拷贝构造函数
1.定义
只有单个形参,该形参是对本类类型对象的引用(一般常用const修饰),在用已存在的类类型对象创建新对象时由编译器自动调用
2.特性
1.拷贝构造函数是构造函数的一个重载形式。
2. 拷贝构造函数的参数只有一个且必须是类类型对象的引用,使用传值方式编译器直接报错,
因为会引发无穷递归调用
3. 若未显式定义,编译器会生成默认的拷贝构造函数。 默认的拷贝构造函数对象按内存存储按
字节序完成拷贝,这种拷贝叫做浅拷贝,或者值拷贝。
4. 编译器生成的默认拷贝构造函数已经可以完成字节序的值拷贝了
eg:
class Date
{
public:
//全缺省构造函数
Date(int year = 1 ,int month = 1, int day = 1 )
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
无参构造函数
//Date()
//{
// _year = 2023;
// _month = 4;
// _day = 17;
//}
//拷贝构造
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
private:
//内置类型
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
//自定义类型
Time _t;
};
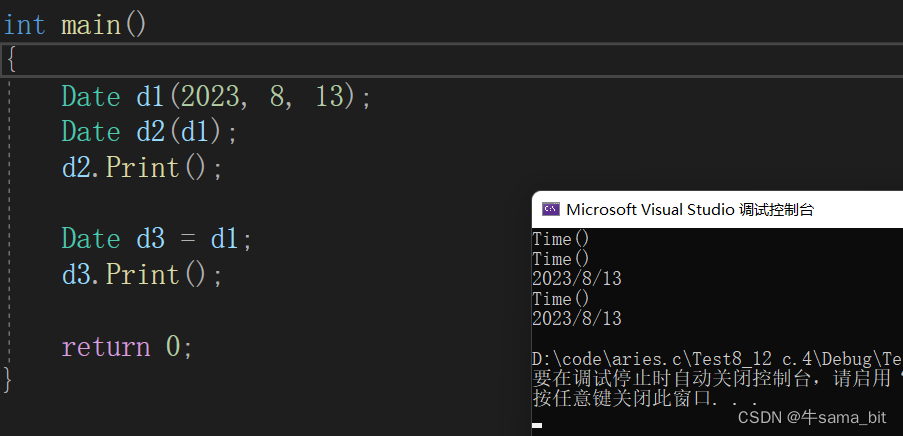
int main()
{
Date d1(2023, 8, 13);
Date d2(d1);
d2.Print();
Date d3 = d1;
d3.Print();
return 0;
}
有关值传递Date(const Date d)引发无穷递归调用的图解:

3.默认拷贝函数
若未显式定义,编译器会生成默认的拷贝构造函数。 默认的拷贝构造函数对象按内存存储按
字节序完成拷贝,这种拷贝叫做浅拷贝,或者值拷贝。
using namespace std;
class Time
{
public:
Time()
{
cout << "Time()" << endl;
_hour = 1;
_minute = 1;
_second = 1;
}
Time(const Time& t)
{
_hour = t._hour;
_minute = t._minute;
_second = t._second;
}
private:
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
};
class Date
{
public:
//全缺省构造函数
Date(int year = 1 ,int month = 1, int day = 1 )
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
无参构造函数
//Date()
//{
// _year = 2023;
// _month = 4;
// _day = 17;
//}
//拷贝构造
//Date(const Date& d)
//{
// _year = d._year;
// _month = d._month;
// _day = d._day;
//}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
private:
//内置类型
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
//自定义类型
Time _t;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(2023, 8, 13);
Date d2(d1);
d2.Print();
/*Date d3 = d1;
d3.Print();*/
return 0;
}

