目录
一. 二叉搜索树
1.1 二叉搜索树的概念
二叉搜索树是在普通的二叉树上进阶的,所以咱们今天的内容也可以说是,数据结构二叉树的进阶。二叉搜索树可谓是起到了承上启下的作用,向前承接了数据结构的二叉树,向后对于map和set的模拟实现也起到了启示作用。
那什么是二叉搜索树呢?

我们对于具有以下特征的二叉树为二叉搜索树:
- 若左子树不为空,则左子树所有节点的值比根节点的值小
- 若右子树不为空,则右子树所有节点的值比根节点的值大
- 左右子树都是二叉搜索树
1.2 二叉搜索树的常用操作以及实现
1.2.1 二叉搜索树的查找操作
查找操作要求我们从跟开始找,如果要找的值小于根节点的值,则走左子树,反之走右子树。
那么我们的实现就可以分为非递归写法和递归写法:
(1)非递归写法:
//非递归写法
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}(2)递归写法:
//递归写法
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if(root->_key>key)
{
_FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if(root->_key<key)
{
_FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}1.2.2 二叉搜索树的插入操作:
如果树为空的话,只需要新增一个节点,赋值给根节点,如果不为空,则先找到该插入的位置,再插入。
(1)非递归写法:
//非递归写法
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}(2)递归写法:
//递归写法
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)//注意引用
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}此处对于形参root指针的引用可谓是妙到了极点。在我们递归过程中,当找到了该插入的位置时,令root等于新插入的节点,而我们上一层递归加引用则表示上一层递归根节点的左子树或者右子树等于新插入的节点,就不用再去考虑插入的节点与父辈节点之间的连接。
1.2.3 二叉搜索树的删除操作:
首先应该查找要删除的节点在不在,若在则可分为下面四种情况:
- 无左右子树
- 只有左子树
- 只有右子树
- 左右子树均存在
那我们来看看该如何实现这几种情况,其实第一种情况可以跟第二和第三种情况合并,那么就剩下三种情况:
对于只有左子树或只有右子树这两种情况,只需删除该节点,再根据删除的节点与父节点之间的连接关系来连接父节点与子节点的关系。
而对于左右子树都有的情况:我们则需要找到右子树中的最小节点,用来替换删除的该节点。

