企业级iptalbes防火墙
CentOS7: Firewalld systemctl stop firewalld 默认开启22端口 CentOS6: IPtables service iptables stop 默认开启22端口
一、IPtables介绍
http://192.168.91.128/login 应用层(http、ssh、ftp、https) 表示层 会话层 传输层(TCP、UDP) ip+port 网络层(icmp) 数据链路层 物理层 Iptables(以下简称Iptables)是unix/linux自带的一款优秀且开源的,基于包过滤(对OSI模型的四层或者是四层以下进行过滤)的防火墙工具,它的功能十分强大,使用非常灵活,可以对流入和流出服务器的数据包进行很精细的控制。主要针对网络访问
iptables其实并不是真正的防火墙,我们可以把他理解为一个客户端的代理,用户是通过iptables这个代理,将用户的安全设定执行到对应的“安全框架”中,这个“安全框架”才是真正的防火墙。这个框架叫做“netfilter”。 netfilter:内核空间,是真正实现防火墙的功能。 iptables:用户空间,在/sbin/iptables存在的防火墙,通过iptables提供管理,修改,删除或者插入规则。 用户和内核交互的一个工具就是iptables。
实际生产环境中:
关闭Linux自身防火墙。(解决安全问题尽量不给服务器配置外网IP.需要访问的话,就使用代理转发。)因为高并发,iptables会加大延迟。除非并发小,如果服务器必须处于公网。考虑开启防火墙。
大并发的情况,不能开iptables,影响性能因为iptables是要消耗CPU的,利用硬件防火墙提升架构安全;
1.iptables工作原理分类
主机防火墙:主要是用来防范单台主机的进出报文;-----filter表 INPUT链 网络防火墙: 能够实现对进出本网络的所有主机报文加以防护----nat表 raw mangle nat filter raw表:用于对数据包进行连接跟踪前的处理。 mangle表:用于修改数据包的IP头或其他信息。 nat表:用于网络地址转换,如源地址转换和目标地址转换。 filter表:用于执行包过滤,是最常用的表,决定数据包是否被接受、丢弃或拒绝。 ======================================================================== iptables缺点: (1)防火墙虽然可以过滤互联网的数据包,但却无法过滤内部网络的数据包。因此若有人从内部网络攻击时,防火墙没有作用。 (2)电脑本身的操作系统亦可能因一些系统漏洞,使入侵者可以利用这些漏洞绕过防火墙过滤,从而入侵电脑。 (3)防火墙无法有效阻挡病毒攻击,尤其是隐藏在数据中的病毒。
没有绝对安全的操作系统,虽然防火墙有这些缺点,但还是能阻挡大多数来自于外网的攻击。
2. iptables工作流程
四表五链
-
防火墙是一层层过滤的。实际是按照配置规则的顺序从上到下,从前到后进行过滤的。此时,第一条规则匹配成功。则不会继续匹配。
-
如果匹配上了规则,即明确表明是阻止还是通过,此时数据包就不在向下匹配新规则了。匹配到即停止继续匹配。
-
如果所有规则中没有明确表明是阻止还是通过这个数据包,也就是没有匹配上规则,向下进行匹配,直到匹配默认规则得到明确的阻止还是通过。
-
防火墙的默认规则是对应链的所有的规则执行完以后才会执行的(最后执行的规则)。
例如:
-
拒绝所有IP ICPM协议
-
拒绝SSH协议
-
拒绝访问http 80端口
默认规则:运行所有ip访问443端口
二、iptables概念
一、iptables名词和术语
1. 什么是 iptables
举个例子,如果把Netfilter看成是某个小区的一栋楼。那么表(tables)就是楼里的其中的一套房子。这套房子"表(tables)"属于这栋楼“Netfilter/iptables”。
2. 什么是表(tables)
表(tables)是链的容器,即所有的链(chains)都属于其对应的表(tables).如上,如果把Netfilter看成是某个小区的一栋楼.那么表(tables)就是楼里的其中的一套房子。
3 什么是链(chains)
链(chains)是规则(Policys)的容器。如果把表(tables)当作有一套房子,那么链(chains)就可以说是房子里的家具(柜子等)。
4 什么是规则(Policy)
规则(Policy)就比较容易理解了,就是iptables系列过滤信息的规范和具体方法条款了.可以理解为柜子如何增加并摆放柜子东西等。
基本术语如下表格所示:
| Netfilter/iptables | 表(tables) | 链(chains) | 规则(Policy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 一栋楼 | 楼里的房子 | 房子里的柜子 | 柜子里衣服,摆放规则 |
三、iptables 表和链
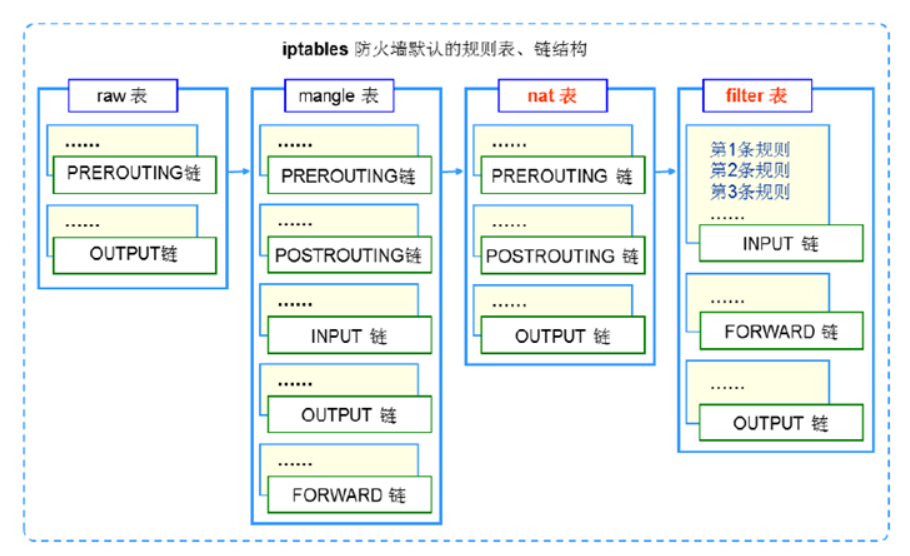
默认情况下,iptables根据功能和表的定义划分包含三个表,filter,nat,mangle,其每个表又包含不同的操作链(chains )。 实际iptables包含4张表和五个链,主要记住filter即可。
1、四张表
必须是小写 raw ------------追踪数据包, ----此表用处较少,可以忽略不计。 mangle ------------给数据包打标记,做标记。 nat ------------网络地址转换即来源与目的的IP地址和port的转换。 filter ------------做过滤的,防火墙里面用的最多的表。 #表的应用顺序:raw-》mangle-》nat-》filter
2、五条链
五链:(必须是大写)链里面写的是规则。 PREROUTING -----------------进路由之前数据包 INPUT -----------------就是过滤进来的数据包(输入) FORWARD -----------------转发 OUTPUT -----------------发出去的数据包 POSTROUTING -----------------路由之后数据包 #所有的访问都是按顺序: 入站:比如访问自身的web服务流量。先PREROUTING(是否改地址),再INPUT(是否允许)到达程序。 转发:经过linux网关的流量.先PREROUTING(是否改地址),然后路由。转发给FORWARD(转发或者丢弃),最后经过POSTROUTING(看看改不改地址。) 出站:源自linux自身的流量.先OUTPUT,再给POSTROUTING(是否改IP)。 #规则顺序:逐条匹配,匹配即停止。
3、四表五链
