1,JDBC概述
1.1 JDBC概念
JDBC 就是使用Java语言操作关系型数据库的一套API
全称:( Java DataBase Connectivity ) Java 数据库连接
2,JDBC快速入门
先来看看通过Java操作数据库的流程
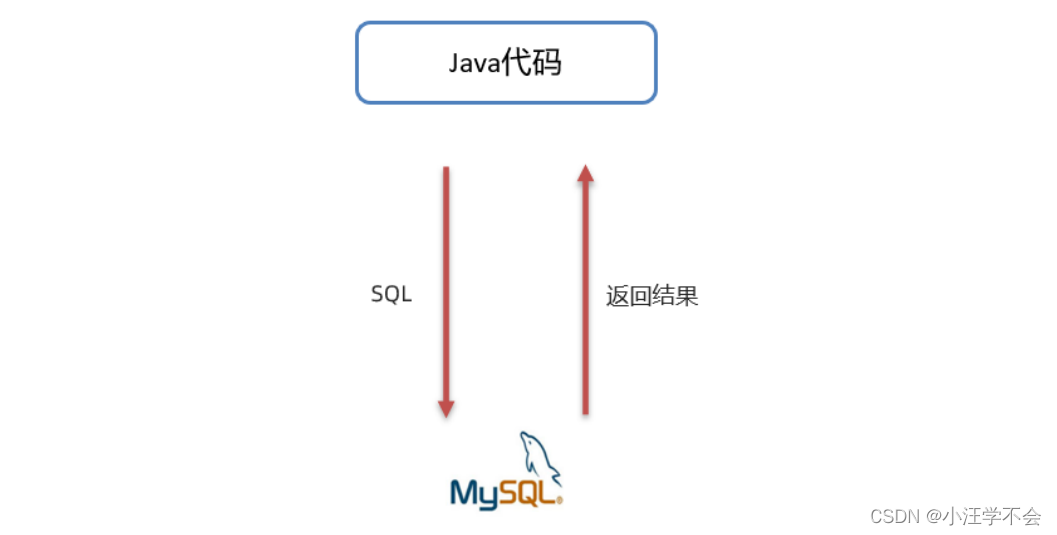
第一步:编写Java代码
第二步:Java代码将SQL发送到MySQL服务端
第三步:MySQL服务端接收到SQL语句并执行该SQL语句
第四步:将SQL语句执行的结果返回给Java代码
2.1 编写代码步骤
0.创建工程,导入驱动jar包
新建一个Project
添加驱动
1. 注册驱动 (可省略)
MySQL 5之后的驱动包,可以省略注册驱动的步骤
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");2.获取连接
Java代码需要发送SQL给MySQL服务端,就需要先建立连接
Connection conn =DriverManager.getConnection(url, username,password);3.定义SQL语句
String sql = “update…” ;4.获取执行SQL对象
执行SQL语句需要SQL执行对象,而这个执行对象就是Statement对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();5.执行SQL
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);6.处理返回结果
7.释放资源
程序设计
package MYSQL;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Connection;
public class TestConnect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dept";
String username = "root";
String password = "20021221wyt";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql = "UPDATE account set money = 2000 where account.id = 1";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(count);
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}3,JDBC API详解
3.1 DriverManager
1.注册驱动

2.获取数据库连接

参数说明:
1)url : 连接路径
语法:jdbc:mysql://ip地址(域名):端口号/数据库名称?参数键值对1&参数键值对2…
示例:jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db1
细节:如果连接的是本机mysql服务器,并且mysql服务默认端口是3306,则url可以简写为:jdbc:mysql:///数据库名称?参数键值对配置 useSSL=false 参数,禁用安全连接方式,解决警告提示
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///dept?useSSL=false";
2) user :用户名
3) poassword :密码
3.2 Connection
Connection(数据库连接对象)作用:
1.获取执行 SQL 的对象
1)普通执行SQL对象
Statement createStatement()2)预编译SQL的执行SQL对象:防止SQL注入
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(sql)3)执行存储过程的对象
CallableStatement prepareCall(sql)
2.管理事务
MySQL事务管理的操作:
开启事务 : BEGIN; 或者 START TRANSACTION;
提交事务 : COMMIT;
回滚事务 : ROLLBACK;
MySQL默认是自动提交事务
JDBC事务管理的方法
Connection几口中定义了3个对应的方法:
开启事务 setAutoCommit(false)

参与autoCommit 表示是否自动提交事务,true表示自动提交事务,false表示手动提交事务。而开启事务需要将该参数设为false。