(1)非递归写法:
//非递归写法
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (!Find(key))
{
return false;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
//替换法找右子树最小的元素
Node* rightminparent = cur;
Node* rightmin = cur->_right;
while (rightmin->_left)
{
rightminparent = rightmin;
rightmin = rightmin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightmin->_key;
if (rightmin == rightminparent->_left)
{
rightminparent->_left = rightmin->_right;
}
else//当cur是根节点的时候,即while循环都没进去
{
rightminparent->_right = rightmin->_right;
}
delete rightmin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}(2)递归写法:
//递归写法
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
Node* rightmin = root->_right;
while (rightmin->_left)
{
rightmin = rightmin->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, rightmin->_key);//目的是把他转换为叶子
return _EraseR(root->_right,key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}二. 二叉搜索树的应用
2.1 K模型
K模型即只存储关键码Key,根据关键码就能找到节点。上面的操作都是K模型下的操作。
我们整体看一下K模型的代码:
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
Node* _left;
Node* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
Destory(_root);
}
//非递归写法
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
//非递归写法
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//非递归写法
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (!Find(key))
{
return false;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
//替换法找右子树最小的元素
Node* rightminparent = cur;
Node* rightmin = cur->_right;
while (rightmin->_left)
{
rightminparent = rightmin;
rightmin = rightmin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightmin->_key;
if (rightmin == rightminparent->_left)
{
rightminparent->_left = rightmin->_right;
}
else//当cur是根节点的时候,即while循环都没进去
{
rightminparent->_right = rightmin->_right;
}
delete rightmin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
//递归写法
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return ;
}
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key<<" ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
//递归写法
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if(root->_key>key)
{
_FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if(root->_key<key)
{
_FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
//递归写法
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)//注意引用
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//递归写法
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
Node* rightmin = root->_right;
while (rightmin->_left)
{
rightmin = rightmin->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, rightmin->_key);//目的是把他转换为叶子
return _EraseR(root->_right,key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* newnode = new Node(root->_key);
newnode->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newnode->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return newnode;
}
void Destory(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return ;
}
Destory(root->_left);
Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* _root;
};2.2 KV模型
KV模型就是需要存储一个键值对<Key,Value>,对于每一个Key,都有对应的Value。
我们同样也来看一下KV模型的整体代码:
template<class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K,V> Node;
Node* _left;
Node* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key,const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
,_value(value)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K,V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key,value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key,value);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (!Find(key))
{
return false;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->left = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->left = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
//替换法找右子树最小的元素
Node* rightminparent = cur;
Node* rightmin = cur->_right;
while (rightmin->_left)
{
rightminparent = rightmin;
rightmin = rightmin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightmin->_key;
if (rightmin == rightminparent->_left)
{
rightminparent->_left = rightmin->_right;
}
else//当cur是根节点的时候
{
rightminparent->_right = rightmin->_right;
}
delete rightmin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key<<" ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root=nullptr;
};三. 二叉搜索树的性能分析
对于比较完美的搜索树,比如下图左边这种情况:
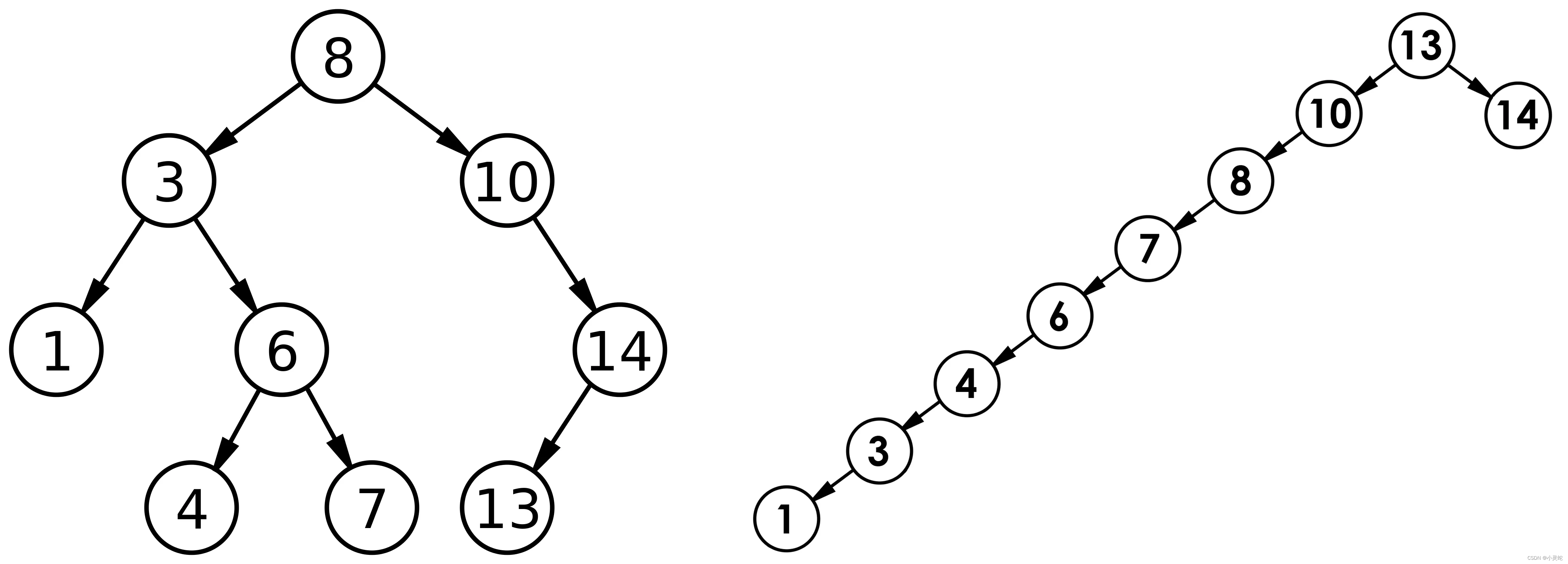
这种时间复杂度是O(logN)的。
而对于右边的这种极端情况,时间复杂度是O(N)的。
总结
好了,到这里今天的知识就讲完了,大家有错误一点要在评论指出,我怕我一人搁这瞎bb,没人告诉我错误就寄了。
祝大家越来越好,不用关注我(疯狂暗示)























 4万+
4万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








