目录
1 ios::out
打开文件用于写入数据。如果文件不存在,则新建该文件;如果文件原来就存在,则打开时清除原来的内容。
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; //引入整个命名空间
int main()
{
fstream file;
file.open("test.txt",ios::out);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;
return 0;
}
return 0;
}项目文件内不存在test.txt文件,则运行后生成。


2 ios::in和is_open
ios::in:打开文件用于读取数据。如果文件不存在,则打开出错。
is_open :用于检查文件流是否成功打开并关联到文件。它返回一个布尔值,指示文件是否已打开。
如果将ios::out换成ios::in,则会提示文件打开失败。

3 put()方法
当 fstream 文件流对象调用 put () 方法时,该方法的功能就变成了向指定文件中写入单个字符。 put () 方法的语法格式如下: 其中,括号内用于指定要写入文件的字符。 该方法会返回一个调用该方法的对象的引用形式。
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
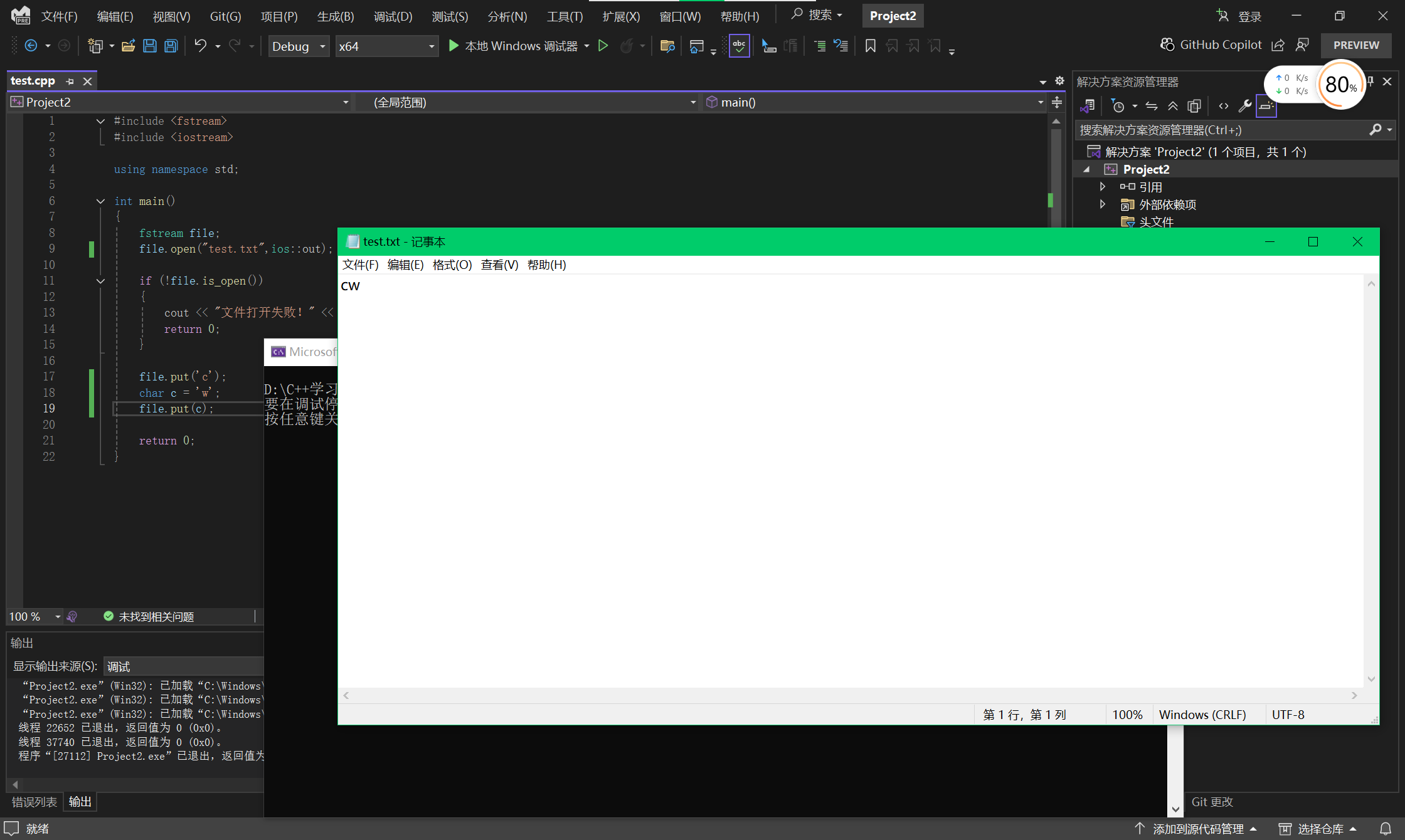
fstream file;
file.open("test.txt",ios::out);
file.put('c');
char c = 'w';
file.put(c);
file.close();
return 0;
}4 get()方法
fstream是C++标准库中用于文件输入输出的类,它继承自iostream。get()方法是fstream(以及其基类istream)提供的一个常用成员函数,主要用于从文件或输入流中读取字符。
注意:
ios:in | ios::out:打开已存在的文件,既可读取其内容,也可向其写入数据。文件刚打开时,原有内容保持不变,如果文件不存在,则打开出错。
4.1 读取单个字符
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
fstream file;
file.open("test.txt",ios::in | ios::out);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;
return 0;
}
char n;
n = file.get();
cout << n;
n = file.get();
cout << n;
n = file.get();
cout << n;
file.close();
return 0;
}
4.2 读取多个字符
首先在test.txt文件存入多行字符。
遇到分隔符时停止读取,但分隔符不会被提取。

