MQTT(MQ Telemetry Transport)是一种消息传递协议,创建该协议是为了满足对向低功耗设备(如工业应用中使用的设备)传输数据的简单而轻量级方法的需求。
随着物联网(IoT)设备的日益普及,MQTT的使用也在增加,导致其被OASIS和ISO标准化。
该协议支持单一的消息传递模式,即发布-订阅模式:客户端发送的每条消息都包含一个相关的“主题”,代理使用该主题将其路由到订阅的客户端。主题名称可以是像“oiltemp”这样的简单字符串,也可以是像字符串“motor/1/rpm”这样的路径。

为了接收消息,客户端使用一个或多个主题的确切名称或包含支持的通配符之一的字符串(“#”表示多级主题,“+”表示单层主题)订阅一个或更多个主题。
安装mosquitto:
- 安装完成, 检查服务:

2修改文件: mosquitto.conf 追加2如下2行:
listener 1883 127.0.0.1
allow_anonymous true
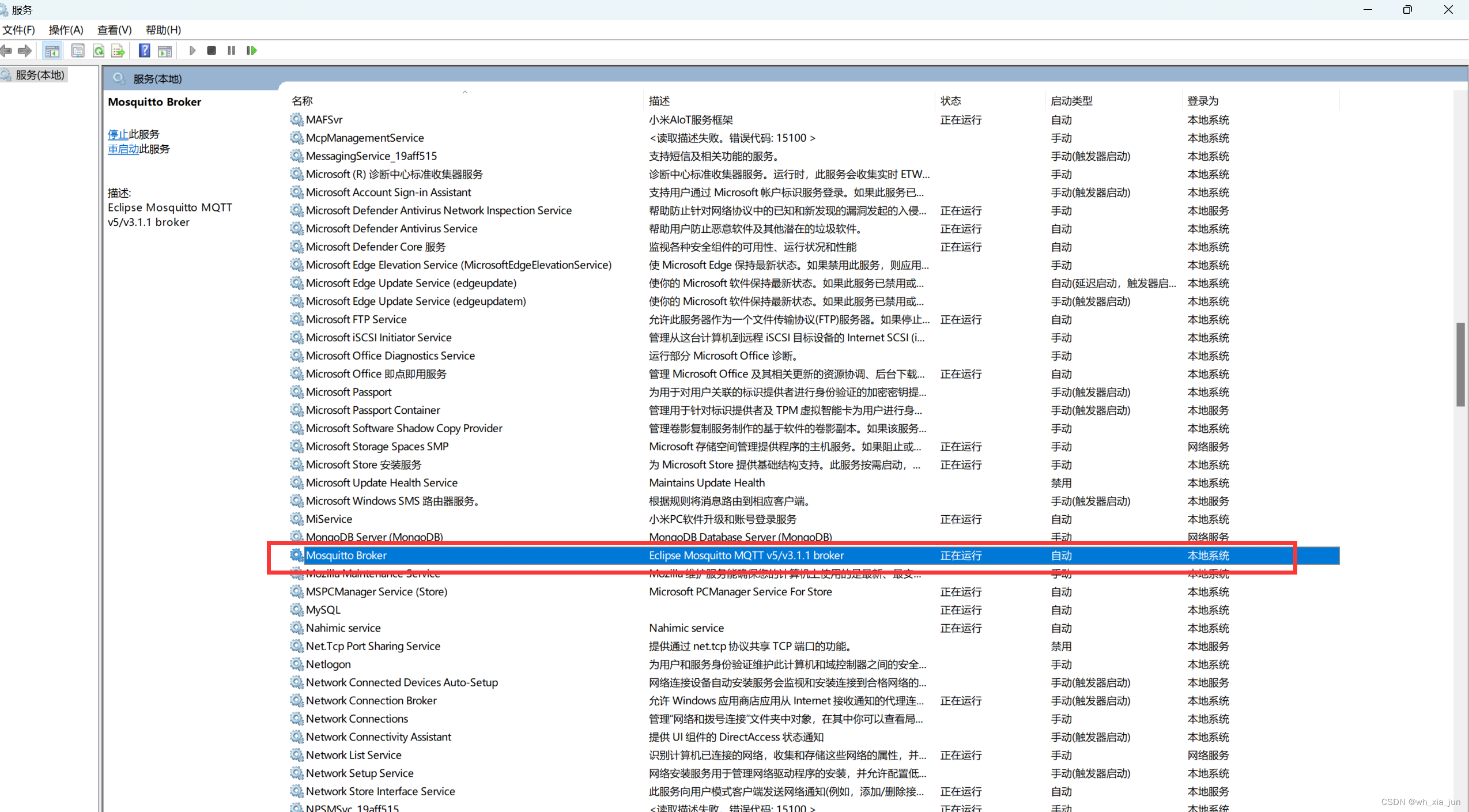
3、部署完后重启下mqtt服务,win+r后输入services.msc找到Mosquitto Broker点击重启动即可。
- 启动mqtt 服务
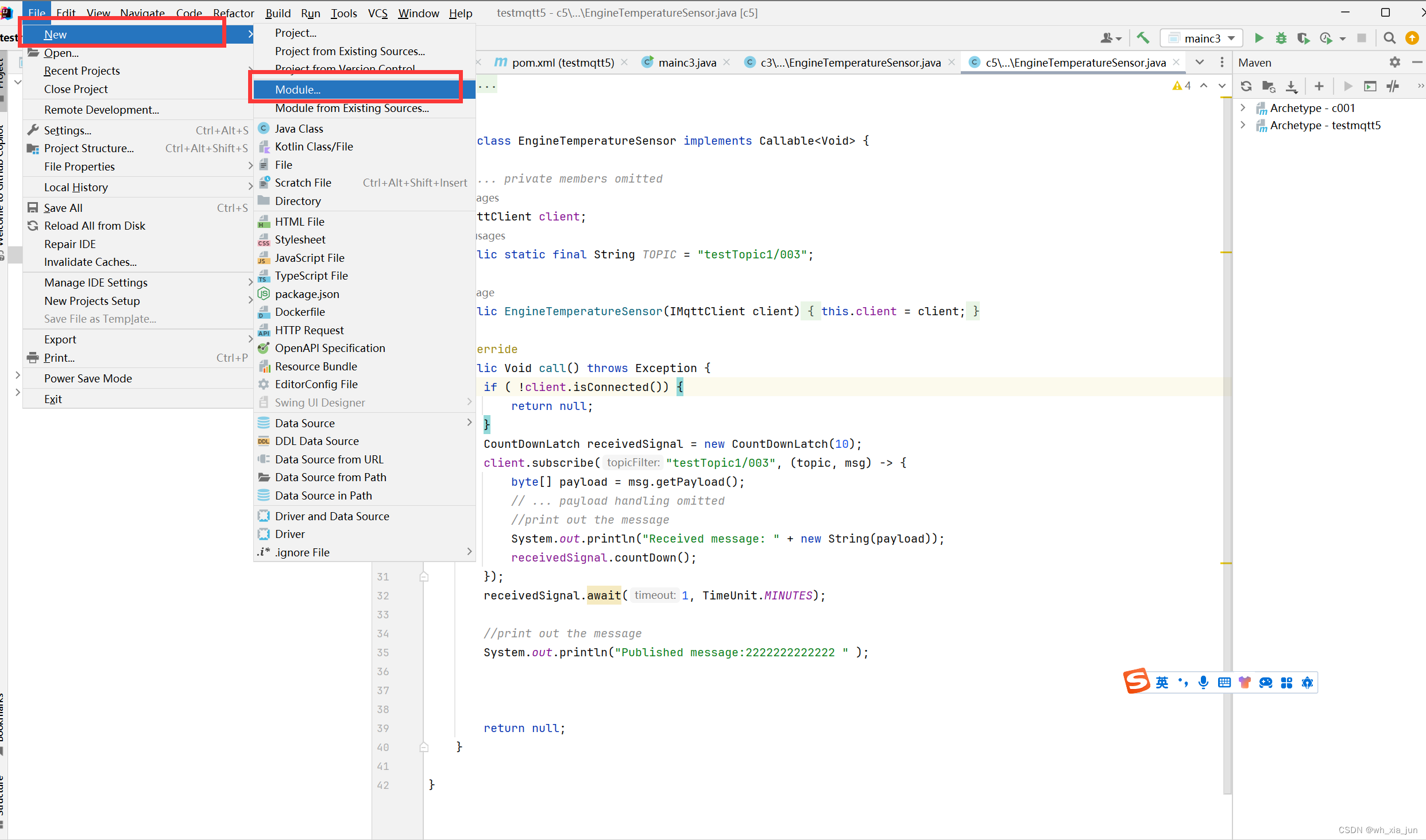
- 创建项目,在项目中添加模块
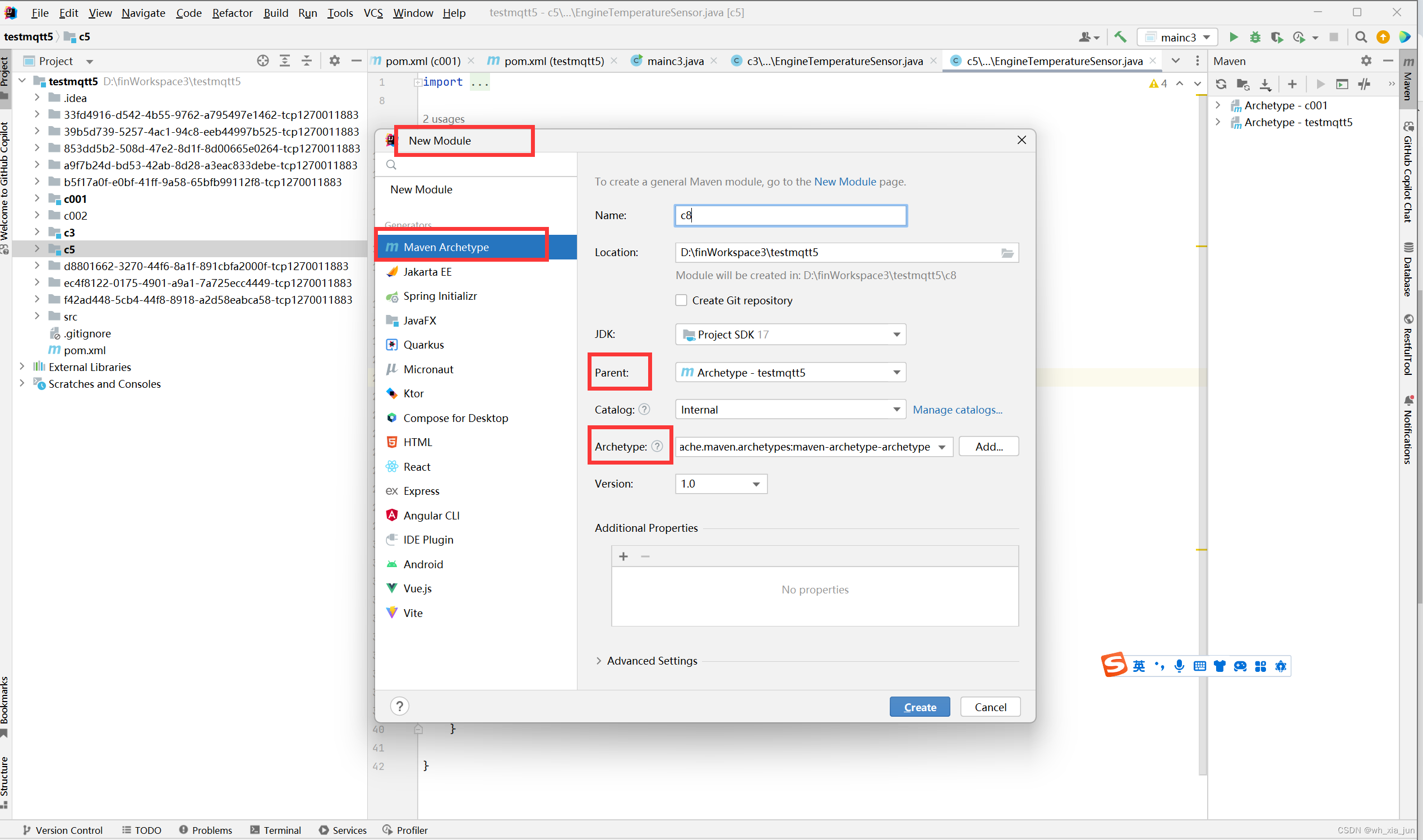
- 添加文件夹

 添加maven依赖
添加maven依赖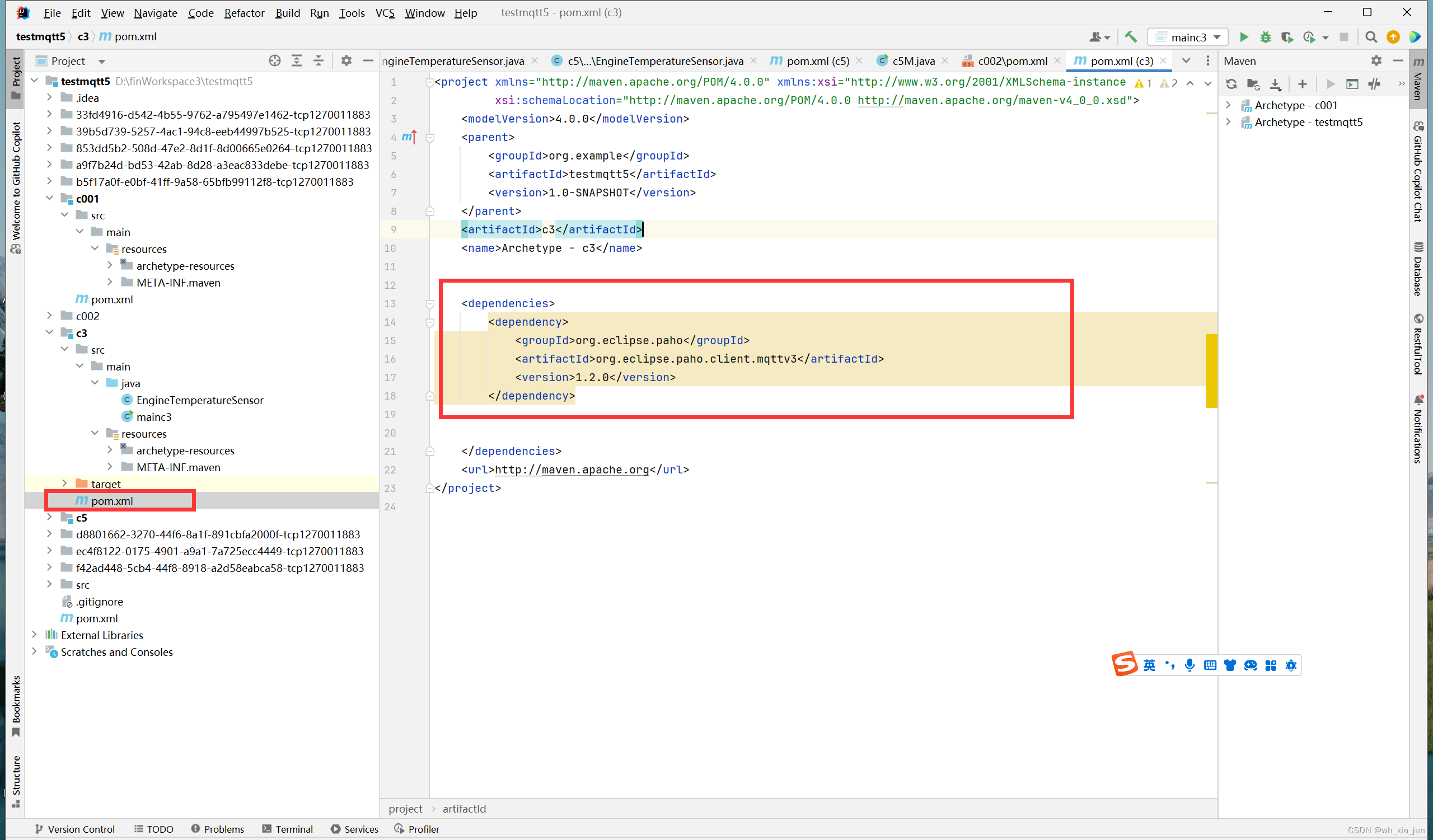
- 添加依赖:
-
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.paho</groupId> <artifactId>org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3</artifactId> <version>1.2.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
当使用Paho库时,为了从MQTT代理发送和/或接收消息,我们需要做的第一件事是获得IMqttClient接口的实现。此接口包含应用程序建立与服务器的连接、发送和接收消息所需的所有方法。
Paho提供了该接口的两种实现,一种是异步实现(MqttAsyncClient),另一种是同步实现(MqttClient)。在我们的案例中,我们将重点关注同步版本,它具有更简单的语义。
设置本身是一个分两步的过程:我们首先创建MqttClient类的一个实例,然后将其连接到服务器。以下小节详细介绍了这些步骤。
客户端设置(Client Setup)
创建新的实例(Creating a New IMqttClient Instance):
