C++知识小菜单:
备赛蓝桥杯过程中的一些小知识积累,持续更新中!
文章目录
1.小数取整:
需要包含的头文件:
#include <cmath>
代码示例:
float num1=3.14;
int ceil_num=(ceil)num1;//ceil_num=4
int floor_num=(floor)num1;//floor_num=3
2.小数点后保留几位:
需要包含的头文件:
#include <iomanip>
代码示例:
float num1=3.1415926525;
cout<<setprecision(5)<<fixed<<num1<<endl;//3.14159
cout<<setprecision(2)<<fixed<<num1<<endl;//3.14
3.数字占几位字符:
需要包含的头文件:
#include <iomanip>
代码示例:
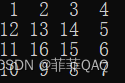
cout << right << setw(2) << 1 <<" "<< setw(2) << 2 <<" "<<setw(2) <<3<<" "<<setw(2) <<4<< endl;
cout << left << setw(2) << 12 <<" "<< setw(2) << 13<<" " <<setw(2) <<14<<" "<<setw(2) <<right<<5<< endl;
cout<<left<<setw(2)<<11<<" "<<setw(2)<<16<<" "<<setw(2)<<15<<" "<<right<<setw(2)<<6<<endl;
cout<<right<<setw(2)<<10<<" "<<setw(2)<<9<<" "<<setw(2)<<8<<" "<<setw(2)<<7<<endl;
//rigth是右对齐,left是左对齐,setw()表示该数字占几位
//如果没有using namespace std,需要在前面加std::,如cout<<std::left<<
输出示例:
4. 求x 的 y 次幂(次方)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <math.h>
代码示例:
double a=pow(2,5);//a=32
5. 求平方根
需要包含的头文件:
#include <math.h>
代码示例:
#include<math.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("%lf",sqrt(4.0));
return 0;
}
6. 万能头文件
需要包含的头文件:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main()
{
// write code here
return 0
}
它是C++中支持的一个几乎万能的头文件,几乎包含所有的可用到的C++库函数。以后写代码就可以直接引用这一个头文件了,不需要在写一大堆vector、string、map、stack……
7. 各个数字类型的范围
整形 int 16位:-32768至+32767
无符号整型 unsigned int 16位:0至65535
短整型 short int 16位:-32768至+32767
无符号短整型 unsigned short int 16位:0至65535
长整型 long 32位:-2147483648至2147483647(-263~263-1)
8. 字符串和整型之间的转化
字符串转整型代码示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <typeinfo>
int main(){
string str="12345";
cout<<str<<endl;
//typeid(a).name()是查看数据类型
int a=str[0]-'0';//-0是为了将字符串转换为普通数字
cout<<"a="<<a<<" "<<typeid(a).name()<<endl;int
char b=a+'0';//+0是为了将数字变成字符串
cout<<"b="<<b<<" "<<typeid(b).name()<<endl;//char
return 0;
}
运行截图:

