string
了解string
string是一个表示字符序列的类
string类是basic_string模板类的一个实例,它使用char来实例化basic_string模板类。
string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,
typedef basic_string<char> string;
- string类管理动态增长的字符数组,这个字符串以
\0结尾,数组存储在堆区。
string类对象的常见构造
函数名称 功能说明 string() 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串 string(const char s)* 用C字符串来构造string类对象 string(size_t n,char c) string类对象中包含n个字符c string(const string& s) 拷贝构造函数 string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos) 拷贝str的下标为pos的位置开始,len个字符构造 string (const char s, size_t n)* 构造函数,C字符串的前n个字符 void test1() { char a[10] = "qwer"; string s1; //构造空的string类对象s1 string s2(a); //用C格式字符串构造string类对象s2 string s3("hello world");//用常量字符串构造string类对象s3 string s4(s2); //拷贝构造s4 string s5(5, 'x');//构造string类对象中包含n个字符c string s6(s3,6,3);//拷贝s3的下标为6的位置开始,三个字符构造s6 string s7(s3,6,100);//超过长度,有多少取多少 string s8(s3,6);//取npos个字符,static const size_t npos = -1; string s9("1234567890",4);//构造s9,C字符串的前四个字符 }注意:
- **
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos)是半缺省,static const size_t npos = -1,如果len**超过长度,有多少取多少
string类赋值重载函数
string s1("hello"); string s2("xxx"); s1=s2; //string类可以赋值 s1="qwer"; //C字符串可以赋值 s1='q'; //单个字符可以赋值
string类对象的容量操作
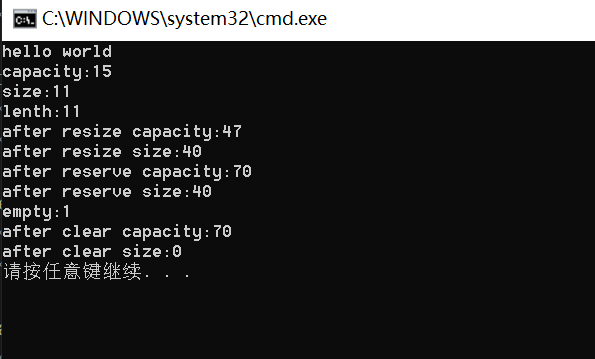
函数名称 功能说明 size 返回字符串有效字符长度 length 返回字符串有效字符长度 capacity 返回空间总大小 empty 检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false clear 清空有效字符 reserve 为字符串预留空间(改变容量) resize 将有效字符的个数改成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充(会初始化('\0’或指定字符)+改变容量) void test() { string s1("hello world"); cout << s1 << endl; cout << "capacity:" << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << "size:" << s1.size() << endl; cout << "lenth:" << s1.length() << endl; s1.resize(40, 'x'); cout << "after resize capacity:" << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << "after resize size:" << s1.size() << endl; s1.reserve(50); cout << "after reserve capacity:" << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << "after reserve size:" << s1.size() << endl; s1.clear(); cout << "empty:" << s1.empty() << endl; cout << "after clear capacity:" << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << "after clear size:" << s1.size() << endl; }
注意:
- size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一 致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。
- clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
- resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小(当元素个数增多时,如果容量不够,扩大底层容量,如果容量足够,底层容量不变),如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
- reserve(size_t res_arg=0);为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
string类对象的访问及遍历操作
string类对象的遍历共有三种方式
下标 + []
operator[]
for(size_t i=0;i<s1.size();i++) { //s1.operator[](i) cout<<s1[i]<<""; }operator[]函数讲解
1、char& operator[] (size_t pos); 2、const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const; 返回值是引用,是为了修改,如果是值返回,返回中间变量,中间变量是具有常属性,不可修改迭代器
概念:迭代器是像指针一样的东西,或者就是指针用来访问数据结构的。
获取迭代器函数
begin():begin获取一个字符的迭代器
end():end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器
rbegin:rbegin获取最后一个字符的迭代器
rend:rend获取第一个字符前一个位置的迭代器四种迭代器
正向迭代器(可读可写)
string s1("Hello World"); string::iterator it = s1.begin(); while(it!=s1.end()) { cout<<*it<<" "; ++it; } cout<<endl;反向迭代器(可读可写)
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); while(rit!=s1.rend()) { cout<<*rit<<" "; ++rit; } cout<<endl;正向迭代器(只读)
