目录
前言
上次我们了解了通用分页的前台代码(http://t.csdn.cn/WaVH1),今天了解的内容是自定义MVC
一、MVC简介
什么是MVC?
Model View Controller
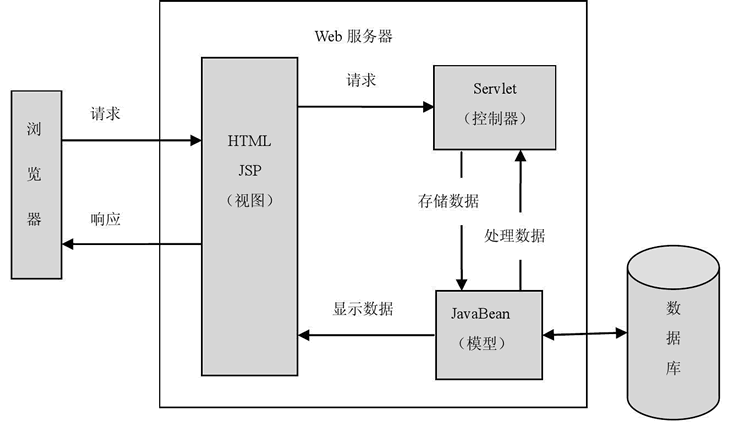
mvc一般指MVC框架。 经典MVC模式中,M是指业务模型,V是指用户界面,C则是控制器,使用MVC的目的是将M和V的实现代码分离,从而使同一个程序可以使用不同的表现形式。其中,View的定义比较清晰,就是用户界面。
基于Servlet的MVC简介图
MVC的优点
1.耦合性低
视图层和业务层分离,这样就允许更改视图层代码而不用重新编译模型和控制器代码,同样,一个应用的业务流程或者业务规则的改变只需要改动MVC的模型层即可。因为模型与控制器和视图相分离,所以很容易改变应用程序的数据层和业务规则
2.重用性高
MVC模式允许使用各种不同样式的视图来访问同一个服务器端的代码,因为多个视图能共享一个模型,它包括任何WEB(HTTP)浏览器或者无线浏览器(wap),比如,用户可以通过电脑也可通过手机来订购某样产品,虽然订购的方式不一样,但处理订购产品的方式是一样的。由于模型返回的数据没有进行格式化,所以同样的构件能被不同的界面使用。
3.部署快,生命周期成本低
MVC使开发和维护用户接口的技术含量降低。使用MVC模式使开发时间得到相当大的缩减,它使程序员(Java开发人员)集中精力于业务逻辑,界面程序员(HTML和JSP开发人员)集中精力于表现形式上。
4.可维护性高
分离视图层和业务逻辑层也使得WEB应用更易于维护和修改。
MVC的缺点
1.完全理解MVC比较复杂。
由于MVC模式提出的时间不长,加上同学们的实践经验不足,所以完全理解并掌握MVC不是一个很容易的过程。
2.调试困难。
因为模型和视图要严格的分离,这样也给调试应用程序带来了一定的困难,每个构件在使用之前都需要经过彻底的测试。
3.不适合小型,中等规模的应用程序
在一个中小型的应用程序中,强制性的使用MVC进行开发,往往会花费大量时间,并且不能体现MVC的优势,同时会使开发变得繁琐。
4.增加系统结构和实现的复杂性
对于简单的界面,严格遵循MVC,使模型、视图与控制器分离,会增加结构的复杂性,并可能产生过多的更新操作,降低运行效率。
5.视图与控制器间的过于紧密的连接并且降低了视图对模型数据的访问
视图与控制器是相互分离,但却是联系紧密的部件,视图没有控制器的存在,其应用是很有限的,反之亦然,这样就妨碍了他们的独立重用。
依据模型操作接口的不同,视图可能需要多次调用才能获得足够的显示数据。对未变化数据的不必要的频繁访问,也将损害操作性能。
二、最初版增删改查
JSP:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>目前增删改查的方法</h3>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/add">增加</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/del">删除</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/edit">修改</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/list">查看</a>
</body>
</html>平常我们没有接触任何框架知识的时候,我们写Web项目都是在Jsp直接跳转向servlet发送请求,基本每实现一个功能就要建立一个Servlet,就能发现,关于单个实体/表操作场景越多,需要新建的类也就越多,造成了项目中类的数量过于庞大。那我们能不能写一个Servlet实现多个方法呢?
答案是可以的,只需要我们跳转时传个参数判断就行
类数量过多问题的优化:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>类数量过多问题的优化</h3>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=add">增加</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=del">删除</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=edit">修改</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=list">查看</a>
</body>
</html>BookServlet :
package com.oyang.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/book.action")
public class BookServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
if("add".equals(methodName)) {
//如果前台传递到后台的是一个新增的请求,那么后台就调用新增方法
add(request,response);
}else if("del".equals(methodName)) {
del(request,response);
}else if("edit".equals(methodName)) {
edit(request,response);
}else if("list".equals(methodName)) {
list(request,response);
}
}
private void list(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用list查询方法");
}
private void edit(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用edit修改方法");
}
private void del(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用del删除方法");
}
private void add(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用add新增方法");
}
}
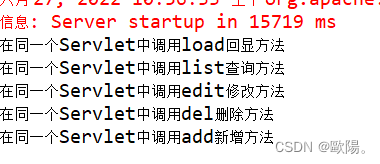
运行结果:

那么问题来了,如果我还需要新增了业务呢?是不是又得去更改BookServlet 中的业务逻辑代码?能否不改变逻辑代码还能增加呢?这时反射版的增删改查就来了。
三、反射版的增删改查
新增一个回显
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=add">增加</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=del">删除</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=edit">修改</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=list">查看</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book.action?methodName=load">回显</a>
</body>
</html>优化BookServlet :
package com.oyang.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/book.action")
public class BookServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//为了区分当前请求的目的:增删改查的目的,就从前台将要调用的方法名传递到后台
String methodName=request.getParameter("methodName");
//methodName可能是add/del/edit/list/load/...
//前台传递什么方法,就调用当前类的对应方法
try {
Method m = this.getClass()//当前类.class
.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class);
//打开权限
m.setAccessible(true);
//调用当前类实例的methodName 方法
m.invoke(this, request,response);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void list(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用list查询方法");
}
private void load(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用load回显方法");
}
private void edit(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用edit修改方法");
}
private void del(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用del删除方法");
}
private void add(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个Servlet中调用add新增方法");
}
}
OK,这样的话就可以只用写一个方法而不用改动逻辑代码了。
但是如果我们能够发现一些问题
- 反射相关的代码在每一个实体类对应的Servlet中都存在
- 每一个servlet中都有doget,dopost方法
所以,我们需要进一步的进行优化,那就是自定义一个MVC框架。
四、自定义MVC
自定义MVC工作原理图
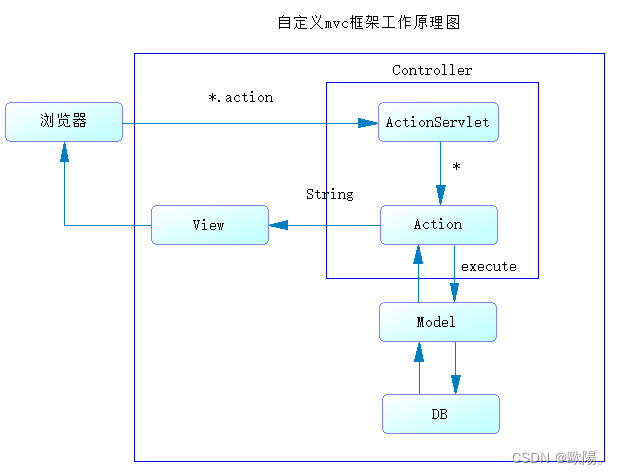
中央控制器(Action)--->子控制器(Action)--->实现处理的方法(execute)--->业务逻辑层处理(方法)
首先创建一个中央控制器(处理所有以.action的请求)
DispatcherServlet :
package com.oyang.framework;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.oyang.servlet.BookAction;
/**
* 中央控制器:
* 主要职能,接收浏览器请求,找到对应的处理人
* @author yang
*
*/
@WebServlet("*.action")
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet{
private Map<String, Action> actions=new HashMap<String,Action>();
//程序启动时 ,只会加载一次
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
actions.put("/book",new BookAction());
actions.put("/order",new BookAction());
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
//只要是以.action结尾的每次请求都会被doPost截取
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
http://localhost:8080/mvc/book.action?methodName=list
String uri = req.getRequestURI();
// 要拿到/book,就是最后一个/到最后一个.为止
uri= uri.substring(uri.lastIndexOf("/"),uri.lastIndexOf("."));
Action action = actions.get(uri);
//取到.action之后 Action action = actions.get(uri);里面定义了对应的方法
action.execute(req, resp);
}
}
主要职能,接收浏览器请求,找到对应的处理人
子容器Action接口:
package com.oyang.framework;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 子控制器
* 对应请求的处理人
* @author yang
*
*/
public interface Action {
void execute(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response);
}
上面这个子控制器就是用来处理不同的请求的请求人。
然后创建一个中转站,用来判断是什么请求
ActionSupport :
package com.oyang.framework;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ActionSupport implements Action {
@Override
public void execute(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String methodName = request.getParameter("methodName");
// methodName可能是add/del/edit/list/load/...
// 前台传递什么方法,就调用当前类的对应方法
try {
Method m = this.getClass()// 当前类.class
.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class);
// 打开权限
m.setAccessible(true);
// 调用当前类实例的methodName 方法
m.invoke(this, request, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
最后我们的servlet就只剩下纯方法代码了(需要继承中转站-ActionSupport)
OrderAction :
package com.oyang.servlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.oyang.framework.Action;
import com.oyang.framework.ActionSupport;
public class OrderAction extends ActionSupport{
private void list(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个OrderServlet中调用list查询方法");
}
private void load(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个OrderServlet中调用load回显方法");
}
private void edit(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个OrderServlet中调用edit修改方法");
}
private void del(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个OrderServlet中调用del删除方法");
}
private void add(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println("在同一个OrderServlet中调用add新增方法");
}
}
请求结果:

敬请期待下篇J2EE基础-自定义MVC(中),下篇将会优化的更多
OK,今日的学习就到此结束啦,如果对个位看官有帮助的话可以留下免费的赞哦(收藏或关注也行),如果文章中有什么问题或不足以及需要改正的地方可以私信博主,博主会做出改正的。个位看官,小陽在此跟大家说拜拜啦!























 1267
1267











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