整型转字符串型代码示例
//普通回文数
bool judge1(int n){
char buffer[8];
sprintf(buffer, "%d", n);
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(buffer[i]!=buffer[7-i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
9.向上向下取整
需要包含的头文件:
#include <math.h>
代码示例:
cout<<floor(1.2)<<endl;//向下取整 1
cout<<ceil(1.2)<<endl;//向上取整 2
cout<<round(1.2) <<endl;//四舍五入到最临近的整数 1
10.冒泡排序
代码示例:
//冒泡排序,从小到大
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<len;j++){
if(arr[i]>arr[j]){//前一个大于后一个,交换
int temp=arr[j];//临时变量
arr[j]=arr[i];//前一个覆盖后一个
arr[i]=temp;//临时值赋值给前一个
}
}
}
使用STL容器,从小到大排序
需要包含的头文件:
#include <algorithm>
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <algorithm>
int main(){
int len;cin>>len;
int arr[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cin>>arr[i];
}
sort(arr,arr+len);
printf("%d",arr[len-1]-arr[0]);
return 0;
}
11.判断质数
判断质数不用从2循环到n/2,循环到n的平方根即可
需要包含的头文件:
#include <math.h>
代码示例:
bool zhi(int n){
if(n==2)return 1;
for(int i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++){
if(n%i==0)return 0;
}
return 1;
}
12.去掉数组中的重复数据
(1)先排序才去重,利用vector和set容器,缺点是打乱了数组的顺序
以洛谷的一道题目为例:
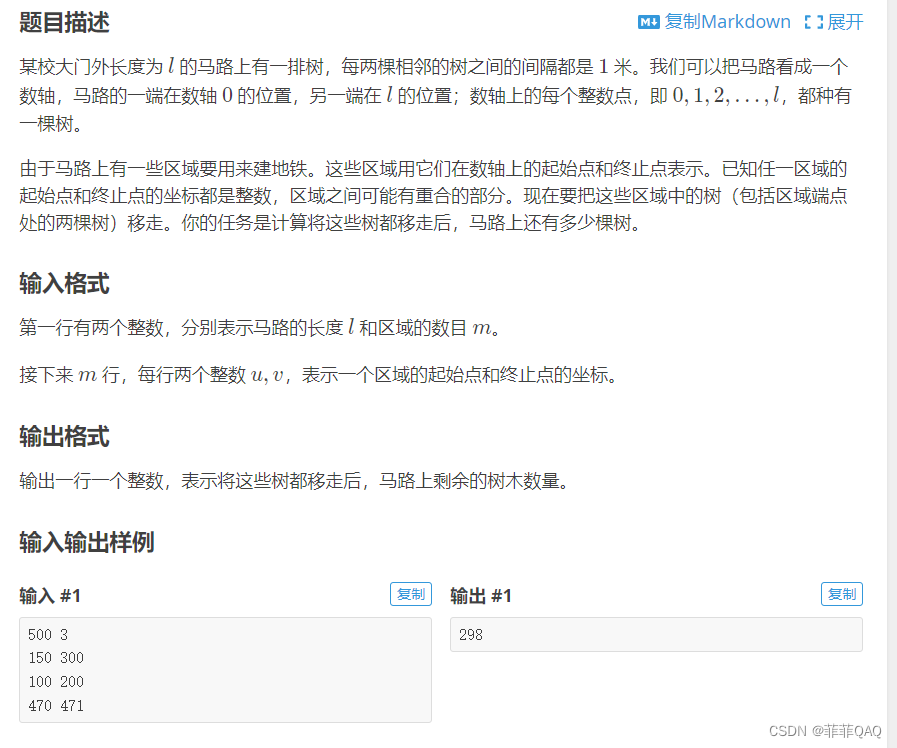
答案代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
int MAX=6553005;
int main(){
int l,m;cin>>l>>m;
int arr[200];
for(int i=0;i<2*m;i++){
cin>>arr[i];
}
int brr[MAX]={0};
int len=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*m;i+=2){
for(int j=arr[i];j<=arr[i+1];j++){
brr[len]=j;
len++;
}
}
sort(brr,brr+len);
vector<int> v(brr,brr+len);
set<int> s(v.begin(),v.end());
v.assign(s.begin(),s.end());
cout<<l-v.size()+1<<endl;
}
(2)不打乱数组顺序,去掉重复数据
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, array[100], flag = 1;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
cin >> array[i];
for (int k = 0; k<i; k++) {
if (array[i] == array[k]) {
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
flag = 1;
}
}

13. 计算绝对值
需要包含的头文件:
#include <math.h>
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <math.h>
int main(){
cout<<abs(5-9)<<endl;
cout<<abs(9-5)<<endl;
return 0;
}
14.字符的大小写转化
第一种方法:
需要包含的头文件:
#include <ctype.h>
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <ctype.h>
int main(){
string s;cin>>s;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++) s[i]=toupper(s[i]);
// printf("%s",&s);
cout<<s;
return 0;
}
运行截图

说明:
toupper是小写转大写函数,其函数原型:
int toupper(int c)
{
if ((c >= 'a') && (c <= 'z'))
return c + ('A' - 'a');
return c;
}
toupper是大写转小写函数,其函数原型:
int tolower(int c)
{
if ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z'))
return c + ('a' - 'A');
return c;
}
它们有一个优点:只会修改英文字母
注意,这两个函数只能一次修改一个字符
第二种方法:
题目示例

