目录
一、Day1
1.1选择题:
(1)方法通常存储在进程的哪一区()
A. 堆区 B. 栈区 C.全局区 D.方法区
正确答案:D
(2)下列选项中属于面向对象设计方法主要特征的是()。
A. 继承 B.自顶向下 C.模块化 D.逐步求精
机构化程序设计原则:模块化,自顶线下,逐步求精
1.2 编程题
组队竞赛链接:组队竞赛__牛客网
import java.util.*;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
int []arr=new int[3*n];
for(int i=0;i<3*n;i++){
arr[i]=in.nextInt();
}
long sum=0;
//将数组序列排序
Arrays.sort(arr);
//每次分组时,由于最大的没法作为队的平均值,因此要选取第二大的作为其平均值
for(int i=arr.length-2;i>=n;i-=2){
sum+=arr[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}二、Day2
2.1 选择题
(1) 阅读如下代码。 请问,对语句行 test.hello(). 描述正确的有()
class Test {
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Test test=null;
test.hello();
}
}A. 能编译通过,并正确运行
B. 因为使用了未初始化的变量,所以不能编译通过
C. 以错误的方式访问了静态方法
D. 能编译通过,但因变量为null,不能正常运行
答案:A
hello是静态方法,是不依赖于对象存在的,即使是空指针也可以通过强制类型转换来调用((Test)null).hello。
(2)如下代码的输出结果是什么?
public class Test{
public int aMethod(){
static int i= 0;
i++;
return i;
}
public static void main(String [] args){
Test test =new Test();
test.aMethod();
int j=test.aMethod();
System.out.println(j);
}
}A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D.编译失败
答案:D
用static修饰的静态常量只能作为类的成员变量,不能够放在静态方法和其他方法的内部,否则编译失败。
(3)下列哪一项叙述是正确的()
A. abstract修饰符可修饰字段、方法和类
B. 抽象方法的body部分必须用一对大括号{ }包住
C. 声明抽象方法,大括号可有可无
D. 声明抽象方法不可写出大括号
答案:D
A:abstract不能修饰字段;
B:抽象方法不可写大括号。
2.2 编程题
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
int []arr=new int[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i]=in.nextInt();
}
int i=0;
int count=0;
while(i<n){
if(arr[i]>arr[i+1]){
while(i<n&&arr[i]>=arr[i+1]){
//while(i<n&&arr[i]>arr[i+1]{
i++;
}
i++;
count++;
}else if(arr[i]==arr[i+1]){
while(arr[i]==arr[i+1]){
i++;
}
i++;
}else{
while (i<n&&arr[i]<=arr[i+1]){
//while(i<n&&arr[i]<arr[i+1]{
i++;
}
i++;
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}该题问的是最少分为多少个子序列,在判断大小时,必须带上等号,上述代码虽然在题中能够通过,但并不是该题的真正的解。如:当输入案例为[2,4,4,8]时,当i指向1下标时,会跳出循环,并再后移一位后再次进入非递减序列。若带上等号则不会出现上述情况。
三、Day3
3.1 选择题
(1)下列哪张说法是正确的?