String publisherId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
IMqttClient publisher = new MqttClient("tcp://127.0.0.1:1883", publisherId);
在这种情况下,我们使用可用的最简单的构造函数,它获取MQTT代理的端点地址和唯一标识我们的客户端的客户端标识符。
在我们的例子中,我们使用了一个随机的UUID,因此每次运行都会生成一个新的客户端标识符。
连接服务(Connecting to the Server)
我们新创建的MqttClient实例没有连接到服务器。我们通过调用其connect()方法来实现这一点,并可选地传递一个MqttConnectOptions实例,该实例允许我们自定义协议的某些方面。
特别是,我们可以使用这些选项来传递附加信息,如安全凭据、会话恢复模式、重新连接模式等。
MqttConnectionOptions类将这些选项公开为简单的属性,我们可以使用普通的setter方法设置这些属性。我们只需要设置场景所需的属性——剩下的属性将采用默认值。
用于建立与服务器连接的代码通常如下所示:
MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions();
options.setAutomaticReconnect(true);
options.setCleanSession(true);
options.setConnectionTimeout(10);
publisher.connect(options);在这里,我们定义了连接选项,以便:
发生网络故障时,库将自动尝试重新连接到服务器
它将丢弃上一次运行中未发送的消息
连接超时设置为10秒
发布(Sending Messages)
使用已连接的MqttClient发送消息非常简单。我们使用publish()方法变体之一,使用以下服务质量选项之一,将始终是字节数组的有效载荷发送到给定的主题:
0–“最多一次”语义,也称为“即发即弃”。当消息丢失是可以接受的,因为它不需要任何类型的确认或持久性时,请使用此选项
1–“至少一次”语义。当邮件丢失是不可接受的并且您的订阅者可以处理重复邮件时,请使用此选项
2–“恰好一次”语义。当邮件丢失是不可接受的并且您的订阅者无法处理重复邮件时,请使用此选项
在我们的示例项目中,EngineTemperatureSensor类扮演模拟传感器的角色,每次我们调用它的call()方法时,它都会产生新的温度读数。

这个类实现了Callable接口,因此我们可以很容易地将其与java.util.concurrent包中的一个ExecutorService实现一起使用:
public class EngineTemperatureSensor implements Callable<Void> {
// ... private members omitted
