Vue开发前的准备
安装Vue工具 Vue CLI
Vue CLI Vue.js 开发的标准工具, Vue CLI 是一个基于 Vue.js 进行快速开发的完整系统
npm install -g @vue/cli
安装之后,你就可以在命令行中访问 vue 命令。你可以通过简单运行 vue ,看看是否展示出了一份所有可用命令的帮助信息,来验证它是否安装成功。
npm install -g @vue/cli
创建一个项目
运行以下命令来创建一个新项目
vue create vue-demo
注意:
在控制台中,可以用上下按键调整选择项
在控制台中,可以用空格(spacebar)选择是否选中和取消选中
可以选择默认项目模板,或者选“手动选择特性”来选取需要的特性。

我们选择 Babel 和 Progressive Web App (PWA) Support 两个选项即可
注意:
在学习期间,不要选中 Linter / Formatter 以避免不必要的错误提示

配置放在哪里? In dedicated config files 专用配置文件或者 In package.json 在package.json文件
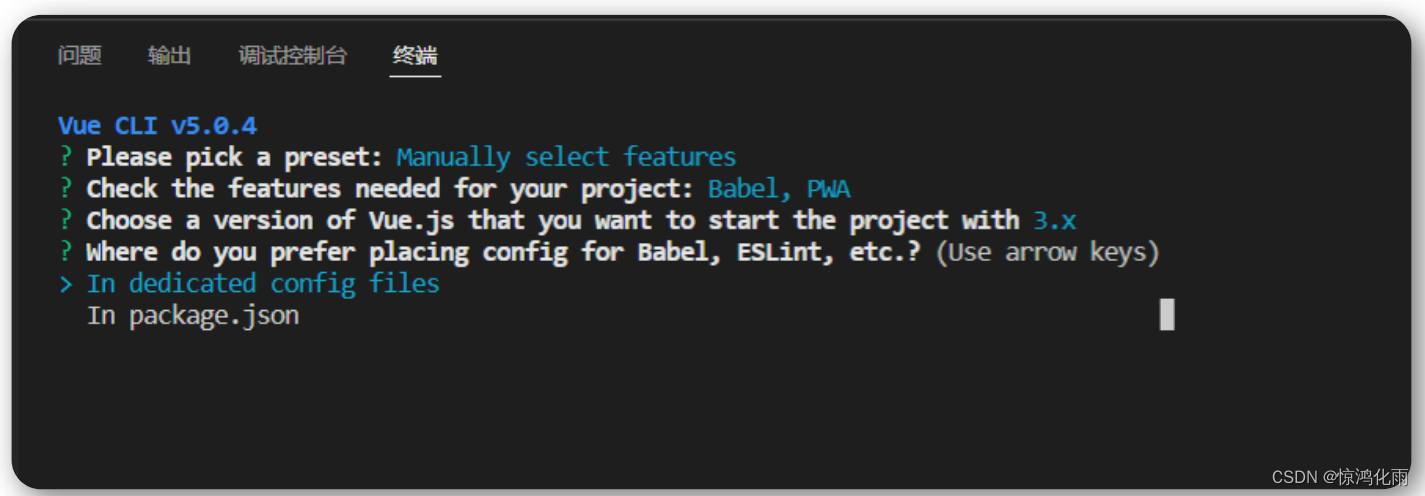
将其保存为未来项目的预置? y 代表保存,并添加名字, n 不保存
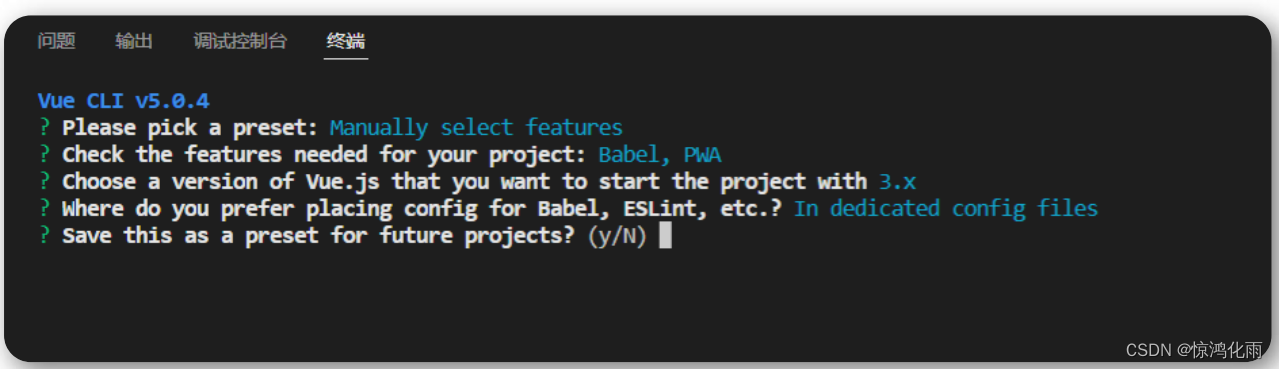
项目创建成功如下提示信息
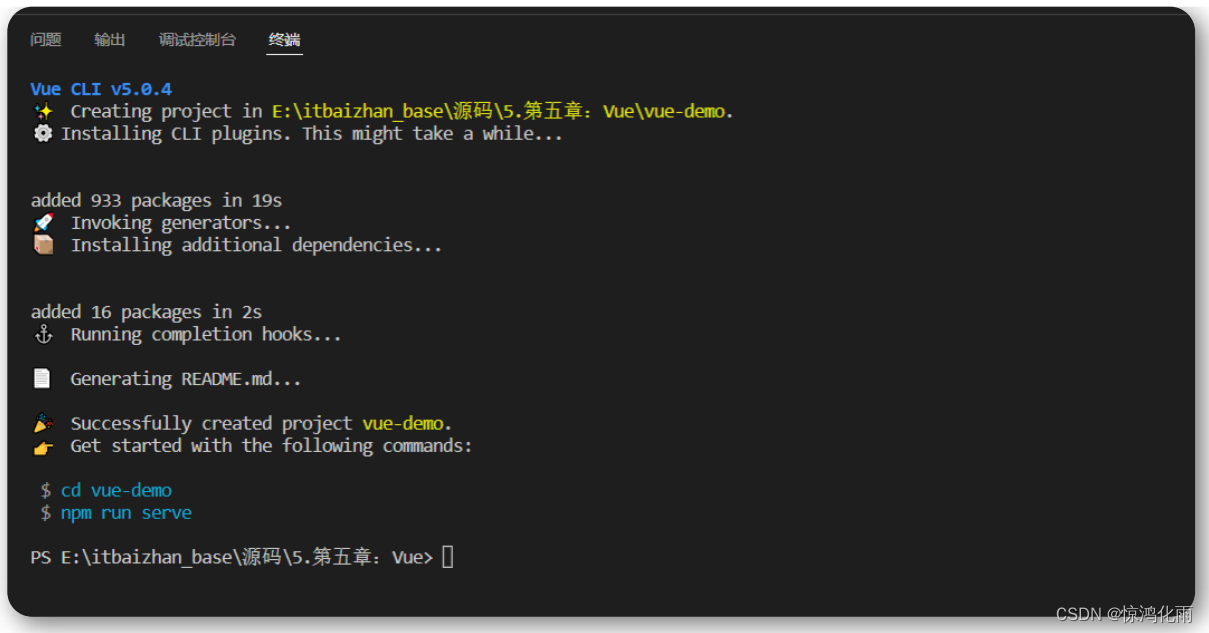
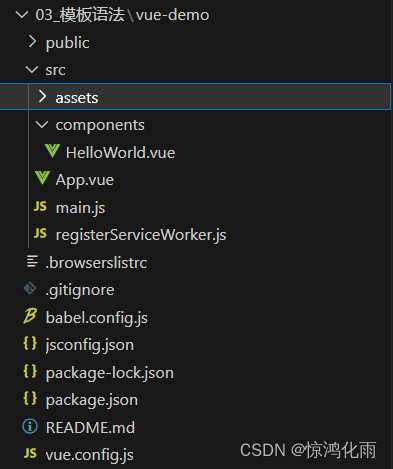
创建完项目的目录我们主要关注src内部的目录
assets 这个文件主要是用来存放静态资源的 (公共的css文件,图片等一些资源文件)
components 代表的公共组件
App.vue是主入口的组件(根组件,所有的组件都是从这里开始的,通过他来进行引入并显示的)
main.js 是主入口文件(所有程序的入口)
运行项目
第一步:进入项目根目录 cd vue-demo
第二步:运行 npm run serve 启动项目
安装Vue高亮插件
VSCode中安装 vetur 或者 volar 都可,前者针对Vue2版本,后者针对Vue3版本
模板语法
文本
数据绑定最常见的形式就是使用“Mustache” (双大括号) 语法的文本插值
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>
一般配合 js 中的 data() 设置数据
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data(){
return{
msg:"消息提示"
}
}
}
属性 Attribute
Mustache 语法不能在 HTML 属性中使用,然而,可以使用 v-bind指令
<div v-bind:id="dynamicId"></div>
data(){
return{
dynamicId:1001
}
}
注意:
v-bind:可以简写成:
使用 JavaScript 表达式
在我们的模板中,我们一直都只绑定简单的 property 键值,Vue.js都提供了完全的 JavaScript 表达式支持
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
这些表达式会在当前活动实例的数据作用域下作为 JavaScript 被解析。有个限制就是,每个绑定都只能包含单个表达式,所以下面的例子都不会生效。
条件渲染
v-if
v-if 指令用于条件性地渲染一块内容。这块内容只会在指令的表达式返回 true 值的时候被渲染。
<p v-if="flag">我是孙猴子</p>
data() {
return {
flag: true
}
}
v-else
你可以使用 v-else 指令来表示 v-if 的“else 块”
<p v-if="flag">我是孙猴子</p>
<p v-else>你是傻猴子</p>
data() {
return {
flag: false
}
}
v-show
另一个用于条件性展示元素的选项是 v-show 指令
<h1 v-show="ok">Hello!</h1>
v-if vs v-show 的区别
v-if 是“真正”的条件渲染,因为它会确保在切换过程中,条件块内的事件监听器和子组件适当地被销毁和重建。(在网页上不会渲染出来不满足的元素)
v-if 也是惰性的:如果在初始渲染时条件为假,则什么也不做——直到条件第一次变为真时,才会开始渲染条件块。
相比之下, v-show 就简单得多——不管初始条件是什么,元素总是会被渲染,并且只是简单地基于 CSS 进行切换。(也就是display:none和display:block 之间切换)