raw表里面: PREROUTING OUTPUT 总结:数据包跟踪 内核模块iptables_raw =============================================================================== mangel表里面有5个链: PREROUTING INPUT FORWARD OUTPUT POSTROUTING 路由标记用的表。内核模块iptables_mangle ================================================================================ nat表里面的链: PREROUTING INPUT OUTPUT POSTROUTING 转换地址的表(改IP,改端口。当网关使用的linux。保护内外网流量。内核模块叫iptable_nat) ================================================================================= filter表有三个链:重点 INPUT #负责过滤所有目标是本机地址的数据包通俗来说:就是过滤进入主机的数据包 FORWARD #负责转发经过主机的数据包。起到转发的作用 OUTPUT #处理所有源地址是本机地址的数据包通俗的讲:就是处理从主机发出的数据包 总结:根据规则来处理数据包,如转或者丢。就是实现主机型防火墙的主要表。 内核模块 iptable_filter
四 iptables操作
1、安装
centos(5/6) 启动防火墙:#/etc/init.d/iptables start centos7 启动防火墙 -----192.168.246.200服务器实验。 # yum install -y iptables iptables-services #一定要记得下载 # systemctl stop firewalld # systemctl disable firewalld # systemctl start iptables 查看版本: [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -V iptables v1.4.21 配置文件: /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config /etc/sysconfig/iptables #记录规则文件
2、参数解释
-L:列出一个链或所有链中的规则信息 -n:以数字形式显示地址、端口等信息 -v:以更详细的方式显示规则信息 --line-numbers:查看规则时,显示规则的序号(方便之处,通过需要删除规则-D INPUT 1 -F:清空所有的规则(-X是清理自定义的链,用的少;-Z清零规则序号) -D:删除链内指定序号(或内容)的一条规则 -P:为指定的链设置默认规则 -A:在链的末尾追加一条规则 -I:在链的开头(或指定序号)插入一条规则 -t: 指定表名 .... 更多参数可通过--help查看
3、参数使用
1.如果不写-t 默认使用filter表 指定表名查看规则 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -t nat -L 默认查看规则: # iptables -L 以数字的形式显示ip和端口与协议 # iptables -nL 显示规则行号 # iptables -nL --line 清空规则: #iptables -F 清空单独的某一个链里面的规则 #iptables -F 链名 清空单独的某一个表里的,某一个链里面的规则 # iptables -t nat -F INPUT 删除某条规则 # iptables -t filter -D INPUT 5 保存规则: 前提: iptables处于运行状态: # systemctl start iptables # service iptables save # iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
4、iptables语法
iptables -t 表名 动作 [链名] [-p 匹配条件] [-j 控制类型] -j:控制类型, 通过前面匹配到之后是丢弃还是保留数据包的处理方式: ACCEPT允许, REJECT拒绝, DROP丢弃。 不会给用户返回任何的拒绝消息,不推荐使用。 ====================================================== 动作:添规则还是删除规则 -p:匹配条件:数据包特征ip,端口等 如果不写-t 默认使用filter表 ======================================================= 动作 修改默认规则: -P (大p) 删除规则:-D 修改规则:-R 追加规则: -A 默认追加到链的末尾 插入规则:-I (大i),在链的开头(或指定序号)插入一条规则
5、查看添加删除规则
观察iptable规则添加的方法,删除和查询的方法。本案例并不是为了体验策略效果。
iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp -j ACCEPT #最后一行 iptables -I INPUT -p udp -j ACCEPT #第一行 iptables -I INPUT 4 -p icmp -j ACCEPT #(插入到第4行)#第4行 iptables -L #查看规则 iptables -D INPUT 3 #删除第三行 iptables -F #清空所有规则 service iptables save #保存规则 systemctl restart iptables #重启服务 注意:如果不保存重启之后规则就不在了。
2、规则匹配条件
1、通用匹配(协议),可以独立使用
协议:-p (小p) tcp ---用的最多 udp icmp ---ping的时候用的协议 #使用协议的时候可以不指定端口,使用端口的时候必须指定协议。 案例: 禁止自己被ping,在filter表的INPUT链插入一个拒绝icmp的规则。 # iptables -F # iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j REJECT ----拒绝 验证: [root@iptables-test ~]# ping 192.168.246.200 PING 192.168.246.200 (192.168.246.200) 56(84) bytes of data. From 192.168.246.200 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable # iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j DROP #丢弃所有icmp数据包
