1. 线性表
线性表是 n 个具有相同特征的数据元素的有限序列。线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串……
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就是说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
2. 顺序表
2.1 概念及结构
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可分为:
- 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
- 动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
需要注意,顺序表的元素的连续存放的。
2.2 顺序表各接口
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致数组大小定大了,造成空间浪费。定小了空间不够用。所以在现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态分配空间大小。所以我们在实现接口的过程中,使用动态顺序表。
那么我们将要实现的接口如下:
// 基本增删查改接口 // 顺序表初始化 void SeqListInit(SeqList * psl); // 检查空间,如果满了,进行增容 void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl); // 顺序表尾插 void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x); // 顺序表尾删 void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl); // 顺序表头插 void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x); // 顺序表头删 void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl); // 顺序表查找 int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x); // 顺序表在pos位置插入x void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x); // 顺序表删除pos位置的值 void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, size_t pos); // 顺序表销毁 void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl); // 顺序表打印 void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl);
2.3 顺序表各接口实现
注意,以下所有的代码都是建立在多文件操作上,头文件的定义、声明以及源文件具体写什么,这里就不做介绍了。相信各位朋友有分辨代码写在哪个文件下的基本能力。
动态顺序表的声明:
//静态顺序表 //#define N 10 //typedef int SLDataType; //typedef struct SeqList //{ // SLDataType a[N]; // int size; //}SL; //动态顺序表 typedef int SLDataType; typedef struct SeqList { SLDataType* a; int size;//元素个数 int capacity;//容量 }SL;我们注意到一条语句,typedef int SLDataType 。这是为了通用多种类型数据而设计的,我们只需要在此语句上修改类型,那么顺序表的元素就不止局限于整形了。
顺序表初始化:
//顺序表初始化 void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl) { assert(psl); psl->a = NULL; psl->size = 0; psl->capacity = 0; }需要注意的是,在进行结构体传参时,在函数内部改变外部内容时,都使用传址调用,并断言确保程序安全性。
顺序表尾插:
//检查容量、增容 static void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl) { assert(psl); if (psl->size == psl->capacity) { int Newcapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2; SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->a, Newcapacity*sizeof(SLDataType)); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc"); exit(-1); } psl->a = tmp; psl->capacity = Newcapacity; } } //顺序表尾插 void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); CheckCapacity(psl); psl->a[psl->size] = x; psl->size++; }注意,检查容量、增容函数不需要被其他文件使用,所以用 stacit 修饰。另外,对于增容为什么要增容原来的 2 倍,这个就是效率空间利用率的问题了,大家自行脑补。
顺序表打印:
//打印 void SeqListPrint(SeqList psl) { for (int i = 0; i < psl.size; i++) { printf("%d ", psl.a[i]); } }打印是不需要改变外部内容的,所以使用传值调用即可。
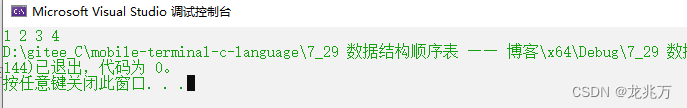
测试:顺序表尾插和打印
void Test() { SeqList s; SeqListInit(&s); SeqListPushBack(&s, 1); SeqListPushBack(&s, 2); SeqListPushBack(&s, 3); SeqListPushBack(&s, 4); SeqListPrint(s); } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
顺序表的尾插、打印功能正常。
顺序表头插:
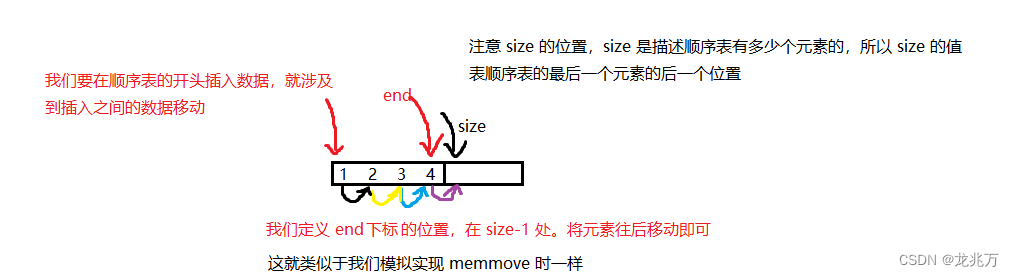
//头插 void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); CheckCapacity(psl); int end = psl->size - 1; while (end >= 0) { psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end]; end--; } psl->a[0] = x; psl->size++; }注意我们插入数据我们都需要检查容量是否合适。那么头插的原理为:
测试:顺序表头插和打印
void Test() { SeqList s; SeqListInit(&s); SeqListPushBack(&s, 1); SeqListPushBack(&s, 2); SeqListPushBack(&s, 3); SeqListPushBack(&s, 4); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPushFront(&s, 40); SeqListPushFront(&s, 30); SeqListPushFront(&s, 20); SeqListPushFront(&s, 10); SeqListPrint(s); } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