代码示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
cin>>s;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(s[i]>='a'&&s[i]<='z'){
s[i]-=32;
}
cout<<s[i];
}
// char a = 'a'-32;
// cout<<a<<endl;
return 0;
}
15.C语言中sscanf函数
需要包含的头文件:
#include <cstdio>
函数定义
int sscanf(const char *str, const char * format, ...);
函数说明
sscanf()定义于头文件stdio.h。sscanf()会将参数str的字符串根据参数format字符串来转换并格式化数据。格式转换形式请参考scanf()。转换后的结果存于对应的参数内。
返回值
成功则返回参数数目,失败则返回-1(也即EOF)。
例如将数字字符串转换成数字:
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a;
char ch[10]="1234";
sscanf(ch,"%d",&a);
cout<<a+1;//1235
return 0;
}
16.递归求括号种类
题目:

代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution{
public:
vector<string>ans;
vector<string> aa(int n){
help(n,n,"");
return ans;
}
void help(int l,int r,string a){
if(l==0 && r==0){
ans.push_back(a);
return ;
}
if(l!=0) help(l-1,r,a+'(');
if(l<r) help(l,r-1,a+')');
}
};
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
Solution s;
vector<string> rs =s.aa(n);
for(int i=0;i<rs.size();i++){
cout<<rs[i]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
17.求阶乘
代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//求全排列
typedef long long ll;
ll c(int a,int b){
ll res=1;
for(int i=a,j=1;j<=b;i--,j++){
res = res*i/j;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<c(a,b);
return 0;
}
18.判断是否闰年
代码示例:
//闰年2月29天,平年2月28天
bool judge(int year){
if( (year%4==0&&year%100!=0) || year%400==0 ){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
19. 求时间差(特殊的输入方法)
题目

代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int second = 1000;
int minute = 60*1000;
int hour = 60*60*1000;
int main(){
int h,m,s;
int h1,m1,s1;
int h2,m2,s2;
scanf("%d:%d:%d",&h,&m,&s);
scanf("%d:%d:%d",&h1,&m1,&s1);
int t=h*hour+m*minute+s*second;
int t1=h1*hour+m1*minute+s1*second;
int rs = t1-t;
h2 = rs/hour;
rs%=hour;
m2 = rs/minute;
rs%=minute;
s2=rs/second;
printf("%02d:%02d:%02d",h2,m2,s2);
return 0;
}
20.最小公倍数和最大公约数
题目示例:

代码示例:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//最大公约数 辗转相除法(欧几里得算法)
int gcd(int x,int y){
return !y?x:gcd(y,x%y);
}
//最小公倍数
int lcm(int x,int y){
return x*y/gcd(x,y);
}
int main(){
cout<<gcd(2,4)<<endl;
cout<<lcm(2,4)<<endl;
return 0;
}
21.背包问题(动态规划)
代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//背包问题 i表示偷前i件背包,j表示当前背包的容量,返回总价值
int f[5][9]={0};
int w[5]={0,2,3,4,5};//背包重量
int v[5]={0,3,4,5,8};//背包的价值
int main(){
int i,j;
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
for(int i=1;i<5;i++){
for(int j=1;j<9;j++){
if(w[i]>j)//背包重量大于当前的容量
f[i][j]=f[i-1][j];//偷不了
else{//背包容量够,可以选择偷或者不偷
// 选择不偷 选择偷
f[i][j]=max(f[i-1][j],f[i-1][j-w[i]]+v[i]);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
for(int j=0;j<9;j++){
printf("f[%d][%d]=%d\n",i,j,f[i][j]);
}
}
return 0;
}
22. 动态规划入门(硬币种类问题)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <math.h>
代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10000
int n;
int coin[MAX];//n种硬币
int sum;
int f[MAX];//f[i]表示当金额为i时所需要的最少硬币数目
void dp(int m){
f[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=sum;i++){//金额从0开始
f[i]=MAX;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){//查看每一枚硬币的面值
if( (i-coin[j])>=0 && (f[i-coin[j]]!=MAX) ){//i-coin[j]表示有该方案,(f[i-coin[j]]!=MAX)表示前一种方案有解
f[i]=min(f[i],f[i-coin[j]]+1);//状态转移方程,
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;//硬币的种类数
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>coin[i];
}
cin>>sum;//输入需要的金额数
dp(sum);
cout<<((f[sum]==MAX)?-1:f[sum])<<endl;//凑齐sum金额需要的最少硬币数目
for(int i=0;i<=sum;i++){
cout<<"i="<<i<<":";
cout<<f[i]<<" "<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
23.
需要包含的头文件:
代码示例:

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