一般来说, v-if 有更高的切换开销,而 v-show 有更高的初始渲染开销。因此,如果需要非常频繁地切换,则使用 v-show 较好;如果在运行时条件很少改变,则使用 v-if 较好
列表渲染
用 v-for 把一个数组映射为一组元素
我们可以用 v-for 指令基于一个数组来渲染一个列表。 v-for 指令需要使用 item in items 形式的特殊语法,其中 items 是源数据数组,而item 则是被迭代的数组元素的别名。
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items">{{ item.message}}</li>
</ul>
data() {
return {
items: [{ message: 'Foo' }, {message: 'Bar' }]
}
}
维护状态
当 Vue 正在更新使用 v-for 渲染的元素列表时,它默认使用“就地更新”的策略。如果数据项的顺序被改变,Vue 将不会移动 DOM 元素来匹配数据项的顺序,而是就地更新每个元素,并且确保它们在每个索引位置正确渲染。
为了给 Vue 一个提示,以便它能跟踪每个节点的身份,从而重用和重新排序现有元素,你需要为每项提供一个唯一的 key attribute:
<div v-for="(item,index) in items" :key="item.id|index">
<!-- 内容 -->
</div>
事件处理
监听事件
我们可以使用 v-on 指令 (通常缩写为@符号) 来监听 DOM 事件,并在触发事件时执行一些 JavaScript。用法为 v-on:click="methodName" 或使用快捷方式 @click="methodName"
<button @click="counter += 1">Add 1</button>
data() {
return {
counter: 0
}
}
事件处理方法
然而许多事件处理逻辑会更为复杂,所以直接把 JavaScript 代码写在 v-on 指令中是不可行的。因此 v-on 还可以接收一个需要调用的方法名称。
<button @click="greet">按钮</button>
methods: {
greet(event) {
// `event` 是原生 DOM event
if (event) {
event.target.innerHTML="点击之后";
alert(event.target.tagName)
}
}
}
内联处理器中的方法
这是官方的翻译称呼,其实我们可以直接叫他 “事件传递参数”
<button @click="say('hi')">Say hi</button>
<button @click="say('what')">Say what</button>
methods: {
say(message) {
alert(message)
}
}
表单输入绑定
你可以用 v-model 指令在表单 <input> 、 <textarea> 及 <select> 元素上创建双向数据绑定。它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。尽管有些神奇,但 v-model 本质上不过是语法糖。它负责监听用户的输入事件来更新数据,并在某种极端场景下进行一些特殊处理。
<input v-model="message" placeholder="editme" />
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
data() {
return {
message:""
}
}
修饰符
.lazy
在默认情况下, v-model 在每次 input 事件触发后将输入框的值与数据进行同步 。你可以添加 lazy 修饰符,从而转为在 change 事件之后进行同步
<input v-model.lazy="message" />
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
data() {
return {
message:""
}
}
.trim
如果要自动过滤用户输入的首尾空白字符,可以给 v-model 添加 trim修饰符
<input v-model.trim="message" />
data() {
return {
message:""
}
}
组件基础
单文件组件
Vue 单文件组件(又名 *.vue 文件,缩写为 SFC)是一种特殊的文件格式,它允许将 Vue 组件的模板、逻辑 与 样式封装在单个文件中
<template>
<h3>单文件组件</h3>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"MyComponent"
}
</script>
<!-- scoped : 如果在style中添加此属性,就代表,当前样式,只在当前组件中生效 -->