提交事务 commit()

回滚事务 rollback()

事务实现的代码:try catch
具体代码实现如下:
/**
* JDBC API 详解:Connection
*/
//1.注册驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接 如果连接的是本机mysql服务器,并且mysql服务默认端口是3306,则url可以简写为jdbc:mysql:///dept
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///dept?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "20021221wyt";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql1 = "UPDATE account set money = 3000 where account.id = 1";
String sql2 = "UPDATE account set money = 3000 where account.id = 2";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
try {
//开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//5.执行sql1
int count1 = stmt.executeUpdate(sql1);
//6.处理结果1
System.out.println(count1);
//事故
//5.执行sql2
int count2 = stmt.executeUpdate(sql2);
//6.处理结果2
System.out.println(count2);
//提交事务
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚事务
conn.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();3.3 Statement
3.3.1 概述
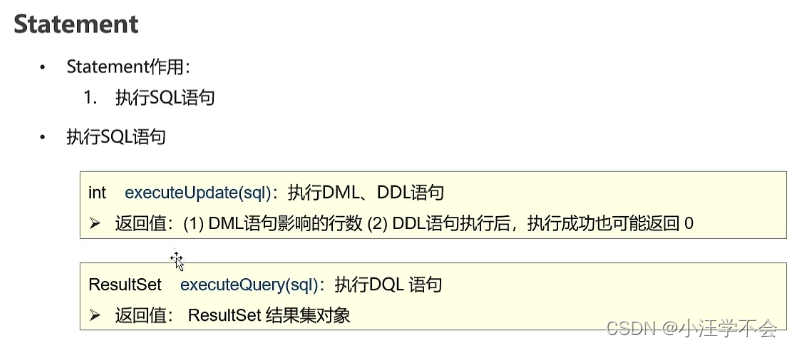
executeUpdate
//5.执行sql
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); //执行完DDL语句后,受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
//System.out.println(count);
if(count>0) {
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else {
System.out.println("修改失败");
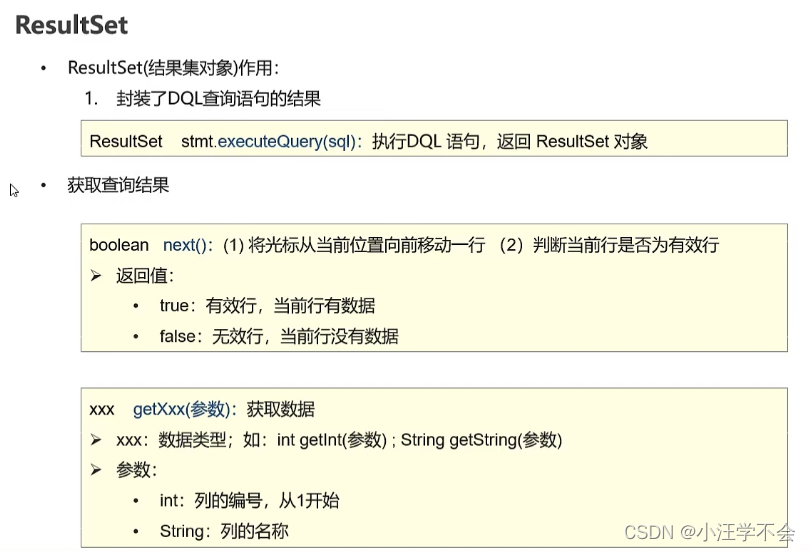
}3.4 ResultSet
3.4.1 概述

/**
* 执行DQL语句
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testResultSet() throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///dept?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "20021221wyt";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); //返回光标位置
//6.处理结果 显示所有数据
while(rs.next()) //光标向下移动一行,并且判断当前行是否有数据
{
//获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
double money = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(money);
System.out.println("----------");
}
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
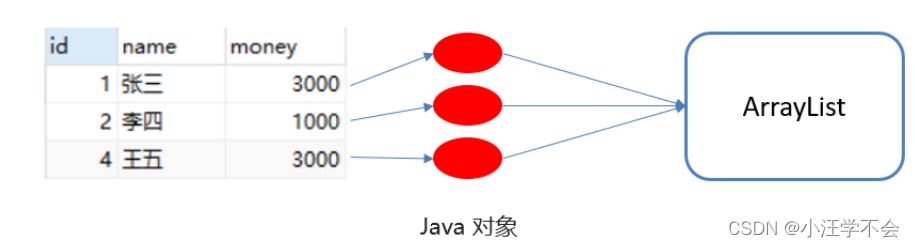