public EngineTemperatureSensor(IMqttClient client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
public Void call() throws Exception {
if ( !client.isConnected()) {
return null;
}
MqttMessage msg = readEngineTemp();
msg.setQos(0);
msg.setRetained(true);
client.publish(TOPIC,msg);
return null;
}
private MqttMessage readEngineTemp() {
double temp = 80 + rnd.nextDouble() * 20.0;
byte[] payload = String.format("T:%04.2f",temp)
.getBytes();
return new MqttMessage(payload);
}
}MqttMessage封装了有效负载本身、请求的服务质量以及消息的保留标志。此标志向代理指示它应该保留此消息,直到被订阅者使用为止。
订阅(Receiving Messages)
为了从MQTT代理接收消息,我们需要使用subscribe()方法变体之一,它允许我们指定:
我们要接收的消息的一个或多个主题筛选器
相关的QoS
用于处理接收到的消息的回调处理程序
在下面的示例中,我们展示了如何将消息侦听器添加到现有的IMqttClient实例中,以接收来自给定主题的消息。我们使用CountDownLatch作为回调和主执行线程之间的同步机制,每次新消息到达时都会递减。
在示例代码中,我们使用了不同的IMqttClient实例来接收消息。我们这样做只是为了更清楚地说明哪个客户端做什么,但这不是Paho的限制——如果您愿意,您可以使用同一个客户端发布和接收消息:
CountDownLatch receivedSignal = new CountDownLatch(10);
client.subscribe("testTopic1/003", (topic, msg) -> {
byte[] payload = msg.getPayload();
// ... payload handling omitted
//print out the message
System.out.println("Received message: " + new String(payload));
receivedSignal.countDown();
});
receivedSignal.await(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES);上面使用的subscribe()变量将IMqttMessageListener实例作为其第二个参数。
