深爱学习的你,在很多场景下一定经常和字符串打交道!

字符串是以‘\0’结尾的字符合集,C语言中提供了一些库函数来处理字符串,让大家在写代码的过程中方便了许多:
字符串函数_Bug程序员小张的博客-CSDN博客字符串函数https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_59351791/article/details/126497146?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502但是,这些库函数和字符串是分离开的,不太符合C++面向对象编程的思想。所以,C++标准库中提供了string类,也就是表示字符串的字符串类!对于常规的字符串操作问题使用string类,更加的简单、方便、快捷。
目录
string类的常用接口
string类对象的常见构造
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1; //构造空string类对象
string s2("zxy hi!");//用字符串构造string类对象
string s3(s2);//拷贝构造
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
return 0;
}c_str()接口功能是返回C格式字符串,这里了解即可,后面会继续测试。

string对象的容量操作
■ size()/length():
两者的功能都是获取字符串有效长度,底层实现原理完全相同。size()是后引入的,引入同功能接口的原因是为了与其他容器接口保持一致。
int main() { string s("zhang xi yang"); cout << s.c_str()<<endl; cout <<"length():" << s.length() << endl; cout <<"size():" << s.size() << endl; return 0; }
■clear():清空有效字符,size清零。
int main() { string s("zxy"); cout << s.size() << endl; cout << s.c_str() << endl; s.clear(); cout << s.size() << endl; cout << s.c_str() << endl; return 0; }
■resize():将有效字符的个数改成n个,多出的空间用字符填充。
功能都是将字符串的有效字符个数变为n个,resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。
int main() { string s("zxy"); cout << s.size() << endl; cout << s.c_str() << endl; s.resize(20,'*'); cout << s.size() << endl; cout << s.c_str() << endl; return 0; }
■capacity(): 返回空间总大小。
int main() { string s("zxy"); cout <<"容量:" << s.capacity() << endl; cout << "字符串长度:" << s.size() << endl; cout <<"字符串:" << s.c_str() << endl; cout << "---------------------------"<<endl; s.resize(16,'x'); cout << "容量:" << s.capacity() << endl; cout << "字符串长度:" << s.size() << endl; cout << "字符串:" << s.c_str() << endl; return 0; }
■reserve():为字符串预留空间。
不会改变有效元素个数!当传入参数大于容量是会扩容,小于容量是并不会缩容,而是保持原容量不变。
int main() { string s("zxy"); cout << "容量:" << s.capacity() << endl; cout << "字符串长度:" << s.size() << endl; cout <<"字符串:" << s.c_str() << endl; cout << "-----测试参数大于string容量-----" << endl; s.reserve(100); cout << "容量:" << s.capacity() << endl; cout << "字符串长度:" << s.size() << endl; cout << "字符串:" << s.c_str() << endl; cout << "-----测试参数小于string容量-----" << endl; s.reserve(50); cout << "容量:" << s.capacity() << endl; cout << "字符串长度:" << s.size() << endl; cout << "字符串:" << s.c_str() << endl; return 0; }
■empty():判断字符串是否为空,空返回false,非空返回true!
int main() { string s("Hello world!"); cout << s.empty() << endl; s.clear(); cout << s.empty() << endl; return 0; }
string类的访问及遍历
■operator[].
int main() { string s("ZhangXiY"); for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) { cout << s[i] << " "; } cout << endl; return 0; }
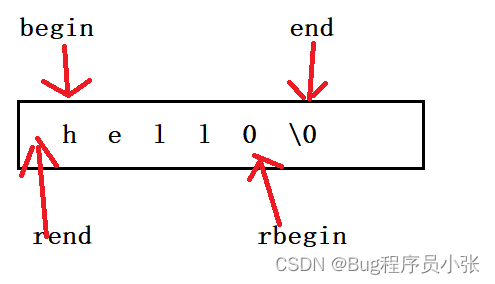
■begin()/end() 和 rbegin()/rend() 。 两组接口的区别如下:
int main() { string s("hello!"); string::iterator it1 = s.begin(); for (it1 = s.begin(); it1 != s.end(); it1++) { cout << *it1 << "-"; } cout <<endl<<"----------------" << endl; string s2("HELLO!"); string::reverse_iterator it2 = s2.rbegin(); for (it2 = s2.rbegin(); it2 != s2.rend(); it2++) { cout << *it2 << "-"; } return 0; }