对于内置类型成员,全部拷贝出相同的的d1值,对于Time_t自定义类型的,会跳转到Time类中调用Time类的拷贝构造
4.深浅拷贝
深拷贝eg:
typedef int DataType;
class Stack
{
public:
Stack(size_t capacity = 10)
{
_array = (DataType*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (nullptr == _array)
{
perror("malloc申请空间失败");
return;
}
_size = 0;
_capacity = capacity;
}
void Push(const DataType& data)
{
// CheckCapacity();
_array[_size] = data;
_size++;
}
~Stack()
{
if (_array)
{
free(_array);
_array = nullptr;
_capacity = 0;
_size = 0;
}
}
private:
DataType* _array;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
int main()
{
Stack s1;
s1.Push(1);
s1.Push(2);
s1.Push(3);
s1.Push(4);
Stack s2(s1);
return 0;
}
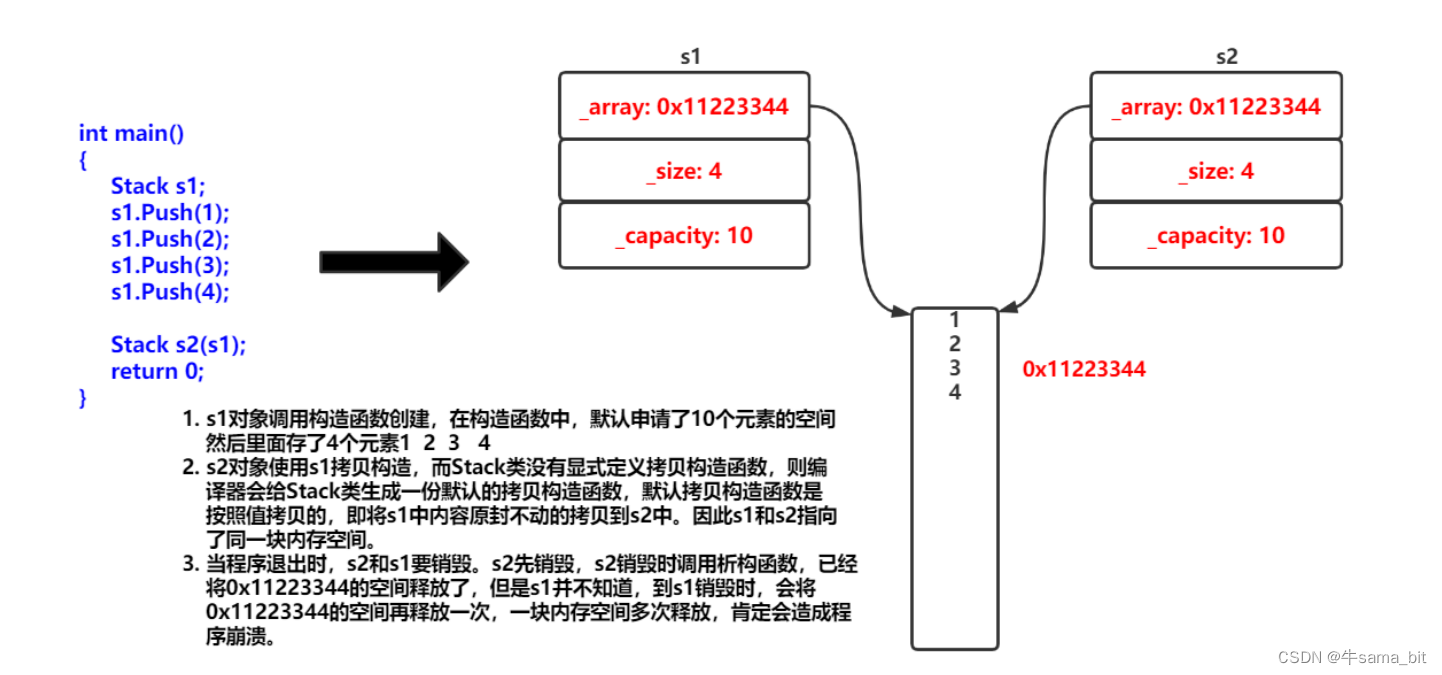
程序调用析构函数,会先析构s2,第一次析构完成后,s2._array指向的空间会被释放,其他置为0,也就是等价于s1._array指向的空间也被释放(同一块空间),此时再执行s1的析构函数时,原本释放的空间会被再一次free,就会报错。这时候就需要我们自己写一个拷贝构造函数了
注意:类中如果没有涉及资源申请时,拷贝构造函数是否写都可以;一旦涉及到资源申请时,则拷贝构造函数是一定要写的,否则就是浅拷贝。
正解:
typedef int STDateType;
class Stack
{
public:
Stack(size_t capacity = 4)
{
cout << "Stack()" << endl;
_array = (STDateType*)malloc(sizeof(STDateType) * capacity);
if (_array == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
_capacity = capacity;
_size = 0;
}
void Push(STDateType x)
{
//CheckCapacity()
_array[_size++] = x;
}
//拷贝函数
Stack(const Stack& s)
{
_array = (STDateType*)malloc(sizeof(STDateType) * s._capacity);
if (_array == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
memcpy(_array, s._array, sizeof(STDateType) * s._size);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
//析构函数
~Stack()
{
cout << "~Stack()" << endl;
free(_array);
_array = nullptr;
_capacity = _size = 0;
}
private:
STDateType* _array;
int _capacity;
int _size;
};




















 7009
7009











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