<style scoped>
h3{
color:red;
}
</style>
加载组件
第一步:引入组件 import MyComponentVue from './components/MyComponent.vue'
第二步:挂载组件 components: { MyComponentVue }
第三步:显示组件 <my-componentVue />
在App.vue中
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<!-- 显示组件 -->
<my-component :title="title" :age="age" :names="names"></my-component>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import MyComponent from "./components/MyComponet.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
title: "我是一个标题",
age:18,
names:["gb","zhangsan","lisi"]
}
},
// 挂载组件
components: {
MyComponent
}
}
</script>
组件的组织
通常一个应用会以一棵嵌套的组件树的形式来组织
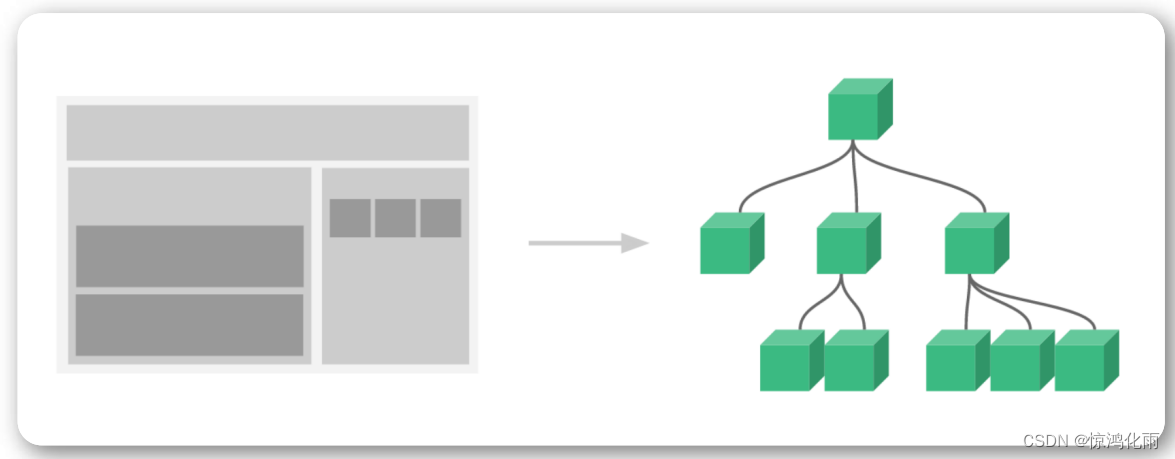
Props组件交互
组件与组件之间是需要存在交互的,否则完全没关系,组件的意义就很小了
Prop 是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义 attribute
在App.vue中像 自定义组件 MyComponent 中传递数据,先在App.vue中定义一些数据
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<!-- 显示组件 -->
<my-component :title="title" :age="age" :names="names"></my-component>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import MyComponent from "./components/MyComponet.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
title: "我是一个标题",
age:18,
names:["gb","zhangsan","lisi"]
}
},
// 挂载组件
components: {
MyComponent
}
}
</script>
在MyComponent 中接受这些数据 ,这个接受数据的形式是固定的模版
<template>
<h3>prop 传递数据</h3>
<p> {{ title }}</p>
<p>{{ age }}</p>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in names " :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:"MyComponent",
props:{
title:{
type:String,
default:""
},
age:{
type:Number,
default:0
},
names:{
type:Array,
//数组和对象必须使用函数进行返回
default:function(){
return []
}
}
}
}
</script>
<!-- scoped : 如果在style中添加此属性,就代表,当前样式,只在当前组件中生效 -->
<style scoped>
h3{
color:red;
}
</style>
Prop 类型
Prop传递参数其实是没有类型限制的
props: {
title: String,//字符串类似
likes: Number,//数字类型
isPublished: Boolean,//布尔类型
commentIds: Array,//数组类型
author: Object,//对象类型
callback: Function //函数类型
}
自定义事件组件交互
自定义事件可以在组件中反向传递数据, prop 可以将数据从父组件传递到子组件,那么反向如何操作呢,就可以利用自定义事件实现$emit
现在从自定义组件MyComponent.vue(子组件)中传递数据到App.vue(父组件)根组件中
<template>
<h3>自定义事件传递数据</h3>
<!-- 通过点击事件将数据传递过去 -->