2、通过端口规则匹配:
端口: --sport ---源端口 --dport --目标端口 案例: 拒绝192.168.246.201这台机器通过ssh连接到这台服务器 # iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.246.201 -p tcp --dport 22 -j REJECT 例子:端口的范围: 拒绝192.168.246.201这台机器通过22端口到80端口的访问,包括22和80端口在内 # iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.246.201 -p tcp --dport 22:80 -j REJECT 验证: # curl -I http://192.168.246.200 curl: (7) Failed connect to 192.168.246.200:80; Connection refused # ssh root@192.168.246.200 ssh: connect to host 192.168.246.200 port 22: Connection refused =============================================================================== 拒绝所有机器通过ssh连接到这台服务器 # iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j REJECT 例子:端口的范围: 拒绝所有机器通过22端口到80端口的访问,包括22和80端口在内 # iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22:80 -j REJECT
3、通过ip地址
1.#禁止源246.201主机ping进来。(换个主机ping一下,就可以通信) [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.246.201 -p icmp -j REJECT -s: 源ip地址 在源ip机器验证: [root@iptables-test ~]# ping 192.168.246.200 PING 192.168.246.200 (192.168.246.200) 56(84) bytes of data. From 192.168.246.200 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable =========================================================================== 2.拒绝多个ip地址:后面跟ip地址可以更多个ip地址用逗号隔开 # iptables -t filter -I INPUT -s 192.168.246.201,192.168.246.133 -p icmp -j REJECT # iptables -t filter -I INPUT -s 192.168.246.201,192.168.246.133 -p tcp --dport 22:80 -j REJECT 验证:在源ip地址通过curl访问。在246.133和246.201机器分别验证 # curl -I http://192.168.246.200 curl: (7) Failed connect to 192.168.246.200:80; Connection refused # ssh root@192.168.246.200 ssh: connect to host 192.168.246.200 port 22: Connection refused ============================================================ 3.举例::#限制源10网段的数据包。 # iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.10.0/24 -j REJECT
4、修改规则
# iptables -L target prot opt source destination REJECT tcp -- 192.168.246.133 anywhere tcp dpts:ssh:http reject-wi REJECT tcp -- 192.168.246.201 anywhere tcp dpts:ssh:http reject-wi REJECT icmp -- 192.168.246.201 anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable 将修改第二条规则访问80端口: # iptables -R INPUT 2 -p tcp --dport 80 -s 192.168.246.201 -j ACCEPT # iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination REJECT tcp -- 192.168.246.133 anywhere tcp dpts:ssh:http reject-with icmp-port-unreachable ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.246.201 anywhere tcp dpt:http REJECT icmp -- 192.168.246.201 anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable 验证在修改为允许访问的源ip机器上: # curl -I http://192.168.246.200 HTTP/1.1 200 OK ======================================================================================= # iptables -R INPUT 1 -p tcp -s 192.168.62.185 --dport 22 -j ACCEPT 验证在修改为允许访问的源ip机器上: # ssh 192.168.62.135 The authenticity of host '192.168.62.135 (192.168.62.135)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:cUexa/Lv/EtkmiiTrsHUJ1zOWsjT9cihPqLxi23w5ws. ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:8c:9c:65:99:b7:6e:df:93:86:c1:7f:38:d9:73:4c:3d. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
5、icmp类型匹配