顺序表尾删:
//尾删 void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据 psl->size--; }对于尾删来说,我们只要做到访问不到最后一个元素即可。那么我们能够释放掉某些空间吗?不能,因为在动态开辟内存的章节中,我们分析过动态内存的常见错误,free 不能释放动态开辟的部分空间。但是,我们可以发现 realloc 函数的一个"bug" 。这个"bug" 就是我们追加的空间是以前的 1/2 。这个从某种角度来说,确实是节省空间了,但是我们要考虑 realloc 的特性,它在堆上开辟的空间不一定是在原空间上追加的,也有可能是重新开辟了一块空间,如果是重新开辟了一块空间的话,那么就得进行数据的拷贝的原空间的释放,那么运行的时间就会增多,导致效率下降。所以我们做的处理是:删除数据不进行空间释放和压缩,从而达到以空间换时间的目的。
测试:顺序表尾删和打印
void Test() { SeqList s; SeqListInit(&s); SeqListPushBack(&s, 1); SeqListPushBack(&s, 2); SeqListPushBack(&s, 3); SeqListPushBack(&s, 4); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPushFront(&s, 40); SeqListPushFront(&s, 30); SeqListPushFront(&s, 20); SeqListPushFront(&s, 10); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPrint(s); } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
顺序表头删:
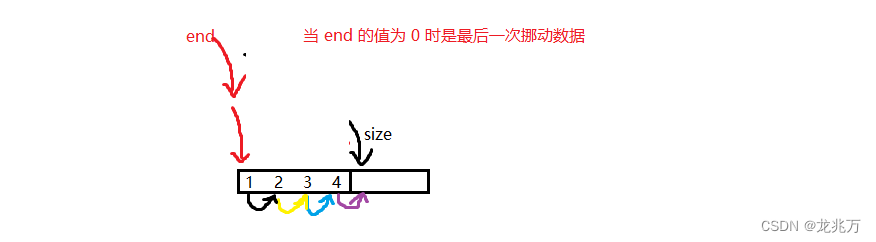
//头删 void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据 int end = 0; while (end < psl->size - 1) { psl->a[end] = psl->a[end + 1]; end++; } psl->size--; }头删的原理也很简单,只需把第一个元素覆盖掉就行了。
测试:顺序表头删和打印
void Test() { SeqList s; SeqListInit(&s); SeqListPushBack(&s, 1); SeqListPushBack(&s, 2); SeqListPushBack(&s, 3); SeqListPushBack(&s, 4); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPushFront(&s, 40); SeqListPushFront(&s, 30); SeqListPushFront(&s, 20); SeqListPushFront(&s, 10); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopFront(&s); SeqListPopFront(&s); SeqListPrint(s); } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
顺序表查找:
//查找 int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据 for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++) { if (psl->a[i] == x) return i; } return -1; }我们的返回值是返回下标,因为顺序表就是一个数组。而且返回值是下标的话可以搭配任意位置插入使用。
在 pos 位置插入:
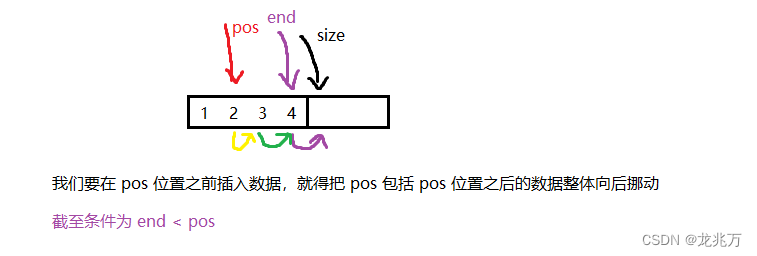
//在 pos 位置插入 void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); if (pos == 0)//当要插入的位置是 0 之前时,直接调用头插 { SeqListPushFront(psl, x); return; } size_t end = psl->size - 1; while (end >= pos) { psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end]; end--; } psl->a[pos] = x; psl->size++; }原理如下:
测试:顺序表查找以及在 pos 位置插入
void Test() { SeqList s; SeqListInit(&s); SeqListPushBack(&s, 1); SeqListPushBack(&s, 2); SeqListPushBack(&s, 3); SeqListPushBack(&s, 4); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPushFront(&s, 40); SeqListPushFront(&s, 30); SeqListPushFront(&s, 20); SeqListPushFront(&s, 10); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopFront(&s); SeqListPopFront(&s); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListInsert(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 30), 300); SeqListInsert(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 1), 100); SeqListPrint(s); } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
这个程序完成了在 30 前面插入 300,在 1 前面插入 100 的任务。
在 pos 位置删除数据:
//在 pos 位置删除数据 void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, size_t pos) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据 size_t del = pos; while (del <= psl->size-2) { psl->a[del] = psl->a[del + 1]; del++; } psl->size--; }原理如下:
测试:在 pos 位置删除数据
void Test() { SeqList s; SeqListInit(&s); SeqListPushBack(&s, 1); SeqListPushBack(&s, 2); SeqListPushBack(&s, 3); SeqListPushBack(&s, 4); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPushFront(&s, 40); SeqListPushFront(&s, 30); SeqListPushFront(&s, 20); SeqListPushFront(&s, 10); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPopBack(&s); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListPopFront(&s); SeqListPopFront(&s); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListInsert(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 30), 300); SeqListInsert(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 1), 100); SeqListPrint(s); SeqListErase(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 300)); SeqListErase(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 100)); SeqListPrint(s); } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