<button @click="sendClickHandle">点击传递数据</button>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:"MyComponent",
data(){
return{
message:"我是MyComponent数据"
}
},
methods:{
sendClickHandle(){
//参数1:字符串 :理论是随便的 但是需要具有意义
//参数2:传递的数据
this.$emit("onEvent",this.message)
}
}
}
</script>
<!-- scoped : 如果在style中添加此属性,就代表,当前样式,只在当前组件中生效 -->
<style scoped>
h3{
color:red;
}
</style>
在App.vue(父组件)中接收数据
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<!-- 定义一个事件的形式接受到数据 @这个名字就是我们在子组件自定义的名字 -->
<my-component @onEvent="getDataHandle"></my-component>
</template>
<script>
import MyComponent from './components/MyComponet.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
message:"123"
}
},
components: {
MyComponent
},
methods:{
getDataHandle(data){
this.message =data;
alert(data)
}
}
}
</script>
组件生命周期

每个组件在被创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程——例如,需要设置数据监听、编译模板、将实例挂载到 DOM 并在数据变化时更新 DOM 等。同时在这个过程中也会运行一些叫做生命周期钩子的函数,这给了用户在不同阶段添加自己的代码的机会
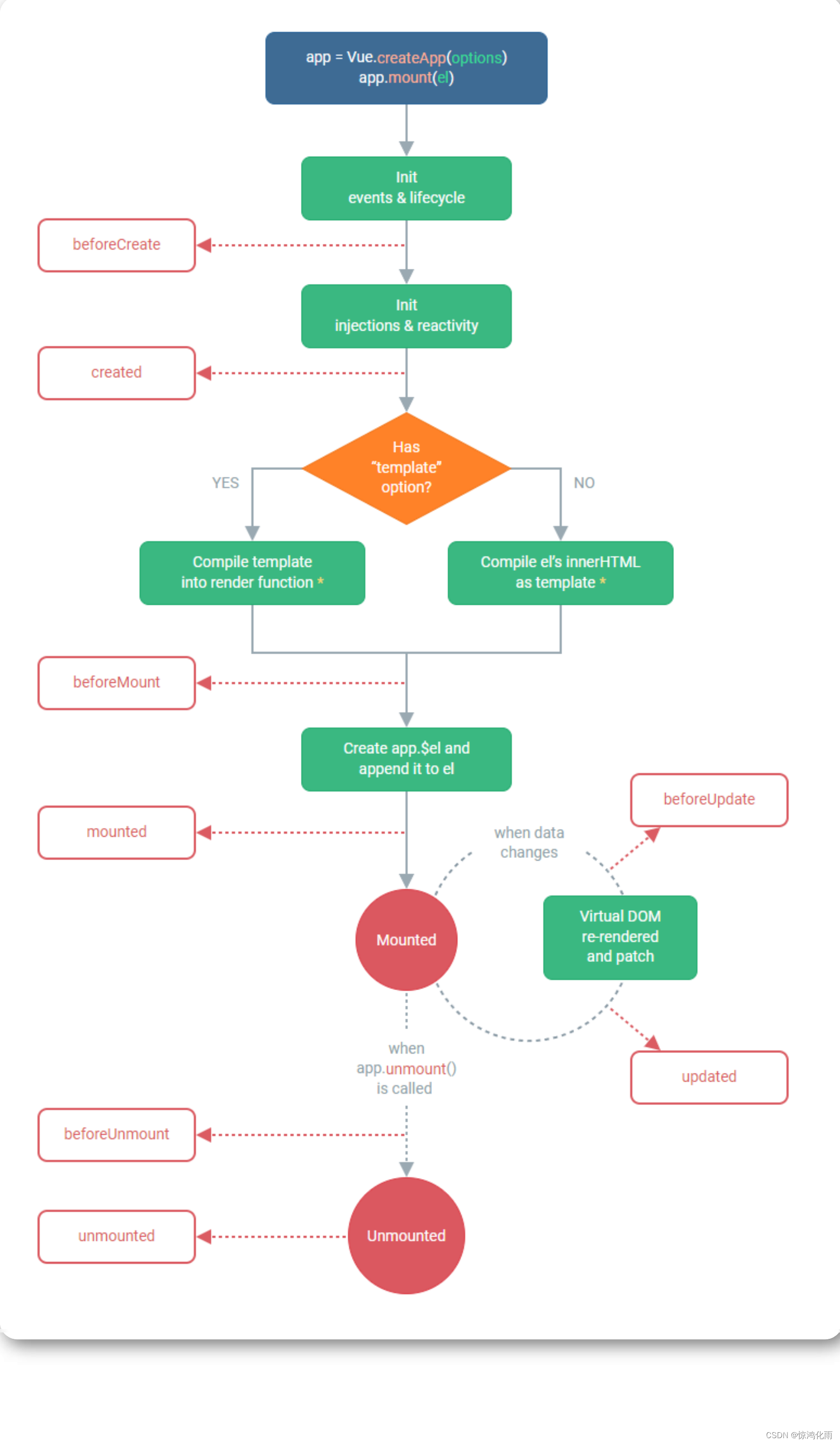
为了方便记忆,我们可以将他们分类:
创建时: beforeCreate 、 created
渲染时: beforeMount 、 mounted
更新时: beforeUpdate 、 updated
卸载时: beforeUnmount 、 unmounted
<template>
<h3>组件生命周期函数</h3>
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button @click="message='数据'">点击</button>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:"MyComponent",
data(){
return{
message:""
}
},
beforeCreate(){
console.log("beforeCreate:组件创建之前")
},
created(){
console.log("created:组件创建完成")
},
beforeMount(){
console.log("beforeMount:渲染完成之前")
},
mounted(){
console.log("mounted:组件渲染完成")
//把网络请求放到这里
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.log("beforeUpdate:组件更新之前")
},
updated(){
console.log("updated:组件更新之后")
},
beforeUnmount(){
console.log("beforeUnmount:组件卸载之前")
// 卸载之前,把消耗性能的处理都干掉
// 清理掉定时器
},
unmounted(){
console.log("unmounted:组件卸载完成")
}
}
</script>
<!-- scoped : 如果在style中添加此属性,就代表,当前样式,只在当前组件中生效 -->
<style scoped>
h3{
color:red;
}
</style>
运行效果:
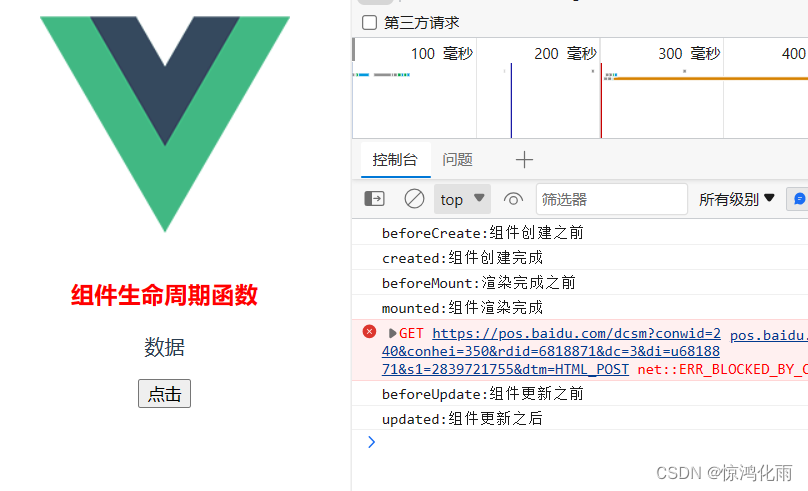
Vue引入第三方
Swiper 开源、免费、强大的触摸滑动插件
Swiper 是纯javascript打造的滑动特效插件,面向手机、平板电脑等移动终端
Swiper 能实现触屏焦点图、触屏Tab切换、触屏轮播图切换等常用效果
官方文档:https://swiperjs.com/vue
安装指定版本:npm instal --save swiper@8.1.6
