Stream流 collect() 方法的使用介绍
//1.
<R> R collect(Supplier<R> supplier,
BiConsumer<R, ? super T> accumulator,
BiConsumer<R, R> combiner);
//2.
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);Stream 流的注意事项:Stream不调用终止方法,中间的操作不会执行。
但是,当我们对 Stream 流中的数据操作完成之后,如果需要将流的结果进行保存,方便我们接下来对结果的继续操作,该怎么办呢?
Stream 流提供了一个 collect() 方法,可以收集流中的数据到【集合】或者【数组】中去。
1.收集 Stream 流中的数据到集合中
//1.收集数据到list集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toList())
//2.收集数据到set集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toSet())
//3.收集数据到指定的集合中
Collectors.toCollection(Supplier<C> collectionFactory)
stream.collect(Collectors.joining())示例如下:
/**
* 收集Stream流中的数据到集合中
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public class CollectDataToCollection{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Stream 流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//收集流中的数据到集合中
//1.收集流中的数据到 list
List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
//2.收集流中的数据到 set
Set<String> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collect);
//3.收集流中的数据(ArrayList)(不收集到list,set等集合中,而是)收集到指定的集合中
ArrayList<String> arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
//4.收集流中的数据到 HashSet
HashSet<String> hashSet = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
}测试结果:
[aaa, bbb, ccc, bbb]
[aaa, ccc, bbb]
[aaa, bbb, ccc, bbb]
[aaa, ccc, bbb]2.收集 Stream 流中的数据到数组中
//1.使用无参,收集到数组,返回值为 Object[](Object类型将不好操作)
Object[] toArray();
//2.使用有参,可以指定将数据收集到指定类型数组,方便后续对数组的操作
<A> A[] toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator);示例如下:
/**
* 收集Stream流中的数据到集合中
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Stream 流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//2.1 使用 toArray()无参
Object[] objects = stream.toArray();
for (Object o : objects) {//此处无法使用.length() 等方法
System.out.println("data:" + o);
}
//2.2 使用有参返回指定类型数组
//无参不好的一点就是返回的是 Object[] 类型,操作比较麻烦.想要拿到长度,Object是拿不到长度的
String[] strings = stream1.toArray(String[]::new);
for (String str : strings) {
System.out.println("data:" + str + ",length:" + str.length());
}
} 3.Stream流中数据聚合/分组/分区/拼接操作
3.Stream流中数据聚合/分组/分区/拼接操作
除了 collect() 方法将数据收集到集合/数组中。对 Stream流 的收集还有其他的方法。比如说:聚合计算,分组,多级分组,分区,拼接等。
附:Student实体类(接下来介绍,将根据Student类来进行聚合、分组、分区、拼接介绍)
/**
* get,set
* 有参构造
* toString方法
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
}1.聚合操作
当我们使用 Stream 流处理数据后,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作。比如获取最大值,获取最小值,求总和,求平均值,统计数量等操作。
//最大值
Collectors.maxBy();
//最小值
Collectors.minBy();
//总和
Collectors.summingInt();/Collectors.summingDouble();/Collectors.summingLong();
//平均值
Collectors.averagingInt();/Collectors.averagingDouble();/Collectors.averagingLong();
//总个数
Collectors.counting();示例如下:
/**
* Stream流数据--聚合操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 772)
);
//聚合操作
//获取最大值(Stream流 max()方法亦可)
//max()方法实现
//Optional<Student> max = studentStream.max((s1, s2) -> s1.getScore() - s2.getScore());
//(聚合)实现
Optional<Student> max = studentStream.collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getScore() - s2.getScore()));
System.out.println("最大值:" + max.get());
//获取最小值(Stream流 min()方法亦可)
//min()方法实现
//Optional<Student> min = studentStream.max((s1, s2) -> s2.getScore() - s1.getScore());
//(聚合)实现
Optional<Student> min = studentStream.collect(Collectors.minBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getScore() - s2.getScore()));
System.out.println("最小值:" + min.get());
//求总和(使用Stream流的map()和reduce()方法亦可求和)
//map()和reduce()方法实现
//Integer reduce = studentStream.map(s -> s.getAge()).reduce(0, Integer::sum);
//(聚合)简化前
//Integer ageSum = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s->s.getAge()));
//(聚合)使用方法引用简化
Integer ageSum = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Student::getAge));
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + ageSum);
//求平均值
//(聚合)简化前
//Double avgScore = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(s->s.getScore()));
