一、数组
注意
- 数组元素在内存中是顺序、连续储存的。
- 使用数组名传递数据时,传递的是地址。
- 声明一个一维对象数组的语法形式:类名 数组名[ 常量表达式 ];指定初始值,例如:
Location a[3]={Location(1, 2), Location(3, 4)};
//没有指定数组元素的初始值,就会调用默认构造函数vector
vector 不是一个类,而是一个类模板。用vector定义动态数组的形式如下:
vector<元素类型> 数组对象名(数组长度); 例如: int x= 10; vector<int>arr (x); //大小为10的int型数组对象arr
注意
- 初始化:普通数组未被初始化时,它的元素将具有不确定的值;vector创建了动态数组,并且在指定了大小的情况(或初始化列表)下,如果是 int型--->全初始化为0;类类型--->调用其默认构造函数。
- 初值也可以自己指定,但只能为所有元素指定相同初值,形式为:
vector<元素类型>数组对象名(数组长度,初值)例:
逆序:调用库函数


二、指针
空指针---nullptr
函数指针:

例如:


new delete 与 malloc free 区别
- 构造函数与析构函数:new 和 delete 操作符会自动调用对象的构造函数和析构函数 ;malloc 和 free 只是简单地分配和释放内存,不会调用任何构造函数或析构函数。
- 类型转换:new 操作符则直接返回指向已分配内存并初始化的适当类型的指针,因此不需要类型转换;malloc 返回的是一个 void* 类型的指针,它表示未定义类型的内存块。因此,你需要将它转换为适当的类型才能使用。
- 关键字与函数:new 和 delete 是C++中的关键字,它们由C++编译器直接支持,并具有特殊的语法和行为;malloc 和 free 则是C语言的标准库函数,通过包含头文件 <cstdlib> 来使用。

new创建:
int new(10) --- 默认创建一个,初始化为10; ( ) ---> 初始化
int new[10] --- [ ]指定创建10个,未初始化。 [ ] ---> 创建个数
new delete:

lamda表达式
[](){}; --> 短小函数就地编写
[capture](arguement){body} == [捕获](形参){函数体}



三、字符串
例子:
append 追加字符串//扩容

this 版本 
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String
{
public:
String(const char *p) : m_p(new char[strlen(p) + 1])
{
strcpy(m_p,p);
}
void show() const
{
cout << m_p << endl;
}
void append(const char *p)
{
char *q = new char[strlen(m_p)+strlen(p)+1];
strcpy(q,m_p);//strcpy(q,this->m_p);
strcat(q,p);
delete []m_p;
m_p = q;
}
void append(const String &other)
{
char *p = new char[strlen(this->m_p)+strlen(other.m_p)+1];
strcpy(p,this->m_p);//hello
strcat(p,other.m_p);//world
delete []this->m_p;
this->m_p = p;
}
size_t length() const
{
return strlen(m_p);
}
private:
char *m_p;
};
int main(void)
{
// String s("Hello");
// s.show();
// cout << s.length() << endl;
// s.append(" World");
// s.show();
// cout << s.length() << endl;
// return 0;
String a("Hello");
String p(" World");
a.show();
cout << a.length() << endl;
a.append(p);
a.show();
cout << a.length() << endl;
return 0;
}