基础实现+添加指示器
<template>
<div class="hello">
<swiper class="mySwiper" :modules="modules" :pagination="{ clickable:true }">
<SwiperSlide><img src="../assets/1.jpg" alt="" class="tupian"></SwiperSlide>
<SwiperSlide><img src="../assets/2.jpg" alt="" class="tupian"></SwiperSlide>
<SwiperSlide><img src="../assets/3.jpg" alt="" class="tupian"></SwiperSlide>
<SwiperSlide><img src="../assets/4.jpg" alt="" class="tupian"></SwiperSlide>
</swiper>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { Swiper, SwiperSlide } from 'swiper/vue';
import { Pagination } from 'swiper';
import 'swiper/css';
import 'swiper/css/pagination';
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data() {
return {
modules: [Pagination]
}
},
components: {
Swiper,
SwiperSlide,
Pagination
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.tupian {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
Axios网络请求
Axios 是一个基于 promise 的网络请求库
安装
Axios的应用是需要单独安装的 npm install --save axios
引入
组件中引入: import axios from "axios"
全局引用:
import axios from "axios"
const app = createApp(App);
app.config.globalProperties.$axios = axios
app.mount('#app')
// 在组件中调用
this.$axios
网络请求基本示例
<template>
<div class="hello">Axios网络请求</div>
<p>{{ chengpin.title }}</p>
<!-- <ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in chengpin.img" :key="index"><a href="item">{{ item }}</a></li>
</ul> -->
</template>
<script>
//import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data(){
return{
chengpin:{}
}
},
mounted(){
//get请求方式
// axios({
// method:"get",
// url:"http://iwenwiki.com/api/blueberrypai/getChengpinDetails.php",
// }).then(res=>{
// //this.chengpin =res.data.chengpinDetails[0];
// })
//post请求方式
// axios({
// method:"post",
// url:"http://iwenwiki.com/api/blueberrypai/getChengpinDetails.php",
// data:{
// user_id:"iwen@qq.com",
// password:"iwen123",
// verification_code:"crfvw"
// }
// }).then(res=>{
// this.chengpin =res.data.chengpinDetails[0];
// console.log(res.data);
// })
//快捷方案
this.$axios.get("http://iwenwiki.com/api/blueberrypai/getChengpinDetails.php").then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