//(聚合)使用方法引用简化
Double avgScore = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Student::getScore));
System.out.println("分数平均值:" + avgScore);
//统计数量(Stream流 count()方法亦可)
//count()方法实现
//long count = studentStream.count();
//(聚合)统计数量
Long count = studentStream.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("数量为:" + count);
}测试结果
最大值:Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=99}
最小值:Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=77}
年龄总和:222
分数平均值:89.75
数量为:42.分组操作
/**
* Stream流数据--分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 56),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 53)
);
//1.按照具体年龄分组
Map<Integer, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((s -> s.getAge())));
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
//2.按照分数>=60 分为"及格"一组 <60 分为"不及格"一组
Map<String, List<Student>> map1 = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> {
if (s.getScore() >= 60) {
return "及格";
} else {
return "不及格";
}
}));
map1.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
//3.按照年龄分组,规约求每组的最大值最小值(规约:reducing)
Map<Integer, Optional<Student>> reducingMap = studentStream.collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge,
Collectors.reducing(
BinaryOperator.maxBy(
Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getScore)
)
)
)
);
reducingMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
}测试结果:
52---->[Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=56}, Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=53}]
56---->[Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}, Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=99}]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
不及格---->[Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=56}, Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=53}]
及格---->[Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}, Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=99}]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
52---->Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=95}
56---->Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}2.1.mapping()
Collectors.mapping() 方法是 Java 8 中新增的一个收集器(Collector)。它可以用于对流中的元素进行映射后,再使用其他收集器进行处理。
mapping() 方法的定义如下:
public static <T, U, A, R> Collector<T, ?, R> mapping(
Function<? super T, ? extends U> mapper,
Collector<? super U, A, R> downstream)
// mapper 是一个函数式接口,用于将流中的每个元素进行映射;
// downstream 是另一个收集器,用于对映射后的元素进行进一步的操作。
// mapping() 方法会对流中的元素应用 mapper 函数,并将结果传递给 downstream 收集器进行进一步处理。最终将结果进行合并,形成最终的结果示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
final List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(
new Student("S1", 8),
new Student("S2", 8),
new Student("S3", 8),
new Student("S4", 8),
new Student("S5", 9),
new Student("S6", 9),
new Student("S7", 9)
);
Map<Integer, List<String>> result = studentList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge,
Collectors.mapping(Student::getName, Collectors.toList())));
System.out.println(result);
}测试结果:
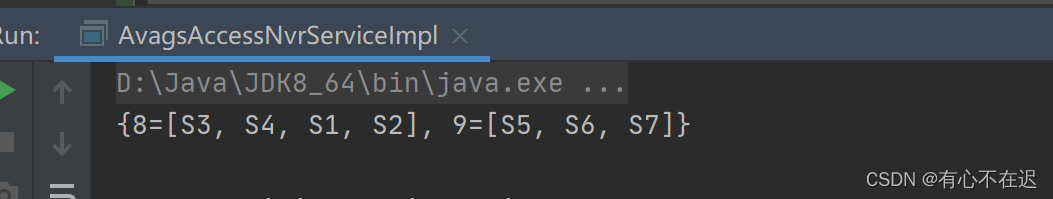
3.多级分组操作
当我们使用 Stream 流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性来将数据进行分组。
//接收两个参数: 1.Function 参数 2.Collector多级分组
groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier,Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream) 示例如下:
/**
* Stream流数据--多级分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 95),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//多级分组
//1.先根据年龄分组,然后再根据成绩分组
//分析:第一个Collectors.groupingBy() 使用的是(年龄+成绩)两个维度分组,所以使用两个参数 groupingBy()方法
// 第二个Collectors.groupingBy() 就是用成绩分组,使用一个参数 groupingBy() 方法
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Map<String, List<Student>>>> map = studentStream
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge, Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getScore, Collectors.groupingBy(a -> {
if (a.getScore() >= 60) {