rs.close();案例:查询account账户表数据,封装为Account对象中,并且存储到ArrayList集合中
创建Account类
package pojo;
public class Account {
private int id ;
private String name ;
private double money;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}DQL查询语句
/**
* 查询account账户表数据,封装为Account对象中,并且存储到ArrayList集合中
* 1.定义实体类Account
* 2.查询数据,封装到Account对象中
* 3.将Accout对象存入ArrayList集合中
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testResultSet2() throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///dept?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "20021221wyt";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); //执行完DML语句后,受影响的行数
//创建集合
List<Account> list = new ArrayList<>();
//6.处理结果,变量数据
while(rs.next()) //光标向下移动一行,并且判断当前行是否有数据
{
Account account = new Account();
//获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
double money = rs.getDouble(3);
//赋值
account.setId(id);
account.setName(name);
account.setMoney(money);
//存入集合
list.add(account);
}
//打印list集合
System.out.println(list);
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
rs.close();
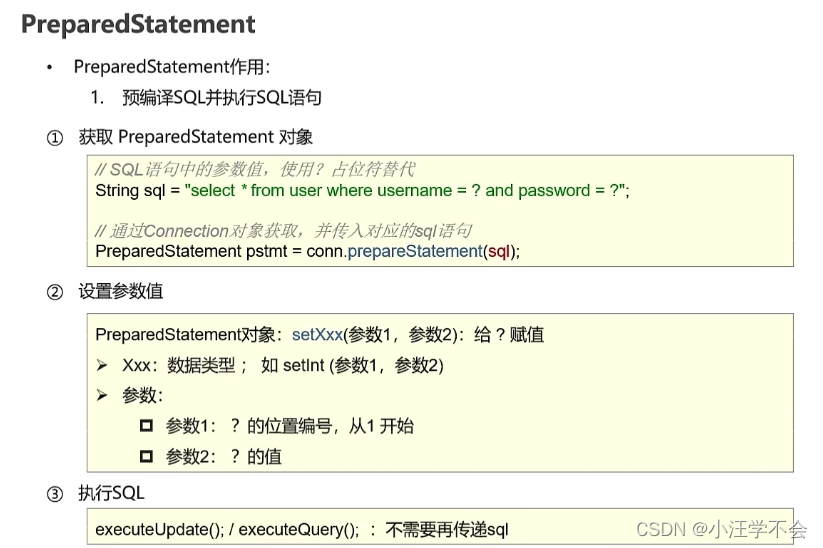
}3.6 PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement作用
1.预编译SQL语句并执行:预防SQL注入问题
SQL注入:
SQL注入是通过操作输入来修改事先定好的SQL语句,用以达到执行代码对服务器进行攻击的方法
实例:
/**
* 演示SQL注入
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testPreparedStatement() throws Exception {
//获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "20021221wyt";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//接收用户输入 用户名和密码
String name = "hhhhhh";
String pwd = "' or '1' = '1";
//定义sql语句
String sql = "select * from tb_user where username = ? and password = ?";
//获取pstmt对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置?的值
pstmt.setString(1, name);
pstmt.setString(2, pwd);
//执行sql
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); //不需要再传递sql
//判断登录是否成功
if(rs.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
rs.close();
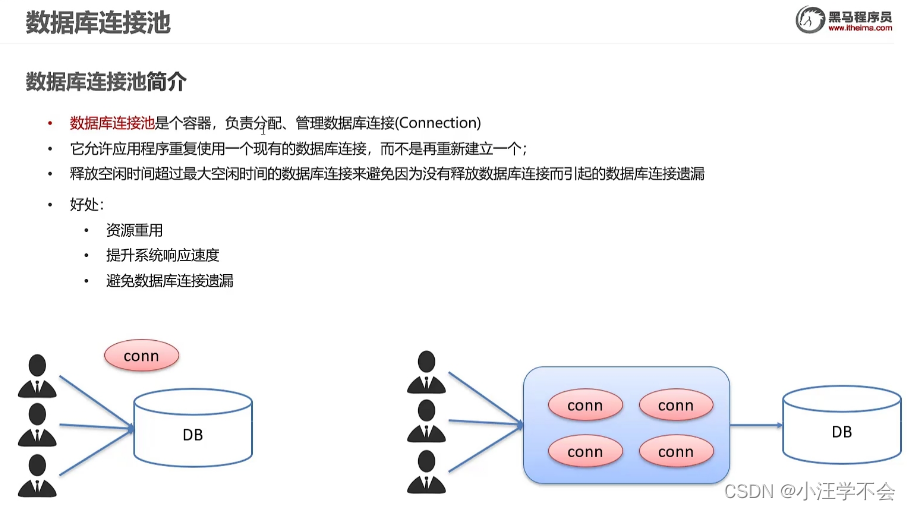
}4,数据库连接池
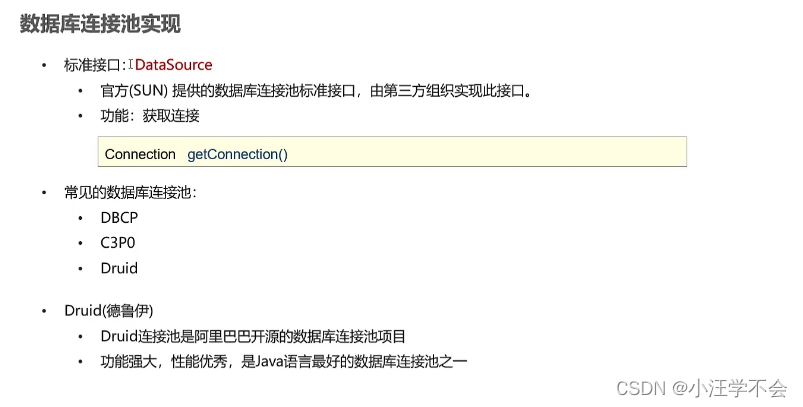

示例:
1.导入jar包