在我们的例子中,我们使用一个简单的lambda函数来处理有效载荷并递减计数器。如果在指定的时间窗口(1分钟)内没有足够的消息到达,await()方法将抛出异常。
在使用Paho时,我们不需要明确确认消息接收。如果回调正常返回,Paho会认为这是一次成功的消费,并向服务器发送一个确认。
MqttMessage封装了有效负载本身、请求的服务质量以及消息的保留标志。此标志向代理指示它应该保留此消息,直到被订阅者使用为止。
下面是相对完整代码:
-
- 编写订阅程序 名字没起好 后面有时间再调整
-
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttClient; import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttMessage; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class EngineTemperatureSensor implements Callable<Void> { // ... private members omitted IMqttClient client; public static final String TOPIC = "testTopic1/003"; public EngineTemperatureSensor(IMqttClient client) { this.client = client; } @Override public Void call() throws Exception { if ( !client.isConnected()) { return null; } CountDownLatch receivedSignal = new CountDownLatch(10); client.subscribe("testTopic1/003", (topic, msg) -> { byte[] payload = msg.getPayload(); // ... payload handling omitted //print out the message System.out.println("Received message: " + new String(payload)); receivedSignal.countDown(); }); receivedSignal.await(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES); //print out the message System.out.println("Published message:2222222222222 " ); return null; } } -
订阅:
-