return "及格";
} else {
return "不及格";
}
}))));
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("年龄:" + key);
value.forEach((k2, v2) -> {
System.out.println("\t" + v2);
});
});
}测试结果:

4.分区操作
我们在前面学习了 Stream流中数据的分组操作,我们可以根据属性完成对数据的分组。接下来我们介绍分区操作,我们通过使用 Collectors.partitioningBy() ,根据返回值是否为 true,把集合分为两个列表,一个 true 列表,一个 false 列表
分组和分区的区别就在:分组可以有多个组。分区只会有两个区( true 和 false)
//1.一个参数
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
//2.两个参数(多级分区)
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate, Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream)示例如下:
/**
* Stream流数据--多级分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//分区操作
Map<Boolean, List<Student>> partitionMap = studentStream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.getScore() > 60));
partitionMap.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
}测试结果:

5.拼接操作
Collectors.joining() 会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。
//无参数--等价于 joining("");
joining()
//一个参数
joining(CharSequence delimiter)
//三个参数(前缀+后缀)
joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix,CharSequence suffix)示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//拼接操作
//无参:join()
String joinStr1 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(joinStr1);
//一个参数:joining(CharSequence delimiter)
String joinStr2 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(joinStr2);
//三个参数:joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix,CharSequence suffix)
String joinStr3 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining("—", "^_^", ">_<"));
System.out.println(joinStr3);
}测试结果:
赵丽颖杨颖迪丽热巴柳岩
赵丽颖,杨颖,迪丽热巴,柳岩
^_^赵丽颖—杨颖—迪丽热巴—柳岩>_<6.toMap()
Collectors.toMap() 方法是把List转Map的操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> employeeList = Arrays.asList(
new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99),
new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66),
new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33),
new Employee(104, "赵六", 8, 7777.77)
);
/**
* id作为Map的key,name作为value的集合
* */
Map<Integer, String> collect1 = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getId, Employee::getName));
System.out.println(collect1);//{101=张三, 102=李四, 103=王五, 104=赵六}
/**
* id作为map的集合,Employee对象作为Map的value
*/
Map<Integer, Employee> collect2 = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getId, a->a));
System.out.println(collect2);//{101=Employee(id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99), 102=Employee(id=102, name=李四, age=59, salary=6666.66), 103=Employee(id=103, name=王五, age=28, salary=3333.33), 104=Employee(id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77)}
/**
* id作为map的集合,Employee对象作为Map的value
*/
Map<Integer, Employee> collect3 = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getId, Function.identity()));
System.out.println(collect3);//{101=Employee(id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99), 102=Employee(id=102, name=李四, age=59, salary=6666.66), 103=Employee(id=103, name=王五, age=28, salary=3333.33), 104=Employee(id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77)}
}在上面代码中,map的ID不能重复,如果重复就会报错,下面我们引入个重载方法。
/**
* id作为Map的key,name作为value的集合。 如果ID相等,则返回第一个id的name
*/
Map<Integer, String> collect1 = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getId, Employee::getName, (n1, n2) -> n1));
System.out.println(collect1);
/**
* id作为Map的key,name作为Employee的集合。 如果ID相等,则返回第一个id的Employee
*/
Map<Integer, Employee> collect2 = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getId, t -> t, (n1, n2) -> n1));
System.out.println(collect2);
/**
* id作为Map的key,name作为Employee的集合。 如果ID相等,则返回第一个id的Employee
*/
Map<Integer, Employee> collect3 = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getId, Function.identity(), (n1, n2) -> n1));
System.out.println(collect3);




















 6096
6096











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