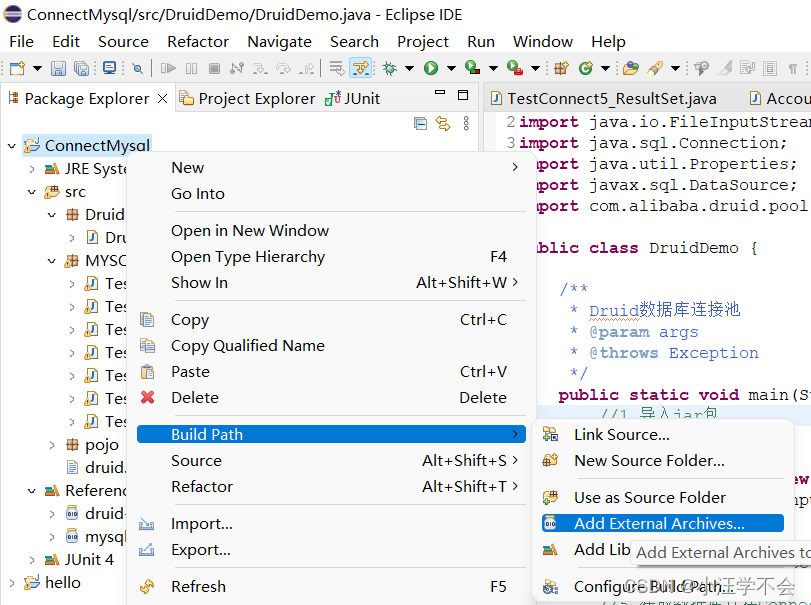
2.定义配置文件
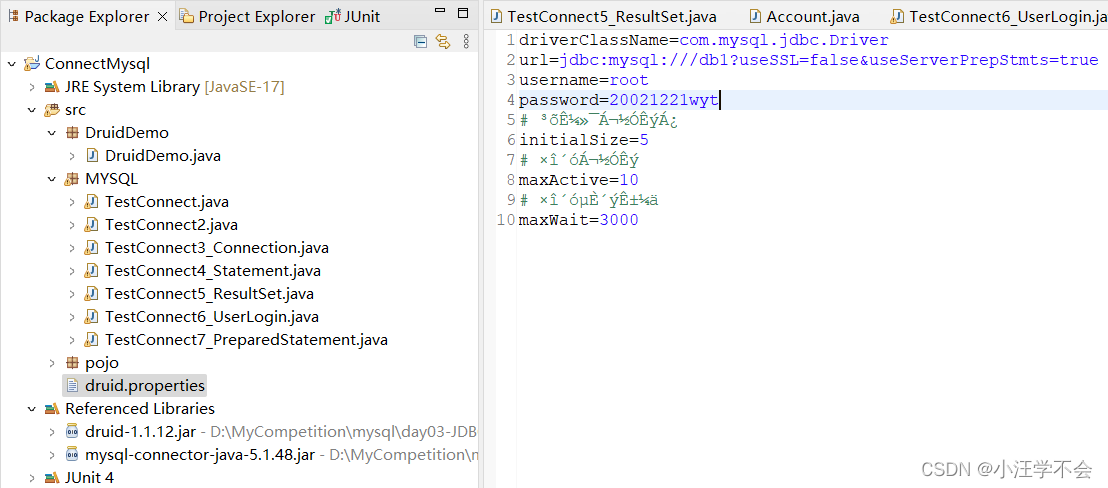
代码如下
package DruidDemo;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
public class DruidDemo {
/**
* Druid数据库连接池
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.导入jar包
//2.定义配置文件
//3.加载配置文件
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//4.获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//5.获取数据库连接Connection
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
}练习
完成商品品牌数据的增删改查操作
1.准备环境:
-数据库表 tb_brand
-- 删除tb_brand表
drop table if exists tb_brand;
-- 创建tb_brand表
create table tb_brand
(
-- id 主键
id int primary key auto_increment,
-- 品牌名称
brand_name varchar(20),
-- 企业名称
company_name varchar(20),
-- 排序字段
ordered int,
-- 描述信息
description varchar(100),
-- 状态:0:禁用 1:启用
status int
);
-- 添加数据
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values ('三只松鼠', '三只松鼠股份有限公司', 5, '好吃不上火', 0),
('华为', '华为技术有限公司', 100, '华为致力于把数字世界带入每个人、每个家庭、每个组织,构建万物互联的智能世界', 1),
('小米', '小米科技有限公司', 50, 'are you ok', 1);
-实体类Brand
package pojo;
/**
* 品牌
* @author 锡盟彭于晏
* 在实体类中,基本数据类型建议使用对应的包装类型
*/
public class Brand {
// id 主键
private Integer id ;
// 品牌名称
private String brandName ;
// 企业名称
private String companyName ;
// 排序字段
private int ordered ;
// 描述信息
private String description ;
// 状态:0:禁用 1:启用
private Integer status ;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBrandName() {
return brandName;
}
public void setBrandName(String brandName) {
this.brandName = brandName;
}
public String getCompanyName() {
return companyName;
}
public void setCompanyName(String companyName) {
this.companyName = companyName;
}
public int getOrdered() {
return ordered;
}
public void setOrdered(int ordered) {
this.ordered = ordered;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public Integer getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Integer status) {
this.status = status;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Brand [id=" + id + ", brandName=" + brandName + ", companyName=" + companyName + ", ordered=" + ordered