禁止ping策略原则 iptables服务器是ping命令发起者或是接受者 -i --in-interface:在INPUT链配置规则中,指定从哪一个网卡接口进入的流量(只能配置在INPUT链上) -o --out-interface:在OUTPUT链配置规则中,指定从哪一个网卡接口出去的流量(只能配置在OUTPUT链上) ==================================================== icmp的类型: 0: Echo Reply——回显应答(Ping应答)ping的结果返回。 8: Echo request——回显请求(Ping请求),发出去的请求。 ===================================================== iptables服务器-----发起者:ping 别的机器 1.自己不能ping别人,但是别人可以ping自己: [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -I OUTPUT -o ens33 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j REJECT #ping发出的请求禁止掉了 验证: [root@iptables-server ~]# ping 192.168.246.133 #将ping请求给禁止掉了。 PING 192.168.246.133 (192.168.246.133) 56(84) bytes of data. ping: sendmsg: Operation not permitted [root@jenkins-server ~]# ping 192.168.246.200 #可以ping通 PING 192.168.246.200 (192.168.246.200) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.246.200: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.280 ms ========================================================================================= iptables服务器作为接受者。也就是别人ping自己: 2.本机可以ping其他机器。其他机器不能ping通本机: 第一种方法: [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -I OUTPUT -o ens33 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT #允许自己ping别人 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -A INPUT -i ens33 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP #将进来的ping请求给丢弃了。 换一种方法: [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -I OUTPUT -o ens33 -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -j REJECT #不给回应icmp包 验证: [root@iptables-server ~]# ping 192.168.246.201 #ping其他机器通 PING 192.168.246.201 (192.168.246.201) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.246.201: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.491 ms [root@iptables-test ~]# ping 192.168.246.200 #其他机器ping不同 PING 192.168.246.200 (192.168.246.200) 56(84) bytes of data. ========================================================================================= 拒绝任何ping的协议: [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j DROP
3、扩展匹配
显示匹配:如端口匹配,IP范围,MAC地址,等特殊匹配
# iptables -m iprange --help 1.指定ip范围: 语法: -m iprange --src-range # iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m iprange --src-range 192.168.246.199-192.168.246.206 -j REJECT 2.指定多端口范围:一次拒绝多个指定端口 语法: -m multiport --sports #源端口 -m multiport --dports #目的端口 # iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80 -s 192.168.246.133 -j REJECT 验证:在246.133机器上 # ssh root@192.168.246.200 #不通 ssh: connect to host 192.168.246.200 port 22: Connection refused 3.MAC地址匹配 拒绝MAC地址的匹配:只能匹配源MAC地址 语法: -m mac --mac-source # iptables -I INPUT -p icmp -m mac --mac-source 0:0c:29:cd:26:77 -j REJECT #拒绝指定的MAC地址服务通过icmp协议请求到本地 # iptables -I INPUT -m mac --mac-source 00:0C:29:64:E3:8D -j REJECT #将指定的MAC地址服务请求全部禁止了