■范围for
C++11中引入了基于范围的for循环。for循环后的括号由冒号“ :”分为两部分:第一部分是范 围内用于迭代的变量,第二部分则表示被迭代的范围。
//范围for int main() { int arr[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; for (auto e : arr) { cout << e << " "; } return 0; }需要注意,如果想要改变数组中元素的值,就要将auto改成auto&.
int main() { int arr[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; for (auto e : arr) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl << "-----------auto-------------" << endl; for (auto e : arr) { e++; } for (auto e : arr) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl<< "-----------auto&-------------"<<endl; for (auto& e : arr) { e++; } for (auto e : arr) { cout << e << " "; } return 0; }
注意:范围for迭代的范围必须是确定的!对于数组而言,就是数组中第一个元素和最后一个元素的范围;对于类而言,begin和end就是for循环迭代的范围。
如下代码就是有问题的:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; void Test(int Arr[]) { for (auto& e : Arr) { cout << e << endl; } } int main() { int arr[] = {2,3,2,3,4,5}; Test(arr); return 0; }
string类对象的修改操作
■ operator+=/append()/push_back().
在string尾部追加字符时,s.push_back(c) / s.append() / s += 'c'三种的实现方式差不多。+=操作用的相对多一些,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。int main() { cout << "-----push_back-----" << endl; string s1("zxy"); s1.push_back(' '); s1.push_back('b'); s1.push_back('c'); cout << s1.c_str() << endl; cout << "-------append------" << endl; string s2("Hello "); s2.append("World!"); cout << s2.c_str() << endl; cout << "-----operator+=-----" << endl; string s3("Hi "); s3 += 'z'; cout << s3.c_str() << endl; s3 += "xy"; cout << s3.c_str() << endl; return 0; }
■c_str()
返回指向string对象值的c-string表示形式的指针。
■npos()
npos是一个静态成员常量值,对于size_t类型的元素具有最大的可能值。
■find()/rfind()
正向和反向查找,从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置!
int main() { std::string str1("Looking back at all the excitement in the past years, you still won the top spot."); std::string str2("still"); size_t found1 = str1.find(str2); if (found1 != string::npos) { cout << "从前向后找,找到了 " << found1 << '\n'; } else { cout << "没找到哦!" << endl; } size_t found2 = str1.rfind(str2); if (found2 != string::npos) { cout << "从后向前找,找到了 " << found2 << '\n'; } else { cout << "没找到呀!" << endl; } return 0; }
非成员函数重载
■>>和<<重载
int main() { string str("zxy"); cout << str << endl; string str1; cin >> str1; cout << str1 << endl; return 0; }
■getline()
int main() { string name; getline(std::cin, name); cout << "I Love You:" << name <<endl; return 0; }
■relational operators()
字符串的关系运算符,在字符串对象str1和str2之间执行适当的比较操作。
int main() { string foo = "clpha"; string bar = "betasss"; if (foo == bar) cout << "foo == equal"; if (foo != bar)cout << "foo != equal\n"; if (foo < bar) cout << "foo < bar\n"; if (foo > bar) cout << "foo > bar\n"; if (foo <= bar) cout << "foo <= bar\n"; if (foo >= bar) cout << "foo >= bar\n"; return 0; }
■字符串翻转:reverse()
int main() { string s("hello world!"); cout << s << endl; reverse(s.begin(),s.end()); cout << s << endl; return 0; }

















































 714
714











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








