📟作者主页:慢热的陕西人
🌴专栏链接:力扣刷题日记
📣欢迎各位大佬👍点赞🔥关注🚓收藏,🍉留言
双指针,BFS和图论
1.日志系统
思路:我们先将所有的数据读入然后按照时间顺序进行排列存储在一个pair数组内部,然后一次去遍历时间区间
[j, i]为时间跨度,我们每次都是将一个长度为小于d的时间区间向前移动,那么我们每次只需要加上新增的日志,并且减去最左边被移除区间的日志,即可快速的计算区间内的日志的点赞数量。
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<utility>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 100010;
PII tid[N];
int cnt[N], st[N];
int n,d,k;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> d >> k;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d%d", &tid[i].x, &tid[i].y);
//对时间排序
sort(tid, tid + n);
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cnt[tid[i].y]++;
while(tid[i].x - tid[j].x >= d)
{
cnt[tid[j].y]--;
j++;
}
if(cnt[tid[i].y] >= k) st[tid[i].y] = true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; ++i)
if(st[i]) cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
2.献给阿尔吉农的花束
思路:广度优先遍历,一个二位数组用于存放当前点的最短距离。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int m, n;
const int N = 210;
char g[N][N];
int dist[N][N];
int bfs(PII start, PII end)
{
queue<PII> q;
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
dist[start.x][start.y] = 0;
q.push(start);
int dx[] = {1, 0, -1, 0}, dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
while (!q.empty())
{
PII t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
int a = t.x + dx[i], b = t.y + dy[i];
if (a >= 0 && a < m && b >= 0 && b < n && g[a][b] != '#' && dist[a][b] == -1)
{
dist[a][b] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
if (end == make_pair(a, b))
return dist[a][b];
q.push({a, b});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int t;
PII start, end;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
cin >> g[i][j];
if (g[i][j] == 'S')
start = {i, j};
else if (g[i][j] == 'E')
end = {i, j};
}
}
int ret = bfs(start, end);
if (ret == -1)
cout << "oop!" << endl;
else
cout << ret << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.交换瓶子
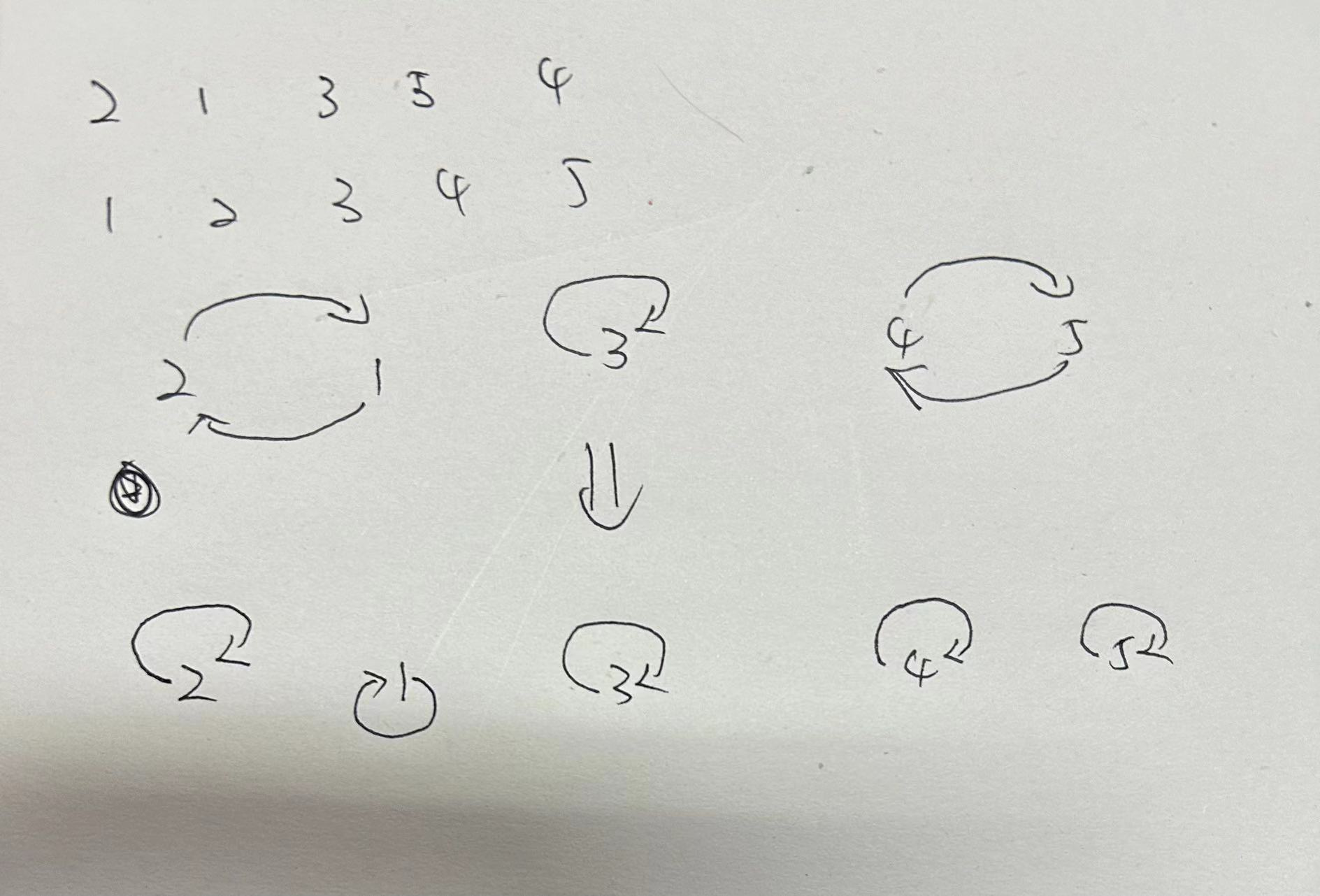
思路:图论的思想,我们将原序列从下标1开始,放入到数组中,这时候我们可以建立起一个序列中元素和数组下标的映射,那么我们会发现会产生若干个环:
并且我们发现,当我们将同一个环内的点进行交换,那么我们就可以得到两个环。
我们将不同环内的点进行交换,那么我们可以将两个环合并为一个环。
所以我们的目标就变成将原来的k个环变成n个环,那么我们需要分别n - k即可;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int g[N];
bool st[N];
int main()
{
int n, cnt = 0;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> g[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if(!st[i])
{
cnt++;
for(int j = i; !st[j]; j = g[j])
st[j] = true;
}
cout << n - cnt;
return 0;
}























 340
340











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










