1. 字符数组基础
(1) 定义与初始化
声明语法:`char s[100];`(容量100字节,含结尾`\0`)
初始化方式:
// 方式一:逐个字符初始化
char s1[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', '\0'}; // 需手动添加\0
// 方式二:字符串字面量初始化(自动补\0)
char s2[] = "hello"; // 等效 {'h','e','l','l','o','\0'} (2) 特殊字符辨析
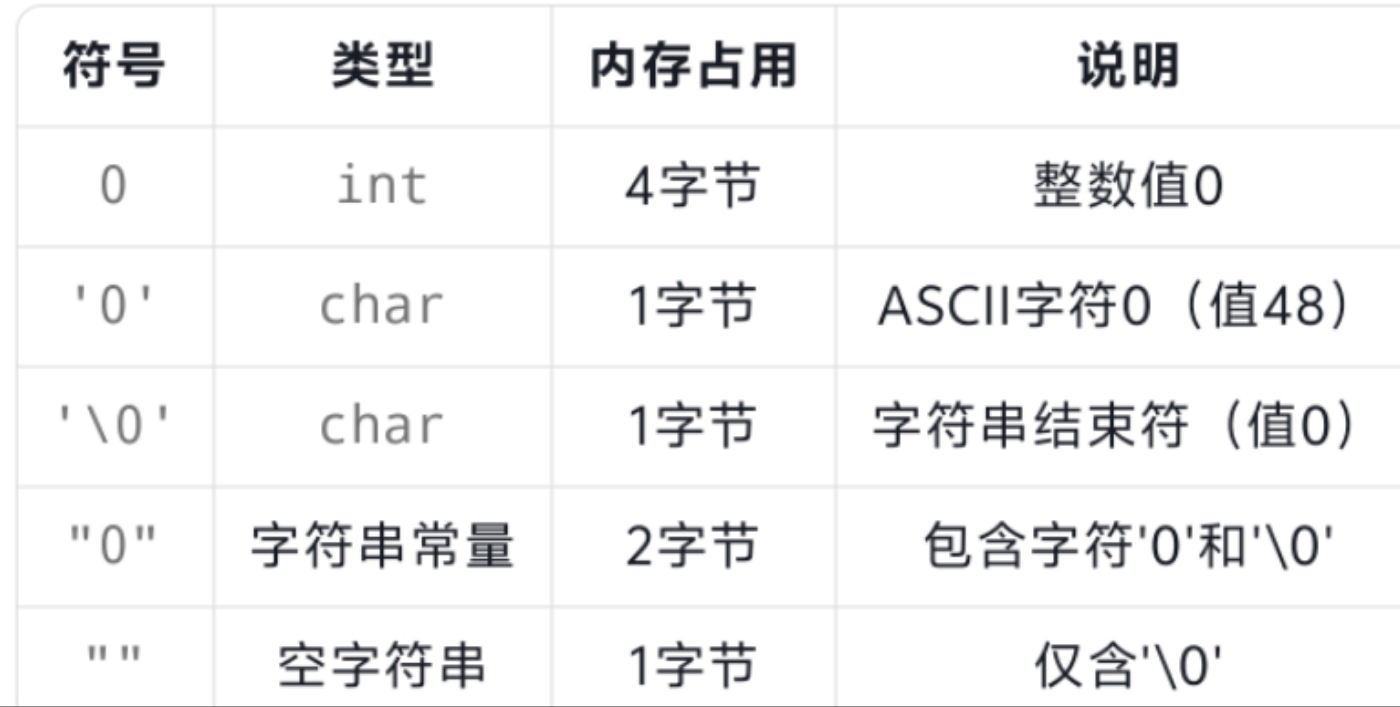
2. 字符数组输入输出
(1) 输出函数
`puts()`:输出字符串并自动换行
char s[] = "hello";
puts(s); // 输出 hello\n (2) 输入函数
`gets()`:
char s[10];
gets(s); // 输入超过9字符会导致缓冲区溢出 `fgets()`:
fgets(s, sizeof(s), stdin); // 最多读取sizeof(s)-1字符(保留\0)
// 示例:输入"abc\n" → s存储"abc\n\0"(输出时puts(s)显示abc后换两行)
3. 字符串处理函数
(1) 长度与容量
`strlen()`:返回字符串有效长度(不含`\0`)
char s[] = "hello";
int len = strlen(s); // len=5 `sizeof()`:返回数组总字节数(含`\0`)
char s[] = "hello";
int len = strlen(s); // len=5 (2) 字符串操作
`strcpy()`:字符串复制(需保证目标空间足够)
char src[] = "hello", dest[10];
strcpy(dest, src); // dest内容为"hello\0" `strcat()`:字符串拼接(目标缓冲区需足够大)
char s1[20] = "hello", s2[] = "world";
strcat(s1, s2); // s1变为"helloworld\0"
`strcmp()`:字符串比较(按ASCII码逐字符比较)
int ret = strcmp("apple", "banana");
// ret <0("apple" < "banana")
// ret=0(字符串相等)
// ret >0(左字符串大) 4. 常见问题与解决
缓冲区溢出:
char s[5];
strcpy(s, "hello world"); // 越界写入导致程序崩溃
预防:手动检查长度
5.基本算法与程序
(1)字符串数组遍历
//字符串数组遍历
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[100] = "Hello";
int i = 0;
while (s[i] != '\0')
{
putchar(s[i++]);
}
printf("\n");
puts(s);
return 0;
}
(2) 小写转大写
//小写转大写
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[100];
fgets(s, sizeof(s), stdin);
int i = 0;
while (s[i] != '\0') /* 原图写成了 while(s != '\0'),其实应该是 s[i] */
{
if (s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'z')
{
s[i] = s[i] - 32;
}
++i;
}