string::const_iterator it = s1.begin(); while(it!=s1.end()) { cout<<*it<<" "; ++it; } cout<<endl;反向迭代器(只读)
string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s1.begin(); while(rit!=s1.end()) { cout<<*rit<<" "; ++rit; } cout<<endl;范围for
for(auto ch:s1) { cout<<ch<<" "; ++it; } cout<<endl;
补充:
[]
越界:断言处理
at
越界:抛异常处理
string类对象的修改操作
函数名称 功能说明 push_back 在字符串后尾插字符c(插入数据,如果容量不够,会扩容(大概1.5倍)) append 在字符串后追加一个字符串 operator+=(最常用) 在字符串后追加字符串str c_str 返回C格式字符串(返回指向str指针) find 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 rfind 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 substr 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回 函数声明:
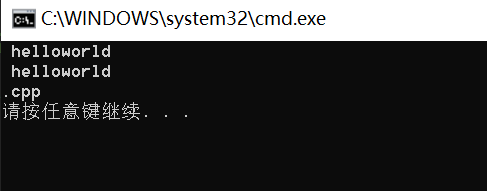
//push_back void push_back (char c); //c_str const char* c_str() const; //find size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const; //rfind size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const; size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const; size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const; //substr string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;void Teststring() { string str; str.push_back(' '); // 在str后插入空格 str.append("hello"); // 在str后追加一个字符"hello" str += 'w'; // 在str后追加一个字符'b' str += "orld"; // 在str后追加一个字符串"it" cout << str << endl; cout << str.c_str() << endl; // 以C语言的方式打印字符串 // 获取file的后缀 string file1("string.cpp"); size_t pos = file1.rfind('.'); string suffix(file1.substr(pos, file1.size() - pos)); cout << suffix << endl; // npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量 // static const size_t npos = -1; }
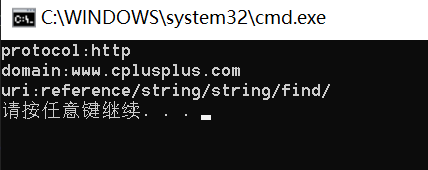
提取url中的协议 域名 uri
string url1("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/"); string& url = url1; // 取出url中的协议 string protocol; size_t pos1 = url.find("://"); if (pos1 != string::npos) { protocol = url.substr(0, pos1); cout << "protocol:" << protocol << endl; } else { cout << "非法url" << endl; } // 取出url中的域名 string domain; size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3); if (pos2 != string::npos) { domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3)); cout << "domain:" << domain << endl; } else { cout << "非法url" << endl; } // 取出url中的uri string uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1); cout << "uri:" << uri << endl;
insert
函数声明:
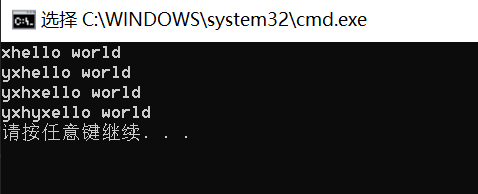
string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c); iterator insert (iterator p, char c);void test() { string s("hello world"); s.insert(0, 1, 'x'); cout << s << endl; s.insert(s.begin(), 'y'); cout << s << endl; s.insert(3, 1, 'x'); cout << s << endl; s.insert(s.begin() + 3, 'y'); cout << s << endl; }
erase
函数声明:
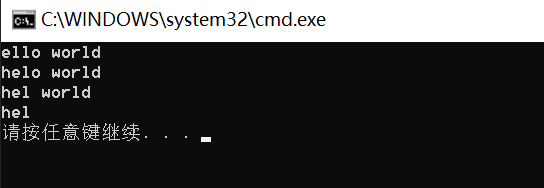
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos); iterator erase (iterator p);void test() { string s("hello world"); s.erase(s.begin()); cout << s << endl; string s1("hello world"); s1.erase(s1.begin() + 3); cout << s1 << endl; string s2("hello world"); s2.erase(3, 2); cout << s2 << endl; string s3("hello world"); s3.erase(3); cout << s3 << endl; //lenth缺省值(-1),删完 }
swap(string类内)
函数声明:
void swap (string& str);void test() { string s1("hello world"); string s2("string"); s1.swap(s1);//效率高(交换指针) swap(s1,s2);//效率低(深拷贝) }注意:
string类内的swap函数是通过交换动态数组的指针,实现交换**(效率高)**
std::swap函数是通过深拷贝实现交换**(效率低)**






















 369
369











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