assign 修改字符串

this 版本

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String
{
public:
String(const char *p) : m_p(new char[strlen(p) + 1])
{
strcpy(m_p,p);
}
void show() const
{
cout << m_p << endl;
}
void assign(const char *p)
{
char *q = new char[strlen(p) + 1];
strcpy(q,p);
delete []m_p;
m_p = q;
}
void assign(const String &other)
{
if (this != &other)
{
char *q = new char[strlen(other.m_p)+1];
strcpy(q,other.m_p);
delete []this->m_p;
this->m_p = q;
}
}
size_t length() const
{
return strlen(m_p);
}
private:
char *m_p;
};
int main(void)
{
// String b("Hello");
// b.show();
// cout << b.length() << endl;
// b.assign("China!!!");
// b.show();
// cout << b.length() << endl;
String q("Hello");
String t("China!!!");
q.show();
cout << q.length() << endl;
q.assign(t);
q.show();
cout << q.length() << endl;
return 0;
}
代码总和
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String
{
public:
String(const char *p) : m_p(new char[strlen(p) + 1])
{
strcpy(m_p,p);
}
String(const String &other) : m_p(new char[strlen(other.m_p) + 1])
{
strcpy(this->m_p,other.m_p);
}
~String()
{
delete []m_p;
}
void show() const
{
cout << m_p << endl;
}
void append(const char *p)
{
char *q = new char[strlen(m_p)+strlen(p)+1];
strcpy(q,m_p);//strcpy(q,this->m_p);
strcat(q,p);
delete []m_p;
m_p = q;
}
void append(const String &other)
{
char *p = new char[strlen(this->m_p)+strlen(other.m_p)+1];
strcpy(p,this->m_p);//hello
strcat(p,other.m_p);//world
delete []this->m_p;
this->m_p = p;
}
void assign(const char *p)
{
char *q = new char[strlen(p) + 1];
strcpy(q,p);
delete []m_p;
m_p = q;
}
void assign(const String &other)
{
if (this != &other)
{
char *q = new char[strlen(other.m_p)+1];
strcpy(q,other.m_p);
delete []this->m_p;
this->m_p = q;
}
}
size_t length() const
{
return strlen(m_p);
}
private:
char *m_p;
};
int main(void)
{
// String s("Hello");
// s.show();
// cout << s.length() << endl;
// s.append(" World");
// s.show();
// cout << s.length() << endl;
// return 0;
// String a("Hello");
// String p(" World");
// a.show();
// cout << a.length() << endl;
// a.append(p);
// a.show();
// cout << a.length() << endl;
// String b("Hello");
// b.show();
// cout << b.length() << endl;
// b.assign("China!!!");
// b.show();
// cout << b.length() << endl;
String q("Hello");
String t("China!!!");
q.show();
cout << q.length() << endl;
q.assign(t);
q.show();
cout << q.length() << endl;
return 0;
}浅复制与深复制
浅复制:创建了一个新的对象,新对象中的某些成员只是简单地复制了原始对象中的指针值,即它们指向了内存中的相同位置。
深复制:不仅创建了一个新的对象,而且它还为原始对象中的每一个动态分配的内存块都分配了新的内存,并将原始数据复制到这些新的内存块中。这样,新对象和原始对象就完全独立了,对其中一个对象的修改不会影响到另一个对象。

