Database architectures数据库架构
数据库和数据库应用一般不在同一台计算机上
客户端Client:
the machine running the user interface of the applications. 运行应用程序的用户界面的机器
数据库服务器Database server:
the machine that runs the DBMS and contains the database.运行DBMS并包含该数据库的机器
分类:
个人数据库Personal databases 双层数据库 twotier databases 多层数据库 Multi-tier databases
个人数据库Personal databases
允许用户以有效的方式管理(存储、更新、删除和检索store, update, delete, and retrieve)少量数据。
能够提高个人生产力,但是数据不能与他人共享。
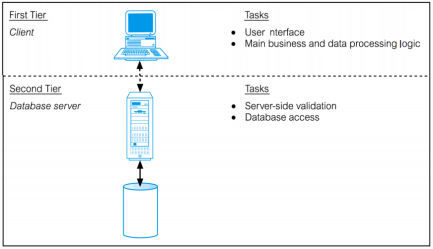
双层数据库 twotier databases/Server Architecture
通过有线网络或无线网络连接起来的客户端Computers (client) connected over wired or wireless local area network (LAN),数据库本身和DBMS存储在一个称为数据库服务器的中央设备上,该服务器也连接到网络
三层客户端-服务器体系结构Three-Tier Client-Server Architecture
多层客户端Multi-tier Client/Server Architecture
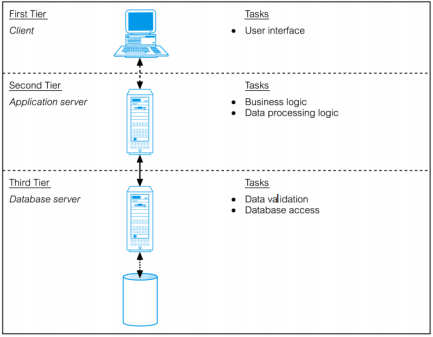
三层体系结构可以扩展到多层,并添加额外的层以提供更多的灵活性和可伸缩性。
用户界面层User interface layer-即在最终用户的计算机(客户端client)上运行的用户界面层
程序服务器-业务逻辑和数据处理层Business logic and data processing layer。这个中间层运行在服务器上
DBMS-存储中间层所需的数据。此层可以在称为数据库服务器的单独服务器上运行
Distributed Database and DDBMS分布式数据库和DDBMS
Distributed Database分布式数据库
一种逻辑上相关的共享数据(以及对该数据的描述)的集合,物理上分布在计算机网络上。A logically interrelated collection of shared data (and a description of this data), physically spread over a computer network.
DDBMS:Distributed DBMS分布式DBMS软件系统
允许管理分布式数据库,并使分发对用户透明,,Software system that permits the management of the distributed database and makes the distribution transparent to users.
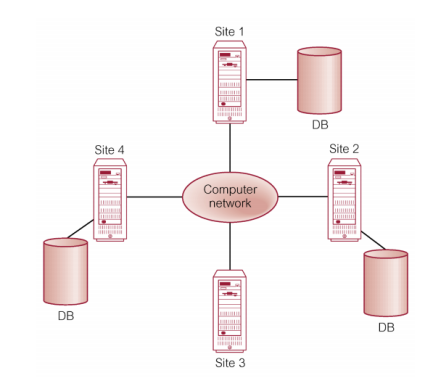
区别:distributed processing:集中式数据库,通过计算机网络访问//DBMS:被分成碎片的单个逻辑数据库,数据碎片分布在一个计算机网络上。
分类:
Homogeneous DDBMS
使用同一个管理系统,设计管理简单,高效处理数据极大
Heterogeneous DDBMS
使用不同的管理系统,甚至不同的数据模型。造成的低效怎么解决:使用一个叫GateWay的软件让他们看起来类似
Functions of a DDBMS:通信 检索 处理 控制 恢复
Extended communication services.
Extended Data Dictionary.
Distributed query processing.
Extended concurrency control.
Extended recovery services.
参考体系结构Reference Architecture:
包含DBMS特性但是没有像DBMS的ANSI/SPARC 3-level 标准结构(Reference DDBMS 让它看起来Centralized)
Set of global external schemas.全局外部架构集
Global conceptual schema (GCS).全局概念模式
Fragmentation schema and allocation schema.碎片化模式和分配模式
Set of schemas for each local DBMS conforming to 3-level ANSI/SPARC.符合3级ANSI/SPARC的每个本地DBMS的模式集
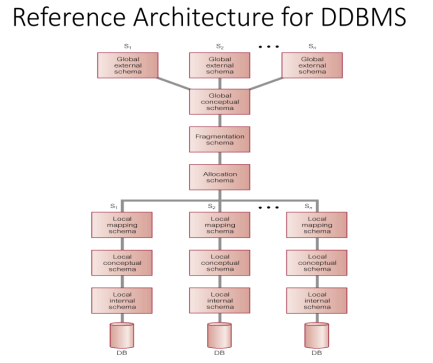
DDBMS的组件体系结构Component Architecture
Local DBMS (LDBMS):
standard DBMS, responsible for controlling the local data at each site that has a database标准DBMS,负责控制带有数据库的每个站点上的本地数据
Data Communications (DC):
software enabling all sites to communicate with each other.使所有站点能够相互通信的软件
Global System Catalogue (GSC):
holds information specific to the distributed nature of the system, such as the fragmentation, replication, and allocation schemas (it can be managed as a distributed
database).保存特定于系统分布式特性的信息,例如碎片化、复制和分配模式(它可以作为分布式数据库进行管理)
Distributed DBMS (DDBMS):
the controlling unit of the entire system整个系统的控制单元
3个核心要义:
Fragmentation
关系合一分成若干分布的子片段
Type:
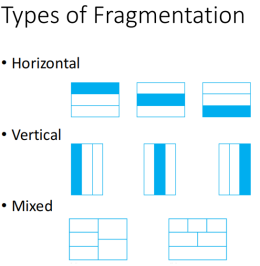
Allocation
每个片段以最优分布储存在站点上Each fragment is stored at the site with “optimal” distribution.