this.chengpin =res.data.chengpinDetails[0];
});
this.$axios.post("http://iwenwiki.com/api/blueberrypai/getChengpinDetails.php",{
user_id:"iwen@qq.com",
password:"iwen123",
verification_code:"crfvw"
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
this.chengpin =res.data.chengpinDetails[0];
});
},
}
</script>
Axios网络请求封装
参考文档:https://www.kancloud.cn/yunye/axios/234845
在日常应用过程中,一个项目中的网络请求会很多,此时一般采取的方案是将网络请求封装起来
在 src 目录下创建文件夹 utils ,并创建文件 request.js ,用来存储网络请求对象 axios
import axios from "axios";
const errorHandle = (status,info) => {
switch(status){
case 400:
console.log("语义有误");
break;
case 401:
console.log("服务器认证失败");
break;
case 403:
console.log("服务器拒绝访问");
break;
case 404:
console.log("地址错误");
break;
case 500:
console.log("服务器遇到意外");
break;
case 502:
console.log("服务器无响应");
break;
default:
console.log(info);
break;
}
}
const instance = axios.create({
//网络请求的公共配置
timeout:5000 //设置网络超时时间,超过这个时间如果还没请求到数据就不管他了 就干掉
})
//拦截器最常用
//发送数据之前
instance.interceptors.request.use(
config =>{
//config:包含网络请求的所有信息
return config;
},
error =>{
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
//获取数据之前
instance.interceptors.response.use(
response => {
return response.status ===200 ? Promise.resolve(response):Promise.reject(response)
},
error => {
const {response} =error;
//错误的处理才是需要关注的
errorHandle(response.status,response.info);
}
)
export default instance;
在 src 目录下创建文件夹 api ,并创建文件 index.js 和 path.js 分别用来存放网络请求方法和请求路径
index.js
import axios from "../utils/request";
import path from "./path"
const api ={
//成品详情地址
getChengpin(){
return axios.get(path.baseUrl+path.chengpin)
}
}
export default api
path.js
const base = {
baseUrl:"http://iwenwiki.com",
chengpin:"/api/blueberrypai/getChengpinDetails.php"
}
export default base;
网络请求跨域解决方案
JS采取的是同源策略
同源策略是浏览器的一项安全策略,浏览器只允许js 代码请求和当前所在服务器域名,端口,协议相同的数据接口上的数据,这就是同源策略.
也就是说,当协议、域名、端口任意一个不相同时,都会产生跨域问题,所以又应该如何解决跨域问题呢
跨域错误提示信息
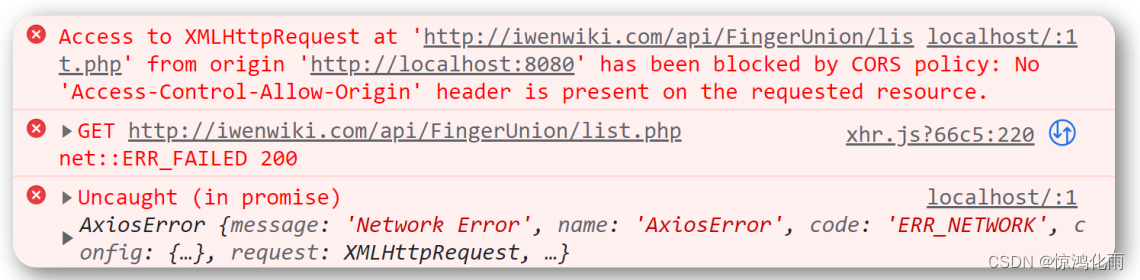
目前主流的跨域解决方案有两种:
- 后台解决:cors
- 前台解决:proxy
在config.js文件中添加下面这段代码
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/api': {
target: '<url>',
changeOrigin: true
}
}
}
注意:
解决完跨域配置之后,要记得重启服务器才行哦!