链表
头插
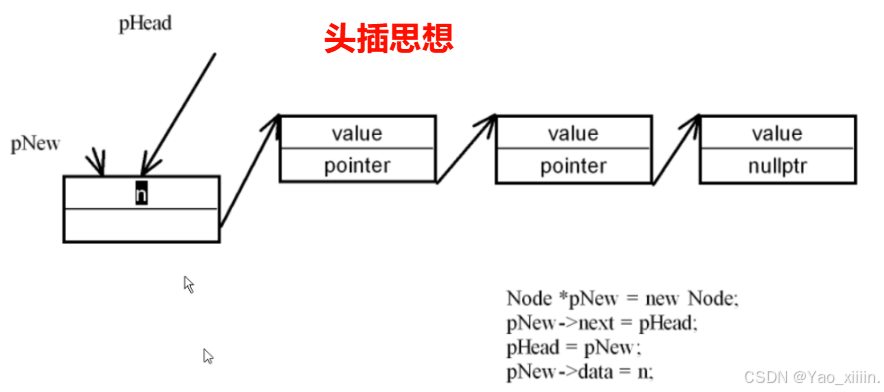
void push_front(int n)
{
Node *pNew = new Node(n);
pNew->next = pHead;
pHead = pNew;
}尾插
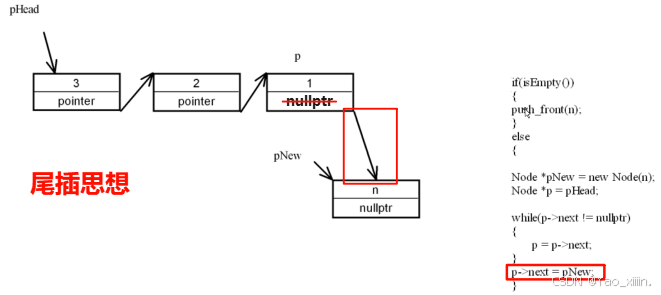
void push_back(int n)
{
if (isEmpty())
{
push_front(n);
}
else
{
Node *pNew = new Node(n);
Node *p = pHead;
while (p->next != nullptr)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = pNew;
}
}头删
void pop_front(void)
{
if (!isEmpty())
{
Node *p = pHead;
pHead = p->next;
delete p;
}
}尾删
void pop_back(void)
{
if (size() >= 2)
{
Node *p = pHead;
while (p->next->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
delete p->next;
p->next = nullptr;
}
else
{
pop_front();
}
}深复制
List(const List &other) : pHead(nullptr)//深复制
{
Node *p = other.pHead;
while (p != nullptr)
{
this->push_back(p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}代码总和
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct Node//类,默认共有
{
Node(int value = 0, Node *p = nullptr)
: data(value), next(p){}
int data;
Node* next;
};
class List//类,默认私有
{
public:
List():pHead(nullptr){}
List(const List &other) : pHead(nullptr)//深复制
{
Node *p = other.pHead;
while (p != nullptr)
{
this->push_back(p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
~List()
{
clear();
cout << "~list" << endl;
}
void clear(void)
{
while (!isEmpty())
{
pop_front();
}
}
void push_front(int n)
{
Node *pNew = new Node(n);
pNew->next = pHead;
pHead = pNew;
}
size_t size() const
{
size_t counter = 0;
Node *p = pHead;
while (p != nullptr)
{
counter++;
p = p->next;
}
return counter;
}
bool isEmpty() const
{
return pHead == nullptr;
}
void show() const
{
Node *p = pHead;
while (p != nullptr)
{
cout << p->data << ", ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "\b \n";//\b退格
}
void push_back(int n)
{
if (isEmpty())
{
push_front(n);
}
else
{
Node *pNew = new Node(n);
Node *p = pHead;
while (p->next != nullptr)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = pNew;
}
}
void pop_front(void)
{
if (!isEmpty())
{
Node *p = pHead;
pHead = p->next;
delete p;
}
}
void pop_back(void)
{
if (size() >= 2)
{
Node *p = pHead;
while (p->next->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
delete p->next;
p->next = nullptr;
}
else
{
pop_front();
}
}
private:
Node *pHead;
};
int main()
{
/*
//头插
List l;
cout << "size = "<< l.size() << endl;
cout << "isEmpty = " << l.isEmpty() << endl;
l.push_front(1);
l.push_front(2);
l.push_front(3);
l.show();
cout << "size = "<< l.size() << endl;
cout << "isEmpty = " << l.isEmpty() << endl;
//尾插
l.push_back(4);
l.push_back(5);
l.push_back(6);
l.show();
//头删
l.pop_front();
l.pop_front();
l.pop_front();
l.show();
//尾删
l.pop_back();
l.pop_back();
l.pop_back();
l.show();
cout << "isEmpty = " << l.isEmpty() << endl;
*/
List l1;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i)
{
l1.push_front(i);
}
l1.show();
cout << "size = "<< l1.size() << endl;
cout << "isEmpty = " << l1.isEmpty() << endl;
List l2(l1);
l2.show();
return 0;
}























 764
764

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