+ ", description=" + description + ", status=" + status + "]";
}
}2.查询功能
/*
* 查询所有
* 1.SQL:Select * from tb_brand
* 2.参数:不需要
* 3.结果:List<Brand>
*
*/
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws Exception {
//1.获取Connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接Connection
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义SQL
String sql = "select * from tb_brand";
//3.获取pstm对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数
//5.执行sql
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//6.处理结果 List<Brand>
Brand brand = null;
List<Brand> brands = new ArrayList<>();
while(rs.next()) {
//获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String brandName = rs.getString(2);
String companyName = rs.getString("company_name");
int ordered = rs.getInt(4);
String description = rs.getString(5);
int status = rs.getInt(6);
//封装Brand对象
brand = new Brand();
brand.setId(id);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setOrdered(ordered);
brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setStatus(status);
//装载集合
brands.add(brand);
}
System.out.println(brands);
//7.释放资源
rs.close();
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}3.添加
/*
* 添加
* 1.SQL:insert into tb_brand(brand_name,company_name, ordered, description, status)values(?,?,?,?,?);
* 2.参数:除了id之外的所有参数信息
* 3.结果:boolean
*/
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception {
//接收页面提交的参数
String brandName = "香飘飘";
String companyName = "香飘飘";
int ordered = 1 ;
String description = "绕地球一圈";
int status = 1 ;
//1.获取Connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接Connection
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义SQL
String sql = "insert into tb_brand(brand_name,company_name, ordered, description, status)values(?,?,?,?,?)";
//3.获取pstm对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数
pstmt.setString(1, brandName);
pstmt.setString(2, companyName);
pstmt.setInt(3, ordered);
pstmt.setString(4, description);
pstmt.setInt(5, status);
