前言
我们经常使用easypoi的@Excel注解来标注列名,但是想实现动态列该怎么办
主要是阅读以下博客的内容并实践
使用 easypoi 导出 excel 实现动态列,完美解决!-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
如有错误请指正
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-base</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-web</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-annotation</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
思路
就是自己单独拎出来一个方法,用来构建列名。然后将展示的数据转化成HashMap格式。key为构建该列时设置的key,value为你想在表格中展示的数据,接下来我用一个demo来演示下
需求
学校会定时发给学生新玩具,现在要统计学生拥有玩具的数量
代码及解析
传输类
public class ExcelDTO {
/**
* 学生姓名
*/
private String studentName;
/**
* 学生学号
*/
private Integer uid;
/**
* 学生拥有的玩具数量列表
*/
private List<ToyDTO> toyDTOList;
}
public class ToyDTO {
/**
* 玩具名
*/
private String toyName;
/**
* 玩具编码
*/
private String toyCode;
/**
* 学生拥有的玩具数量
*/
private Integer quantity;
}
以上两个类的关系很简单,就是一个学生会拥有多个玩具,也就有多个玩具拥有的数量关系
控制逻辑层(为了方便,我把业务逻辑写在controller里面)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/dynamic")
public class DynamicExcelController {
@GetMapping(value = "/excel/export")
public void exportDynamicExcel(HttpServletResponse response){
//构建数据(模拟从数据库中查询出来的数据)
//用玩具的名称当作列名,而玩具的种类是不确定的,所以只能用动态列
List<ToyDTO> toyDTOList = new ArrayList<>();
toyDTOList.add(new ToyDTO("白雪公主","SnowWhite",1));
toyDTOList.add(new ToyDTO("漫画书","Caricature",22));
toyDTOList.add(new ToyDTO("乐高","Lego",3));
toyDTOList.add(new ToyDTO("凹凸曼","Altman",0));
toyDTOList.add(new ToyDTO("高达","Gundam",0));
//构建多个学生和玩具的关系
List<ExcelDTO> excelDTOList = new ArrayList<>();
ExcelDTO excelDTO1 = new ExcelDTO("周老八",1,toyDTOList);
ExcelDTO excelDTO2 = new ExcelDTO("李老八",2,toyDTOList);
ExcelDTO excelDTO3 = new ExcelDTO("孙老八",3,toyDTOList);
ExcelDTO excelDTO4 = new ExcelDTO("田老八",4,toyDTOList);
excelDTOList.add(excelDTO1);
excelDTOList.add(excelDTO2);
excelDTOList.add(excelDTO3);
excelDTOList.add(excelDTO4);
//以上数据构建完毕,本质就是模拟从数据库中查询出来的数据。接下来是重点
//1.构建列名
//根据玩具列表动态构建列名(方法在下面)
List<ExcelExportEntity> colList = addExcelCol(toyDTOList);
//2.构建数据格式为Map
//使用stream流(也可以用循环)将List中的对象修改成Map格式
List<Map<String,Object>> ExcelDataMapList = excelDTOList.stream().map(data -> {
Map<String,Object> dataMap = new HashMap<>();
//将姓名和学号添加进去
dataMap.put("studentName",data.getStudentName());
dataMap.put("uid",data.getUid());
//循环将玩具编码和数量放入map中
data.getToyDTOList().forEach(toyDTO -> {
dataMap.put(toyDTO.getToyCode(),toyDTO.getQuantity());
});
return dataMap;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//3.构建表格
ExportParams exportParams = new ExportParams();
exportParams.setType(ExcelType.XSSF);
//构建工作薄(第二个参数是我们动态列的列表,第三个参数是Map的列表)
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(exportParams, colList, ExcelDataMapList);
String fileName = "学生拥有玩具数量.xlsx";
//4.构建返回体
try {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
response.setHeader("Content-disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
workbook.write(response.getOutputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Excel导出失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 构建列名方法
* @param toyDTOList
* @return
*/
public List<ExcelExportEntity> addExcelCol(List<ToyDTO> toyDTOList) {
//表头的集合,用于添加表头
List<ExcelExportEntity> entityList = new ArrayList<>();
//1.可以自己写死列名,如下(第一个参数是列名,第二个参数是列的key,也就是controller里我们构建成Map的key,第三个参数是列的宽度)
ExcelExportEntity channelOrgName = new ExcelExportEntity("学生名字", "studentName", 30);
entityList.add(channelOrgName);
ExcelExportEntity socialCreditCode = new ExcelExportEntity("学号", "uid", 30);
entityList.add(socialCreditCode);
//2.可以根据数据动态添加
for(ToyDTO toyDTO : toyDTOList){
ExcelExportEntity entity = new ExcelExportEntity(toyDTO.getToyName(),toyDTO.getToyCode(),30);
entityList.add(entity);
}
return entityList;
}
}
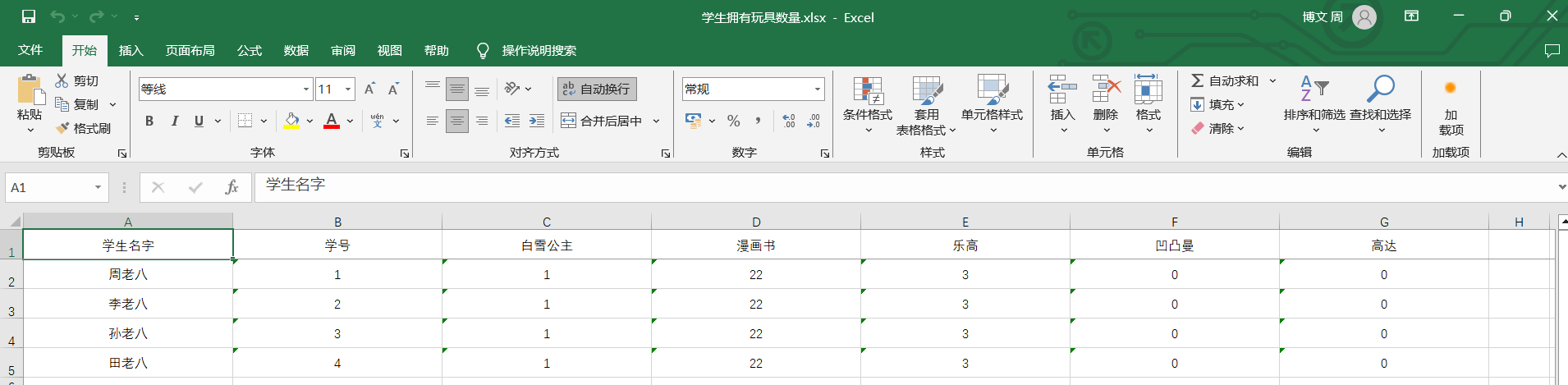
结果展示






















 2859
2859

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