Vue引入路由配置
在Vue中,我们可以通过 vue-router 路由管理页面之间的关系
Vue Router 是 Vue.js 的官方路由。它与 Vue.js 核心深度集成,让用 Vue.js 构建单页应用变得轻而易举
在Vue中引入路由
第一步:安装路由 npm install --save vue-router
第二步:配置独立的路由文件
import {createRouter,createWebHashHistory} from "vue-router";
import HomeView from "../views/HomeView"
import AboutView from "../views/AboutView"
//配置信息中需要页面的相关配置
const routes =[
{
path:"/",
component:HomeView
},
{
path:"/about",
component:AboutView
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history:createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
export default router;
第三步:引入路由到项目
// main.js
import router from './router'
app.use(router)
第四步:指定路由显示入口 <router-view/>
第五步:指定路由跳转
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>
路由传递参数
页面跳转过程中,是可以携带参数的,这也是很常见的业务
例如:在一个列表项,点击进入查看每个列表项的详情
第一步:在路由配置中指定参数的 key
{
path:"/list/:name",
name:"list",
//这是异步加载方式
component:() =>import("../views/ListView.vue")
}
第二步:在跳转过程中携带参数
<li><router-link to="/list/内蒙">内蒙旅游十大景区</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/list/北京">北京旅游十大景区</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/list/四川">四川旅游十大景区</router-link></li>
第三步:在详情页面读取路由携带的参数
<p>{{ $route.params.name }}城市旅游景区详情</p>
嵌套路由配置
路由嵌套是非常常见的需求
第一步:创建子路由要加载显示的页面
第一个页面 AboutUs.vue
<template>
<h3>关于我们</h3>
</template>
第二个页面 AboutInfo.vue
<template>
<h3>关于信息</h3>
</template>
第二步:在路由配置文件中添加子路由配置
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
redirect:'/about/us',//重定向 就是默认的路径
component: () => import('../views/AboutView.vue'),
children:[
{
//二级导航不要加斜杠
path:'us',
component:()=>import("../views/AboutSub/AboutUs.vue")
},
{
//二级导航不要加斜杠
path:'info',
component:()=>import("../views/AboutSub/AboutInfo.vue")
}
]
}
]
第三步:指定子路由显示位置 <router-view></router-view>
第四步:添加子路由跳转链接
<template>
<div class="about">
<router-link to="/about/us">关于我们</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about/info">关于信息</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
第五步:重定向配置 redirect:"/about/us"
Vue状态管理(Vuex)
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式 + 库。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
简单来说,状态管理可以理解成为了更方便的管理组件之间的数据交互,提供了一个集中式的管理方案,任何组件都可以按照指定的方式进行读取和改变数据
引入Vuex的步骤
第一步:安装Vuex npm install --save vuex
第二步:配置Vuex文件
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
//Vuex 的核心作用就是帮我们管理组件之间的状态的
export default createStore({
//所有的状态都放在这里(数据)
state:{
counter:0
}
})
第三步:在主文件中引入Vuex
import store from './store'
app.use(store)
第四步:在组件中读取状态
<p>counter:{{ $store.state.counter }}</p>
// 或者
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
computed:{
...mapState(["counter"])
}
Vue状态管理核心(Vuex)
最常用的核心概念包含: State 、 Getter 、 Mutation 、 Action
Getter
对Vuex中的数据进行过滤
Mutation
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)和一个回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数
Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import axios from 'axios'
//Vuex 的核心作用就是帮我们管理组件之间的状态的
export default createStore({
//所有的状态都放在这里(数据)
state:{
counter:10
},
//对数据进行过滤
getters: {
getCounter(state){
return state.counter >0?state.counter:"counter数据异常"
}
},
//
mutations: {
addCounter(state,num){
state.counter+=num
}
},
// 有异步操作的时候才用
// 为异步操作所准备的
actions: {
asyncAddCount({commit}){ //括号里是对象的结构赋值
axios.get("http://iwenwiki.com/api/generator/list.php")
.then(res=>{
commit("addCounter",res.data[0])
//console.log(rex.data)
})
}
},
modules: {
}
})
在HomeView中显示数据
<template>
<div class="home">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="../assets/logo.png">
<p>count={{ $store.getters.getCounter }}</p>
<p>count={{ getCounter }}</p>
<!-- 通过事件实现方法 -->
<button @click="addClickHandle">增加</button>
<!-- 通过异步增加 -->
<button @click="addAsyncClickHandle">异步增加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions } from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {
},
computed:{
...mapGetters(["getCounter"])
},
methods:{
...mapMutations(["addCounter"]),
...mapActions(["asyncAddCount"]),
addClickHandle(){
//固定的调用方式
// this.$store.commit("addCounter",15)
// 引入后的 快捷方式
this.addCounter(20)
},
addAsyncClickHandle(){
//固定的调用方式
//this.$store.dispatch("asyncAddCount")
// 引入后的 快捷方式
this.asyncAddCount();
}
}
}
</script>
Vue3新特性1
六大亮点
- Performance:性能更比Vue 2.0强。
- Tree shaking support:可以将无用模块“剪辑”,仅打包需要的。
- Composition API:组合API
- Fragment, Teleport ,Suspense:“碎片”,Teleport即Protal传送门,“悬念”
- Better TypeScript support:更优秀的Ts支持
- Custom Renderer API:暴露了自定义渲染AP
ref或者reactive
在2.x中通过组件data的方法来定义一些当前组件的数据
data() {
return {
