在多线程编程中,正确处理并发访问是至关重要的。Java提供了多种并发同步机制,其中包括自旋锁和重入锁。本文将介绍自旋锁和重入锁的概念、特性以及如何在Java中使用它们。
自旋锁:
自旋锁是一种基于忙等待的锁机制。它的特点是当线程请求锁时,如果锁已被其他线程占用,该线程将循环等待(自旋),并不断尝试获取锁,而不是进入阻塞状态。这种方式避免了线程切换和上下文切换的开销,适用于锁占用时间较短的情况。
package com.struggle.lock;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* 自旋锁,不具备重入功能
*/
public class SpinLock {
private Thread owner;
private volatile int state;
private Unsafe unsafe;
private long stateOffset;
public SpinLock() {
Field theUnsafe;
try {
theUnsafe = unsafeClass.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafe.setAccessible(true);
Object o = theUnsafe.get(null);
unsafe = (Unsafe) o;
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(SpinLock.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static final Class<Unsafe> unsafeClass = Unsafe.class;
public void lock() {
while (!cas(0, 1)) {
// 自旋等待获取锁
}
owner = Thread.currentThread();
}
public void unlock() {
if (Thread.currentThread() == owner) {
cas(1, 0);
owner = null;
}
}
private boolean cas(int oldValue, int newValue) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, oldValue, newValue);
}
}测试代码:
package com.struggle.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class LockTest {
private static int count = 0;
private static SpinLock spinLock = new SpinLock();
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 自旋锁测试
Runnable spinLockTask = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
spinLock.lock();
count++;
spinLock.unlock();
}
};
Thread spinLockThread1 = new Thread(spinLockTask);
Thread spinLockThread2 = new Thread(spinLockTask);
spinLockThread1.start();
spinLockThread2.start();
spinLockThread1.join();
spinLockThread2.join();
System.out.println("自旋锁: " + count);
}
}不加锁的情况,会因为cpu的上下文切换导致结果小概率的是我得到的数字(20000),而自旋锁回应为拿不到锁,不停的循环拿锁导致进程一直运行结束不了。重入锁就可以解决这个问题
重入锁:
重入锁是一种支持线程重入的锁机制。它允许一个线程多次获取同一个锁,避免了死锁的情况。每次线程获取锁时,需要记录获取次数,并在释放锁时相应减少次数。只有当获取次数为0时,其他线程才能获取该锁。
package com.struggle.lock;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ReentrantLock {
private Thread owner;
private volatile int state;
private int count;
private Unsafe unsafe;
private long stateOffset;
private long countOffset;
public ReentrantLock() {
Field theUnsafe = null;
try {
theUnsafe = unsafeClass.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafe.setAccessible(true);
Object o = theUnsafe.get(null);
unsafe = (Unsafe) o;
stateOffset= unsafe.objectFieldOffset(MyLock.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static final Class<Unsafe> unsafeClass = Unsafe.class;
public void lock() {
if (Thread.currentThread() == owner) {
count++;
return;
}
while (!cas(0, 1)) {
// 自旋等待获取锁
}
owner = Thread.currentThread();
count = 1;
}
public void unlock() {
if (Thread.currentThread() == owner) {
count--;
if (count == 0) {
cas(1, 0);
owner = null;
}
}
}
private boolean cas(int oldValue, int newValue) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, oldValue, newValue);
}
}测试代码:
package com.struggle.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class LockTest {
private static int count = 0;
private static SpinLock spinLock = new SpinLock();
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 重入锁测试
Runnable reentrantLockTask = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
reentrantLock.lock();
count++;
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
};
Thread reentrantLockThread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTask);
Thread reentrantLockThread2 = new Thread(reentrantLockTask);
reentrantLockThread1.start();
reentrantLockThread2.start();
reentrantLockThread1.join();
reentrantLockThread2.join();
System.out.println("重入锁: " + count);
}
}结果:
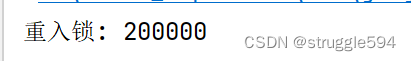
重入锁还可以解决嵌套锁的问题。
结论:
自旋锁和重入锁是Java中用于处理并发访问的两种重要机制。它们在不同的情况下具有不同的优势和适用性。自旋锁适用于锁占用时间短且竞争不激烈的情况,可以减少线程切换开销。重入锁适用于需要多次获取同一个锁的情况,避免了死锁并提供了更大的灵活性。
对于并发编程,选择适当的锁机制非常重要。根据具体的场景和需求,我们可以选择自旋锁、重入锁或其他更高级的并发工具来实现线程安全和性能优化。根据这个加入合适可运行的代码





















 741
741











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