Type:
1、中心化Centralized
用同一个DB和DBMS对用户在DDB里面的操作进行管理。a single database and DBMS stored at one site with users distributed across the network –essentially distributed processing
2、分块化Fragemented or Partitioned
数据库分成块 块与块之间不重叠 每块放一个地方。Database partitioned into disjoint fragments, each fragment assigned to one site
3、完全重复Complete Replication
每部分包括完整的数据库情况(完整副本)。Consists of maintaining complete copy of database at each site.
4、选择性复制Selective Replication(前三者的结合)
Combination of fragmentation, replication, and centralization
Replication复制
片段的副本可以在几个站点上保存Copy of fragment may be maintained at several sites.
DDB Design
DDB的优点:
1、能反映原始结构2、提高共享性 自治性3、提高可行性 可读性 和运行表现
缺点:
1复杂 2花费大 3安全性能 4标准和管理经验缺乏 5设计更复杂
Transparency in a DDBMS透明度
目的:不希望认为使用DDB非常复杂,4种透明,看起来Centralized(集中的)。
Distribution Transparency分配透明度
使用DDB的用户要让它看起来是个Single, logical Entity.若没有,则用户需要知道数据如何碎片化、碎片的位置
用户会忽略数据的碎片化方式(碎片透明度)、数据项的位置(位置透明度)、片段的复制(复制透明度)The user ignores how• data is fragmented (fragmentation transparency), • location of data items (location transparency),• replication of fragments (replication transparency)
//Naming Transparency
原则:独一无二,不能重复。
如何区别?类似java 用.表示大类小类,但太复杂了?只保留最大的Site后续直接自定义个名字就行。
名字等级划分:Site 具体名 Fragementno Copyno 从大到小
Transaction Transparency事务透明度
为了保证数据库一致性和完整性
Distributive Transaction被分成很多个Sub-Tranaction放在子类里面进行,每个必须访问的站点对应一个,DDBMS必须确保全局事务和每个子事务的同步。
//Concurrency Transparency 并发透明度
所有事务必须独立执行,如果每次按任意顺序执行一个事务,则在逻辑上与获得的结果一致,,与集中式DBMS(centralized DBMS)的基本原则相同,,确保全局和本地事务不会冲突,,确保全局事务处理的全部子事务的一致性
//Failure Transparency
保全局事务的原子性和持久性,,确保全局事务的子事务全部提交或全部中止,,DDBMS必须同步全局事务,以确保所有子事务都已成功完成,,必须在存在站点和网络故障时这样做
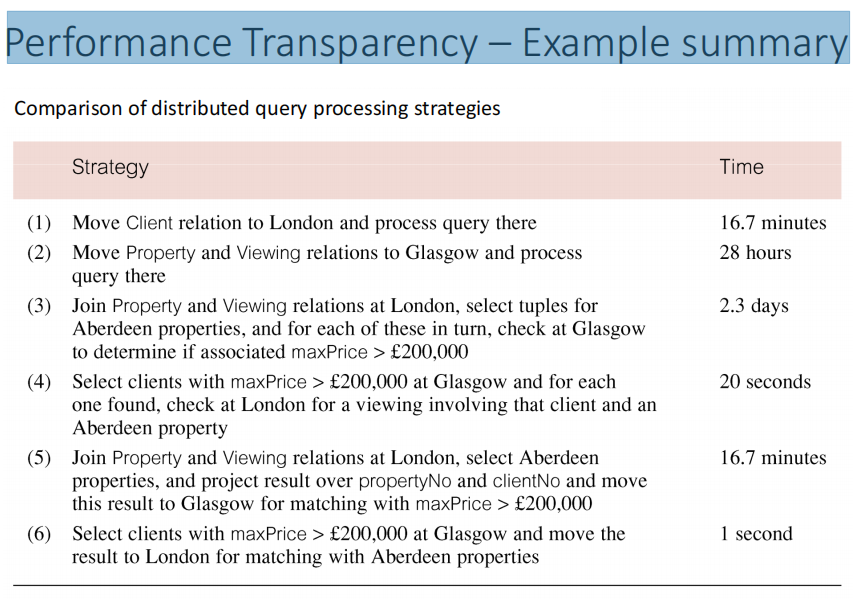
Performance Transparency
DDBMS性能不下降,执行最经济有效,必须作为一个集中的DBMS来处理数据
//DQP
生成针对某些成本函数进行优化的执行策略--I/O cost; CPU cost; communication cost.
Distributed Query Processor (DQP) maps data request into ordered sequence of operations on local databases. 分布式查询处理器(DQP)将数据请求映射到本地数据库上的有序操作序列中
• DQP has to decide:
1. which fragment to access;要访问哪个片段;2. which copy of a fragment to use;要使用哪个片段的副本3. which location to use要使用哪个位置
DBMS Transparency






















 354
354











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








