前言:我们学习顺序表时会发现有点问题:
- 在顺序表中间或者头部的插入和删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
- 在增容时会浪费一定的的空间,并且增容需要申请新的空间拷贝数据,释放旧的空间,也会有不小的消耗。
为了解决这些问题,我们便来学习链表。
一、认识链表
链表是一种物理存储结构上的非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
首先介绍的是无头单向链表,其结构如下图
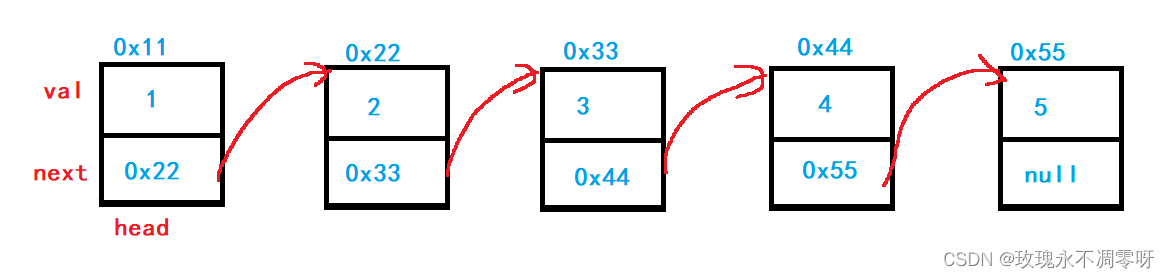
二、链表的实现(无头单向非循环链表)
- 构造静态内部类
static class Node{
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node head;- 头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}- 尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
Node node = new Node(data);
if (head == null){
head = node;
}else {
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}-
任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new IndexNotLegalException("index位置不合法");
}
}
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
checkIndex(index);
if (index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
Node cur = findIndexSubOfOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
private Node findIndexSubOfOne(int index) {
Node cur = head;
while (index-1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
-
查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}- 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if (head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能进行删除!");
return;
}
if (this.head.val == key){
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null){
if (cur.next.val == key){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}-
删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if (this.head == null){
return;
}
Node cur = this.head.next;
Node prev = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (this.head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}- 得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
Node cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}- 清空链表
public void clear(){
//this.head = null;
Node cur = head;
Node curNext = null;
while (cur != null){
curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
}
三、LinkedList的模拟实现
LinkedList底层就是一个双向链表,我们来实现一个双向链表。
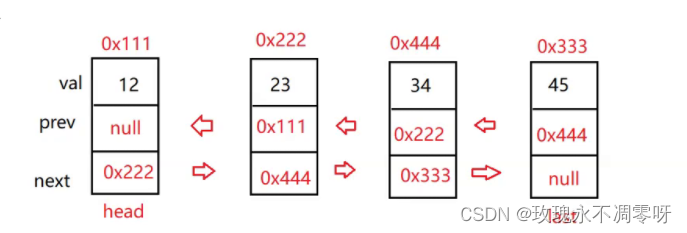