puts(s);
return 0;
}
(3) 有效字符个数
//有效字符个数
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[100] = "Hello World";
int counterer = 0; /* 原图里写了 counterer,但没用到 */
int i = 0;
while (s[i] != '\0')
{
++i;
}
printf("%d\n", i);
return 0;
}
(4) 字符串的拷贝
//字符串的拷贝
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello World!";
char s2[100];
int i = 0;
while (s1[i] != '\0')
{
s2[i] = s1[i];
++i;
}
s2[i] = '\0';
puts(s2);
return 0;
}
(5) 字符串的拼接(拷贝)
//字符串的拼接(拷贝)
#include <stdio.h>
// #include <string.h> /* 如果要用 strlen 或 sizeof 可以打开 */
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello";
char s2[100] = "World";
int i = 0, j = 0;
/* 找到 s1 的末尾 */
while (s1[i] != '\0')
{
++i;
}
/* 把 s2 接到 s1 后面 */
while (s2[j] != '\0')
{
s1[i] = s2[j];
++i;
++j;
}
s1[i] = '\0';
// printf("%d\n%d\n", sizeof(s1), strlen(s1)); /* 100 10 */
puts(s1);
return 0;
}
(6) 三字符串比较,取“最大”者
//三字符串比较,取“最大”者
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello";
char s2[100] = "World";
char s3[100] = "China";
char max[100];
if (strcmp(s1, s2) > 0)
{
strcpy(max, s1);
}
else
{
strcpy(max, s2);
}
if (strcmp(s3, max) > 0)
{
strcpy(max, s3);
}
puts(max);
return 0;
}
(7)字符串逆序
//字符串逆序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[100] = "Hello";
int len = strlen(s);
int i;
char t;
for (i = 0; i < len / 2; ++i)
{
t = s[i];
s[i] = s[len - i - 1];
s[len - i - 1] = t;
}
puts(s);
return 0;
}
6.总结
1. 字符数组本质:以`\0`结尾的字符序列
2. 安全输入:优先使用`fgets`避免缓冲区溢出
3. 函数选择:
长度计算 → `strlen`(逻辑长度) vs `sizeof`(物理容量)
字符串操作 → 严格检查目标空间大小
4. 嵌入式注意:内存有限时需精确控制字符数组长度























 1229
1229

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