#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
fstream file;
file.open("test.txt",ios::in || ios::out);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;
return 0;
}
char str[4][1024] = { 0 };
//get方法读到换行符就停止了,所以每读完一行需要把该行的换行符读掉
file.get(str[0],1024);//读取第1行
file.get();
file.get(str[1], 1024);//读取第2行
file.get();
file.get(str[2], 1024);//读取第3行
file.get();
file.get(str[3], 1024);//读取第4行
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cout << str[i] << endl;
}
file.close();
return 0;
}
4.3 设置终结符
get()支持人为设置终结符。
file.get(str[0], 1024, 't');//设置终结符为‘t’,读到t停止
cout << str[0];
5 getline()
类似get(),但会提取并丢弃分隔符。
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
fstream file;
file.open("test.txt",ios::in || ios::out);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;
return 0;
}
char str[4][1024] = { 0 };
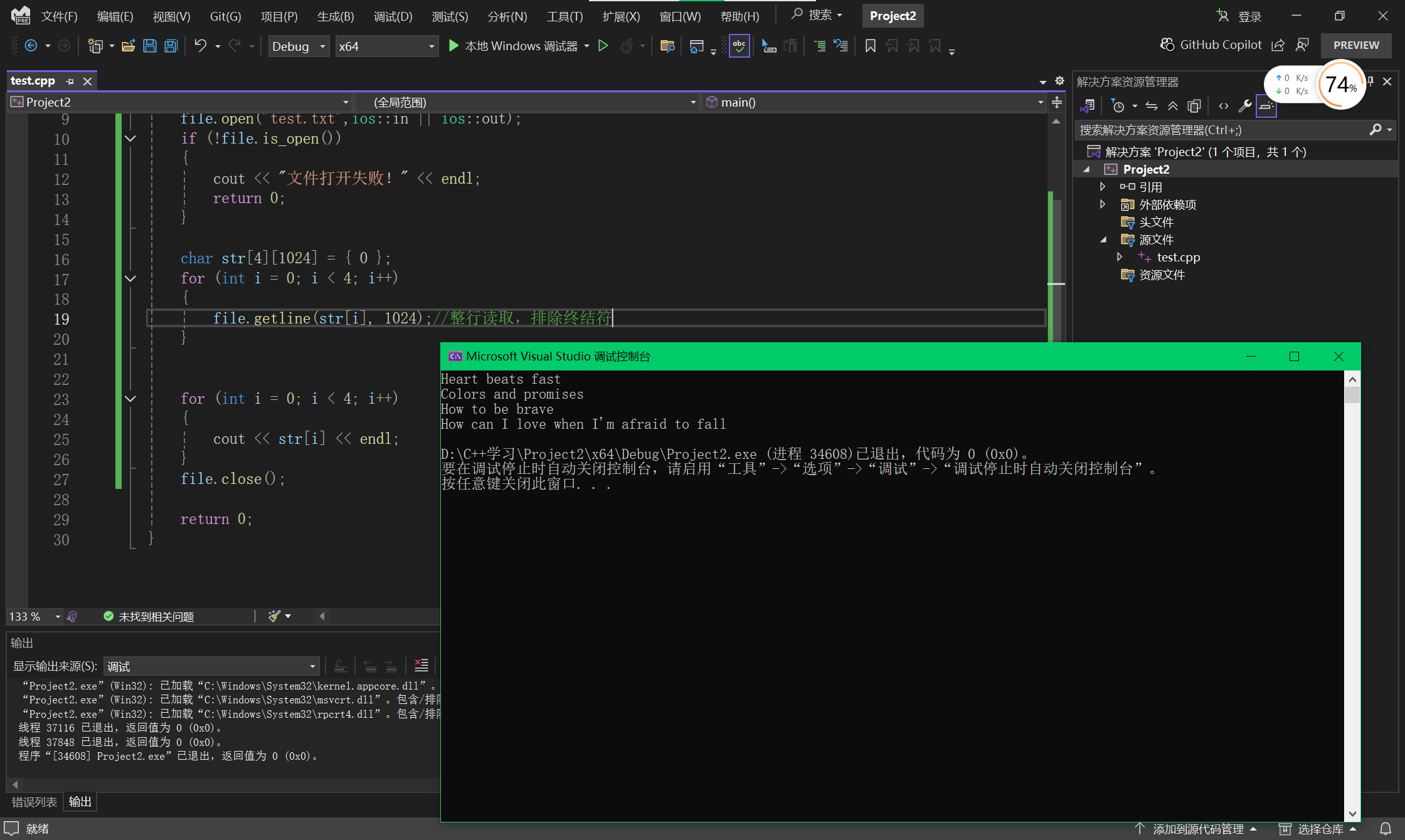
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
file.getline(str[i], 1024);//整行读取,排除终结符
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cout << str[i] << endl;
}
file.close();
return 0;
}

























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