name: 'iwen',
list: [],
}
}
在3.x中通过ref或者reactive创建响应式对象
import { ref,reactive } from "vue"
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
setup(){
const name = ref("iwen")
const state = reactive({
list:[]
})
return{
name,
state
}
}
}
methods中定义的方法写在setup()
在2.x中methods来定义一些当前组件内部方法
methods:{
http(){}
}
在3.x中直接在setup方法中定义并return
setup()中使用props和context
在2.x中,组件的方法中可以通过this获取到当前组件的实例,并执行data变量的修改,方法的调用,组件的通信等等,但是在3.x中,setup()在beforeCreate和created时机就已调用,无法使用和2.x一样的this,但是可以通过接收setup(props,ctx)的方法,获取到当前组件的实例和props
<template>
<div class="hello">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in names.list" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<button @click="clickHandle">按钮</button>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,reactive} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
props:{
msg:String
},
// 组合式API
setup(props,ctx){
//setup 中没有this关键字 有context
console.log(this);
console.log(ctx);
console.log(props.msg);
//ref
const message =ref('我是消息')
//reactive 一边生命对象类型的数据,复杂一点的数据
const names =reactive({
list:["gb","zhangsan","lisi"],
})
function clickHandle(){
//通过message的value去修改数据
message.value ="我是新的消息"
console.log("点击按钮");
}
//获取父组件传递过来的数据
const msg = props.msg;
//所有的数据都必须返回才能拿到数据
return {
message,
names,
clickHandle,
msg
}
}
}
</script>
Vue3新特性2
在setup中使生命周期函
你可以通过在生命周期钩子前面加上 “on” 来访问组件的生命周期钩子。
下表包含如何在 setup () 内部调用生命周期钩子
| Options API | Hook inside setup |
|---|---|
| beforeCreate | Not needed* |
| created | Not needed* |
| beforeMount | onBeforeMount |
| mounted | onMounted |
| beforeUpdate | onBeforeUpdate |
| updated | onUpdated |
| beforeUnmount | onBeforeUnmount |
| unmounted | onUnmounted |
Provide / Inject
- provide() 和 inject() 可以实现嵌套组件之间的数据传递。
- 这两个函数只能在 setup() 函数中使用。
- 父级组件中使用 provide() 函数向下传递数据。
- 子级组件中使用 inject() 获取上层传递过来的数据。
- 不限层级
父组件中App.vue
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
</template>
<script>
import { provide } from 'vue';
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
setup(){
//只能父组件往子组件中传递
provide("message","这是我想传递的消息")
}
}
</script>
子组件中HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<div class="hello">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { inject, onMounted } from 'vue';
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
setup() {
//比以前有优势,以前同一个生命周期只能存在一个,现在可以存在多个
onMounted(() => console.log("生命周期函数1:onMounted"))
onMounted(() => console.log("生命周期函数2:onMounted"))
//在子组件中接收 数据
const message = inject("message");
return {
message
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>
Fragment
Fragment翻译为:“碎片”
- 不再限于模板中的单个根节点
Vue3加载Element-plus
Element,一套为开发者、设计师和产品经理准备的基于 Vue 2.0 的桌面端组件库
Element Plus 基于 Vue 3 ,面向设计师和开发者的组件库
安装Element-Plus
npm install element-plus --save
完整引用
如果你对打包后的文件大小不是很在乎,那么使用完整导入会更方便
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import ElementPlus from 'element-plus'
import 'element-plus/dist/index.css'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(ElementPlus)
app.mount('#app')
按需导入
按需导入才是我们的最爱,毕竟在真实的应用场景中并不是每个组件都会用到,这会造成不小的浪费
首先你需要安装 unplugin-vue-components 和 unplugin-auto-import 这两款插件
npm install -D unplugin-vue-components unplugin-auto-import
然后修改 vue.config.js 配置文件
const { defineConfig } = require('@vue/cli-service')
const AutoImport = require('unplugin-auto-import/webpack')
const Components = require('unplugin-vue-components/webpack')
const { ElementPlusResolver } = require('unplugin-vue-components/resolvers')
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
configureWebpack: {
plugins: [
AutoImport({
resolvers: [ElementPlusResolver()]
}),
Components({
resolvers: [ElementPlusResolver()]
})
]
}
})
最后,可以直接在组件中使用
<template>
<el-button>Default</el-button>
<el-button type="primary">Primary</elbutton>
</template>
Vue3加载Element-plus的字体图标
Element-plus 不仅仅是提供了各种组件,同时还提供了一整套的字体图标方便开发者使用
安装 icons 字体图标
npm install @element-plus/icons-vue
全局注册
在项目根目录下,创建 plugins 文件夹,在文件夹下创建文件 icons.js 文件
import * as components from "@element-plus/icons-vue";
export default {
install: (app) => {
for (const key in components) {
const componentConfig =components[key];
app.component(componentConfig.name,componentConfig);
}
},
};
引入文件
在 main.js 中引入 icons.js 文件
import elementIcon from "./plugins/icons";
app.use(elementIcon)
使用方式
接下来就可以直接在组件中引入使用了
<el-icon class="expand" color="#409EFC":size="30">
<expand />
</el-icon>






















 7542
7542











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