//5.执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); //影响的函数
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(count>0);
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}4.修改
/*
* 修改
* 1.SQL:
update tb_brand
set brand_name = ?,
company_name= ?,
ordered = ?,
description = ?,
status = ?
where id = ?
* 2.参数:所有的数据
* 3.结果:boolean
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
//接收页面提交的参数
String brandName = "香飘飘";
String companyName = "香飘飘";
int ordered = 1 ;
String description = "绕地球一圈";
int status = 1 ;
int id = 4 ;
//1.获取Connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接Connection
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义SQL
String sql = "update tb_brand\r\n"
+ " set brand_name = ?,\r\n"
+ " company_name= ?,\r\n"
+ " ordered = ?,\r\n"
+ " description = ?,\r\n"
+ " status = ?\r\n"
+ " where id = ?";
//3.获取pstm对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数
pstmt.setString(1, brandName);
pstmt.setString(2, companyName);
pstmt.setInt(3, ordered);
pstmt.setString(4, description);
pstmt.setInt(5, status);
pstmt.setInt(6, id);
//5.执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); //影响的函数
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(count>0);
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}5.删除
/*
* 添加
* 1.SQL:delete from tb_brand where id = ?;
* 2.参数:id
* 3.结果:boolean
*/
@Test
public void testDelectById() throws Exception {
//接收页面提交的参数
int id = 3 ;
//1.获取Connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接Connection
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义SQL
String sql = "delete from tb_brand where id = ?";
//3.获取pstm对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数
pstmt.setInt(1, id);
//5.执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); //影响的函数
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(count>0);
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}




















 280
280











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