通过网卡接口
# iptables -I INPUT -i ens33 -j DROP #谁也连不上了.
保存和删除规则
删除: # iptables -D INPUT 3 #通过查看行号,指定行号删除; ========================================================================================= 保存: [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables #保存到文件里面,方式一 [root@iptables-server ~]# service iptables save #第二种方式,推荐 iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[ OK ] 最后写完规则后记得保存!
题库: 1. 开放本机的22端口,对所有地址开放? iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT 2. 开放本机的80端口,对所有地址开放? iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT 3.只允许192.168.91.171来访问本机的3306端口? iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3306 -j REJECT iptables -t filter -I INPUT -p tcp -s 192.168.91.171 --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT
企业案例:
工作中。Mysql,Redis等服务一般放在内网服务器上,但是为了保证其绝对的安全性,可能会把防火墙打开,打开之后,需要我们配置一些规则,来拒绝大都数的访问,只允许指定的ip地址来访问自身的服务
案例:redis服务器允许指定ip地址访问自身服务:
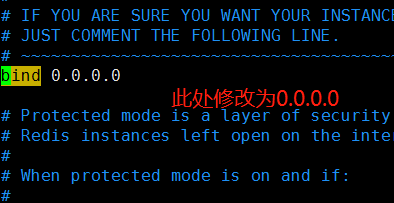
redis服务器上操作: # iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 6379 -s 192.168.62.188 -j ACCEPT # iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 6379 -s 192.168.62.185 -j ACCEPT # iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 6379 -j REJECT 注意,顺序不能乱 被允许ip服务器上验证: # telnet 192.168.62.135 6379 #测试本机是否能连同对方的6379端口号
作业:Mysql服务器允许指定ip地址访问自身服务
五、iptables NAT模式-网络地址转换(企业级应用)
网络地址转换NAT(企业应用,虚拟机做实验效果不佳)
案例图:
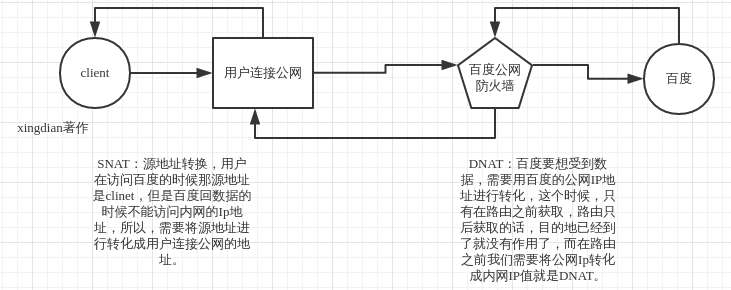
1.SNAT:把内网地址转换成公网地址(源地址转换)
一个数据包在经过路由之后(或者说在通过防火墙的过滤之后)才能知道他的源IP是谁,在路由之前只能看到目标IP,如果我看不到你的源IP,那怎么匹配想过滤的数据包并进行源地址转换?我防火墙根本就不能确定你是否是符合匹配条件的IP,所以只能使用POSTROUTING

2.DNAT:要把公网ip换到内网IP -----公网ip只有一个, 内网ip有多个。(目标地址转换)
如果不在路由之前就把目标地址转换完成,很显然当数据包到达入口IP之后,他的目的已经达到了,因为他本来的目标IP就是防火墙的对外公网IP,那么数据包还会往里面走吗?显然不可能了,所以只能使用PREROUTING

#企业常用案例功能小结: 1)linux主机防火墙,单机作为防火墙(表filter)。 2)局域网共享上网(表nat POSTROUTING)。 3)外部地址映射为内部地址和端口(表nat PREROUTING)
六、企业级Firewalld防火墙
rhel 7:firewall-cmd工具,firewalld服务
1、区域:
firewalld将网卡对应到不同的区域(zone),通过不同的zone定义了不同的安全等级
trusted :允许所有流量通过 home/internal:仅允许ssh数据通过 work:仅允许ssh,ipp-client,dhcpv6-client数据通过 public:默认区域,仅允许ssh,dhcpv6-client数据通过 external:仅允许ssh数据通过,通过该区域的数据将会伪装(SNAT/DNAT) dmz:仅允许ssh数据通过 block:任何传入的网络数据包都将被阻止。拒绝所有流量 drop:丢弃所有流量,没有返回回应消息
2、命令详解
firewall-cmd --permanent --permanent #永久生效的配置参数、资源、端口以及服务等信息 1、域zone相关的命令 --get-default-zone #查询默认的区域名称 --set-default-zone=<区域名称> #设置默认的区域 --get-active-zones #显示当前正在使用的区域与网卡名称 --get-zones #显示总共可用的区域 2、services管理的命令 --add-service=<服务名> --zone=<区域> #设置指定区域允许该服务的流量 --remove-service=<服务名> --zone=<区域> #设置指定区域不再允许该服务的流量 3、Port相关命令 --add-port=<端口号/协议> --zone=<区域> #设置指定区域允许该端口的流量 --remove-port=<端口号/协议> --zone=<区域> #设置指定区域不再允许该端口的流量 4、查看所有规则的命令 --list-all --zone=<区域> 显示指定区域的网卡配置参数、资源、端口以及服务等信息 --reload #让“永久生效”的配置规则立即生效,并覆盖当前的配置规则
3、firewalld配置使用
查看默认区域:
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone public 验证: 在192.168.246.201机器上访问192.168.246.200 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 #不通 curl: (7) Failed connect to 192.168.246.200:80; No route to host [root@iptables-test ~]# ssh root@192.168.246.200 #ssh 可以 root@192.168.246.200's password:
2、更改默认区域