顺序表销毁:
//顺序表销毁 void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl) { assert(psl); free(psl->a); psl->a = NULL; psl->size = 0; psl->capacity = 0; }
3. 顺序表完整代码
3.1 SeqList.h 头文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
//静态顺序表
//#define N 10
//typedef int SLDataType;
//typedef struct SeqList
//{
// SLDataType a[N];
// int size;
//}SL;
//动态顺序表
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
int size;//元素个数
int capacity;//容量
}SeqList;
// 基本增删查改接口
// 顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList * psl);
// 检查空间,如果满了,进行增容
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, size_t pos);
// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList psl);3.2 SeqList.c 源文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
//顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl)
{
assert(psl);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}
//检查容量、增容
static void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
{
int Newcapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->a, Newcapacity*sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
exit(-1);
}
psl->a = tmp;
psl->capacity = Newcapacity;
}
}
//顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
CheckCapacity(psl);
psl->a[psl->size] = x;
psl->size++;
}
//打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList psl)
{
for (int i = 0; i < psl.size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", psl.a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
CheckCapacity(psl);
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[0] = x;
psl->size++;
}
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据
psl->size--;
}
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据
int end = 0;
while (end < psl->size - 1)
{
psl->a[end] = psl->a[end + 1];
end++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
if (psl->a[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//在 pos 位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
if (pos == 0)//当要插入的位置是 0 之前时,直接调用头插
{
SeqListPushFront(psl, x);
return;
}
size_t end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}
//在 pos 位置删除数据
void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, size_t pos)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);//保证顺序表有数据
size_t del = pos;
while (del <= psl->size-2)
{
psl->a[del] = psl->a[del + 1];
del++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl)
{
assert(psl);
free(psl->a);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}3.3 test.c 源文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
void Test()
{
SeqList s;
SeqListInit(&s);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);
SeqListPrint(s);
SeqListPushFront(&s, 40);
SeqListPushFront(&s, 30);
SeqListPushFront(&s, 20);
SeqListPushFront(&s, 10);
SeqListPrint(s);
SeqListPopBack(&s);
SeqListPopBack(&s);
SeqListPrint(s);
SeqListPopFront(&s);
SeqListPopFront(&s);
SeqListPrint(s);
SeqListInsert(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 30), 300);
SeqListInsert(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 1), 100);
SeqListPrint(s);
SeqListErase(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 300));
SeqListErase(&s, SeqListFind(&s, 100));
SeqListPrint(s);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}





























 1188
1188











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










