, panic or sysrq.
*/
char desc[WORKER_DESC_LEN];
/* used only by rescuers to point to the target workqueue */
struct workqueue_struct *rescue_wq; /* I: the workqueue to rescue */
};
struct worker_pool {
spinlock_t lock; /* the pool lock */
int cpu; /* 绑定到CPU的workqueue,代表CPU IDI: the associated cpu */
int node; /* 非绑定类型的workqueue,代表内存Node IDI: the associated node ID */
int id; /* I: pool ID */
unsigned int flags; /* X: flags */
struct list_head worklist; /*pending状态的work添加到本链表 L: list of pending works */
int nr_workers; /* pending状态的work添加到本链表L: total number of workers */
/* nr_idle includes the ones off idle_list for rebinding */
int nr_idle; /* L: currently idle ones */
struct list_head idle_list; /*处于IDLE状态的worker添加到本链表 X: list of idle workers */
struct timer_list idle_timer; /* L: worker idle timeout */
struct timer_list mayday_timer; /* L: SOS timer for workers */
/* a workers is either on busy_hash or idle_list, or the manager */
DECLARE_HASHTABLE(busy_hash, BUSY_WORKER_HASH_ORDER);
/*工作状态的worker添加到本哈希表中 L: hash of busy workers */
/* see manage_workers() for details on the two manager mutexes */
struct mutex manager_arb; /* manager arbitration */
struct worker *manager; /* L: purely informational */
struct mutex attach_mutex; /* attach/detach exclusion */
struct list_head workers; /*worker_pool管理的worker添加到本链表中 A: attached workers */
struct completion *detach_completion; /* all workers detached */
struct ida worker_ida; /* worker IDs for task name */
struct workqueue_attrs *attrs; /* I: worker attributes */
struct hlist_node hash_node; /*用于添加到unbound_pool_hash中 PL: unbound_pool_hash node */
int refcnt; /* PL: refcnt for unbound pools */
/*
* The current concurrency level. As it's likely to be accessed
* from other CPUs during try_to_wake_up(), put it in a separate
* cacheline.
*/
atomic_t nr_running ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/*
* Destruction of pool is sched-RCU protected to allow dereferences
* from get_work_pool().
*/
struct rcu_head rcu;
} ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
worker_pool是一个资源池,管理多个worker,也就是管理多个内核线程;
针对绑定类型的工作队列,worker_pool是Per-CPU创建,每个CPU都有两个worker_pool,对应不同的优先级,nice值分别为0和-20;
针对非绑定类型的工作队列,worker_pool创建后会添加到unbound_pool_hash哈希表中;
worker_pool管理一个空闲链表和一个忙碌列表,其中忙碌列表由哈希管理;
struct pool_workqueue {
struct worker_pool *pool; /*指向worker_pool I: the associated pool */
struct workqueue_struct *wq; /*指向所属的workqueue I: the owning workqueue */
int work_color; /* L: current color */
int flush_color; /* L: flushing color */
int refcnt; /* L: reference count */
int nr_in_flight[WORK_NR_COLORS];
/* L: nr of in_flight works */
int nr_active; /*活跃的work数量 L: nr of active works */
int max_active; /*活跃的最大work数量 L: max active works */
struct list_head delayed_works; /*延迟执行的work挂入本链表 L: delayed works */
struct list_head pwqs_node; /*用于添加到workqueue链表中 WR: node on wq->pwqs */
struct list_head mayday_node; /*用于添加到workqueue链表中 MD: node on wq->maydays */
/*
* Release of unbound pwq is punted to system_wq. See put_pwq()
* and pwq_unbound_release_workfn() for details. pool_workqueue
* itself is also sched-RCU protected so that the first pwq can be
* determined without grabbing wq->mutex.
*/
struct work_struct unbound_release_work;
struct rcu_head rcu;
} __aligned(1 << WORK_STRUCT_FLAG_BITS);
总结
上半部称为硬中断(hardirq),下半部有3种:软中断(softirq)、小任务(tasklet)和工作队列(workqueue)。3种下半部的区别:
- 软中断和小任务不允许睡眠,工作队列是使用内核线程实现的,处理函数可以睡眠。
- 软中断的种类是编译时态定义的,在运行时不能添加或删除;小任务可以在运行时添加或删除。
- 同一种软中断的处理函数可以在多个处理器上同时执行,处理函数必须是可以重入的,需要使用锁保护临界区;一个小任务同一时刻只能在一个处理器上执行,不要求处理函数是可以重入的。


























 536
536











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