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=trusted success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone trusted 验证: 在192.168.246.201机器上访问192.168.246.200 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 #访问成功 HTTP/1.1 200 OK ================================================================================== 修改回默认区域: [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success
3.向public区域添加服务
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http --zone=public success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload #重新加载配置文件 success 验证: 在192.168.246.201机器上访问192.168.246.200 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 HTTP/1.1 200 OK 移除: [root@firewalld ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-service=http success [root@firewalld ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success
4.指定IP地址为192.168.246.201/24的客户端进入drop区域
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-source=192.168.246.201/24 --zone=drop #/24代表整个网段 success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success 验证: 在192.168.246.201的机器上访问246.200 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 #访问不通
5.将192.168.246.201/24移除drop区域
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-source=192.168.246.201/24 --zone=drop success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success 验证: 在192.168.246.201的机器上面访问246.200 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 #访问成功 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
6.向pubic区域添加服务,以添加端口的方式
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp --zone=public success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success 验证: 用192.168.246.201访问192.168.246.200机器 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
7.删除服务、端口
[root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=http --zone=public success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=80/tcp --zone=public success [root@iptables-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success 验证: 在192.168.246.201访问192.168.246.200机器 [root@iptables-test ~]# curl -I http://192.168.246.200 #访问失败 curl: (7) Failed connect to 192.168.246.200:80; No route to host
8.允许指定ip访问某个端口 仍以Redis为例
Redis服务端操作: # firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.142.16" port protocol="tcp" port="6379" accept" 被允许ip地址验证: # telnet 192.168.62.135 6379
七、企业级防火墙配置
1、清除防火墙规则
# iptables -F
2、修改默认规则为拒绝(修改前先放行22端口,保证自己能够连上主机)
[root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT #放开22号端口 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -P INPUT DROP #将默认所有进来的请求设置为全部拒绝掉 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -P FORWARD DROP #将默认所有的转发的规则设置为全部拒绝掉 注意:修改默认规则: 只能使用ACCEPT和DROP # iptables -P INPUT DROP ----拒绝 # iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT ----允许
3、放行指定的端口
[root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT #允许通过lo网卡进入的请求 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dport 80,443 -j ACCEPT #允许访问80和443端口 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.246.0/24 -j ACCEPT #允许这个内网网段连接服务器
4、保存iptables配置
[root@iptables-server ~]# service iptables save iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[ OK ] 或者 [root@iptables-server ~]# iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables






















 626
626

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