public class LinkedList {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else {
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = last.next;
}
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()){
System.out.println("index不合法!");
return;
}
if (index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
private ListNode findIndex(int index){
ListNode cur = head;
while (index != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
//处理头部问题
if (cur == head){
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
//防止只有一个节点
head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null){
//删除的不是尾巴节点
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
//删除的是尾巴节点
last = cur.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
//处理头部问题
if (cur == head){
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
//防止只有一个节点
head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null){
//删除的不是尾巴节点
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
//删除的是尾巴节点
last = cur.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur.prev = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
last = null;
}
}3.2 LinkedList的使用
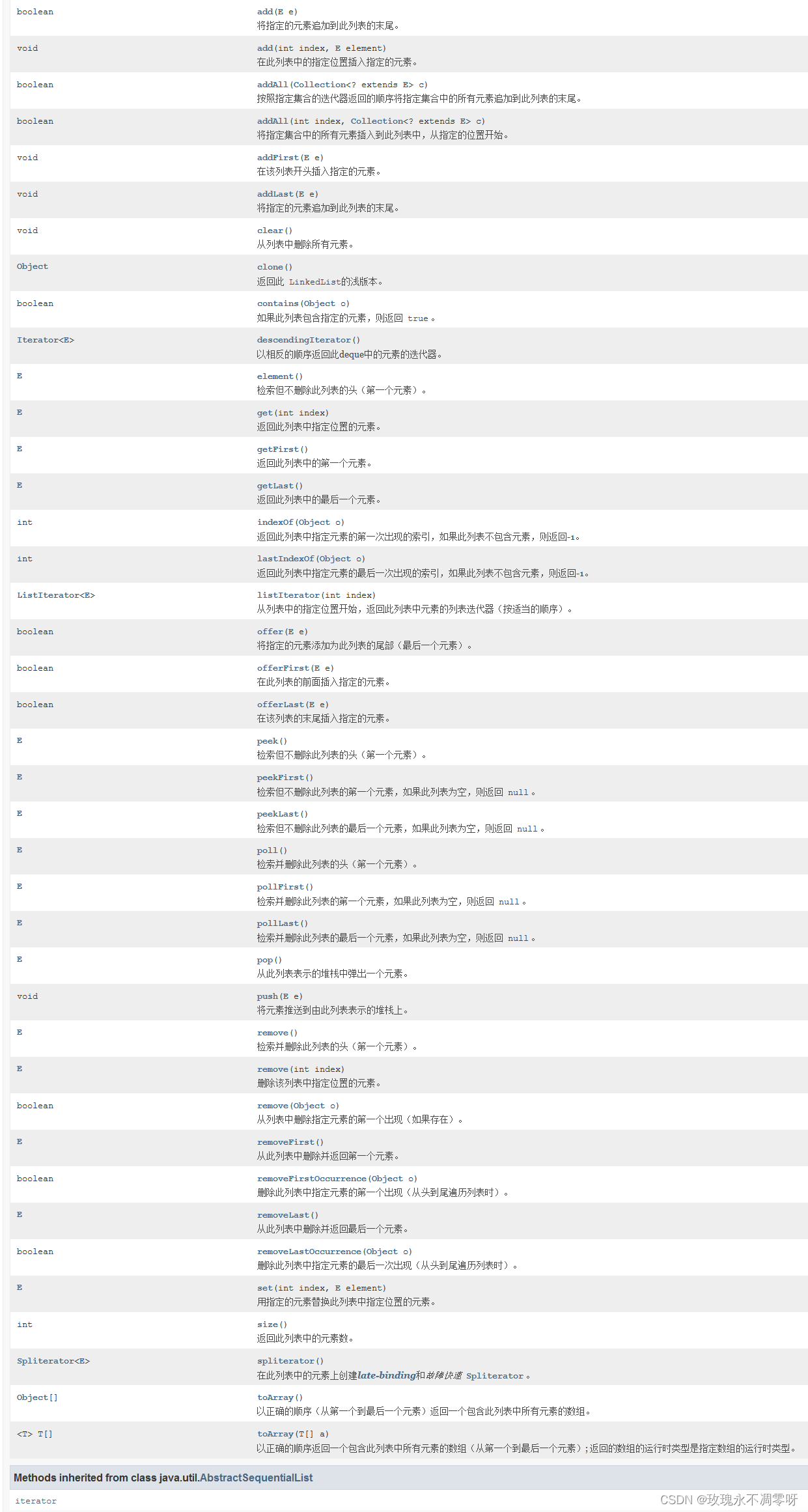
- 其常用的方法:
3.3 LinkedList的遍历
1、foreach遍历:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
// foreach遍历
for (int e:list) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
} System.out.println();
}2、使用迭代器遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
} System.out.println();
// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (rit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
} System.out.println();
}四、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
- 存储方式:顺序表使用的是一块连续的地址来存储数据,所以相邻数据的地址也是相邻的。而链表不需要使用连续的地址(这是链表的优点之一)。
- 使用场景:如果数据频繁的进行插入和删除的情况下,使用LinkedList来实现();如果数据频繁的进行查询修改和高效存储的情况下,使用ArrayList来实现。
- 空间扩容:ArrayList在空间不够得到情况下需要进行扩容处理,而LinkedList没有容量的概念。
- 在头插时:ArrayList的时间复杂度为O(N),LinkedList得到时间复杂度为O(1)。
- 随机访问:ArrayList支持,O(1),LinkedList不支持随机访问。






















 1025
1025











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