A.实例方法可直接调用超类的实例方法
B.实例方法可直接调用超类的类方法
C.实例方法可直接调用本类的类方法
D.实例方法可直接调用其他类的实例方法
A:调用父类的示例方法需要借助关键字super
B:调用超类的类方法法需要借助父类的类名
D:需要其他类的实例对象来调用
(2)以下程序的输出结果为
class Base{
public Base(String s){
System.out.print("B");
}
}
public class Derived extends Base{
public Derived (String s) {
System.out.print("D");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new Derived("C");
}
}A. BD B. DB C.C D.编译错误
实例化子类的构造方法会先调用父类的无参构造方法,由于父类中没有无参的构造方法,编译错误
3.2 编程题
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String str=in.nextLine();
int i=0;
//cur存放当前遍历字符串
String cur="";
//ret存放最大字符串
String ret="";
for(;i<str.length();i++ ){
char ch=str.charAt(i);
//当字符是数字字符时,放进cur字符串
if(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
cur=cur+ch+"";
}else{
//只有cur字符串大于ret字符串长度时才会改变ret指向
if(cur.length()>ret.length()){
ret=cur;
}else{
cur="";
}
}
}
if(cur.length()>ret.length()){
ret=cur;
}
System.out.print(ret);
}
}四、Day4
4.1 选择题
(1)下列关于栈叙述正确的是()。
A. 算法就是程序
B.设计算法时只需要考虑数据结构的设计
C.设计算法时只需要考虑结果的可靠性
D.以上说法都不对
答案:D
算法是解决问题的步骤,程序是对问题的具体代码实现。算法和程序都是指令的有限序列,但是程序是算法,而算法不一定是程序。它们的主要区别在语言描述上和执行实践上。在语言描述上,程序必须是规定的程序设计语言来写,而算法很随意。在执行时间上,算法所描述的步骤一定是有限的,而程序可以无限的执行下去。所以:程序=数据结构+算法。
(2)结构程序化的三种基本结构是()
A.递归、迭代和回溯
B.过程、函数和子程序
C.顺序、选择和循环
D.调用、返回和选择
答案:C
结构化程序设计是进行以模块功能和处理过程设计为主的详细设计的基本原则。结构化程序设计是过程式程序设计的一个子集,它对写入的程序使用逻辑结构使得理解和修改更有效更容易
(3)下面选项中,哪些是interface中合法方法定义?()
A. public void main(String [] args);
B. private int get Sum();
C.boolean setFlag(Boolean [] test);
D. public float get (int x);
答案:A,C,D
(4)下面哪些类实现或继承了Collection接口?
A.HashMap
B.ArrayList
C.Vector
D.Iterator
答案:B,C
4.2 编程题
题目描述:给定一个十进制数M,以及需要转换的进制数N。将十进制数M转化为N进制数
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
int m=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
if(m==0){
System.out.print("0");
return ;
}
boolean flag=false;
String str="0123456789ABCDEF";
StringBuilder sbu=new StringBuilder("");
if(m<0){
m=-m;
flag=true;
}
while(m>0){
int num=m%n;
m/=n;
sbu.append(str.charAt(num));
}
if(flag){
System.out.print("-");
}
str=sbu.toString();
for(int i=str.length()-1;i>=0;i--){
System.out.print(str.charAt(i));
}
}
}五、Day5
5.1 选择题
(1)以下代码结果是什么?
public class foo {
public static void main(String sgf[]) {
StringBuffer a=new StringBuffer("A");
StringBuffer b=new StringBuffer("B");
operate(a,b);
System.out.println(a+"."+b);
}
static void operate(StringBuffer x,StringBuffer y) {
x.append(y);
y=x;
}
}A.代码可以编译运行,输出“AB.AB”。
B.代码可以编译运行,输出“A.A”。
C.代码可以编译运行,输出“AB.B”。
D.代码可以编译运行,输出“A.B”.
答案:C
y是一个形参,拷贝了对象b,当指向改变后,并不会影响b的内容。
(2)下面代码的运行结果是()
public static void main(String []args){
String s;
System.out.pringln("s="+s);
}A.代码编译成功,并输出"s="
B.代码编译成功,并输出"s=null"
C.由于String s没有初始化,代码不能编译通过
D.代码编译成功,但捕获到NullPointExecption异常
C
(3)在 Java7中,下列不能做switch()的参数类型是?
A.int型
B.枚举类型
C.字符串
D.浮点型
答案:D
float,double,long,boolean类型都不能作为switch的参数。
(3) 指出以下程序运行的结果是
public class Example{
String str=new String("good");
char[]ch={'a','b','c'};
public static void main(String args[]){
Example ex=new Example();
ex.change(ex.str,ex.ch);
System.out.print(ex.str+" and ");
System.out.print(ex.ch);
}
public void change(String str,char ch[]){
//引用类型变量,传递的是地址,属于引用传递。
str="test ok";
ch[0]='g';
}
}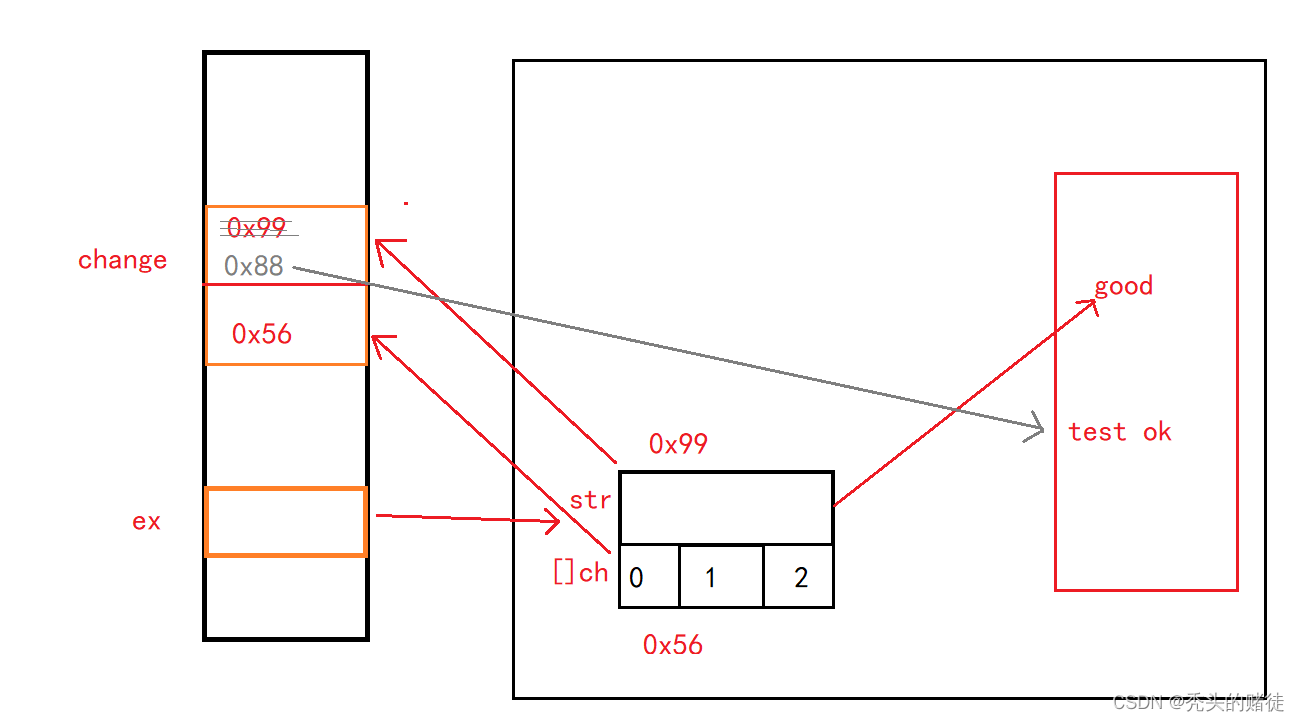
答案:good and gbc
在change函数栈帧中,change中的str指向别的地址,但并不影响ex栈帧中str的指向。而在两个函数栈帧中的数组是同一个地址,change改变0下标会导致ex栈帧中的0下标数值也改变。
(4)下列有关java异常处理的叙述中正确的是()
A.finally是为确保一段代码不管是否捕获异常都会被执行的一段代码
B.throws是用来声明一个成员方法可能抛出的各种非运行异常情况
C.final用于可以声明属性和方法,分别表示属性的不可变及方法的不可继承
D.throw是用来明确地抛出一个异常情况
答案:C
final修饰方法表示方法不可重写。
(5)以下代码返回值是什么?
public boolean returnTest(){
try{
return true;
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
return false;
}
}
答案:false
首先会返回true;但由于finally中的语句一定会执行,最终返回fals将true覆盖。
5.2 编程题
public class Main {
public static int getmax(int a,int b){
return a>b?a:b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
int []array=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
array[i]=in.nextInt();
}
int max=array[0];
int sum=array[0];
for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
sum=getmax(sum+array[i],array[i]);
if(sum>max){
max=sum;
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
}状态方程 dpi[i]=getMax(dpi[i]+array[i],array[i];
dpi[i]表示以i为结尾的子序列和






















 2810
2810

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