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttClient; import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttMessage; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class EngineTemperatureSensor implements Callable<Void> { // ... private members omitted IMqttClient client; public static final String TOPIC = "testTopic1/003"; public EngineTemperatureSensor(IMqttClient client) { this.client = client; } @Override public Void call() throws Exception { if ( !client.isConnected()) { return null; } CountDownLatch receivedSignal = new CountDownLatch(10); client.subscribe("testTopic1/003", (topic, msg) -> { byte[] payload = msg.getPayload(); // ... payload handling omitted //print out the message System.out.println("Received message: " + new String(payload)); receivedSignal.countDown(); }); receivedSignal.await(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES); //print out the message System.out.println("Published message:2222222222222 " ); return null; } }
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttConnectOptions;
public class c5M {
//main5
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
String publisherId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
try {
IMqttClient subscriber = new MqttClient("tcp://127.0.0.1:1883", publisherId);
MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions();
options.setAutomaticReconnect(true);
options.setCleanSession(true);
options.setConnectionTimeout(10);
subscriber.connect(options);
// 调用EngineTemperatureSensor
EngineTemperatureSensor sensor = new EngineTemperatureSensor(subscriber);
executor.submit(sensor); // 提交任务,但不阻塞主线程
// 这里可以添加代码来等待用户输入或者其他信号来安全地关闭程序
// 例如,你可以使用System.in.read()来等待用户输入
System.out.println("Press Enter to exit...");
new Scanner(System.in).nextLine(); // 等待用户输入
} catch (Exception e) {
//print e message
//print seperator line
System.out.println("))))))))))))))))))))))))");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 确保最后关闭ExecutorService和MQTT客户端
executor.shutdown(); // 提交的任务将不再被接受
try {
// 等待任务完成(可选,取决于你是否需要确保所有任务都完成)
if (!executor.awaitTermination(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
executor.shutdownNow(); // 取消正在执行的任务
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
executor.shutdownNow(); // 当前线程被中断,需要关闭ExecutorService
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 保留中断状态
}
// 关闭MQTT客户端(如果有必要的话)
// 注意:这里可能需要额外的逻辑来处理MQTT客户端的关闭,具体取决于你的实现
}
}
}
发布代码:
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttMessage;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class EngineTemperatureSensor implements Callable<Void> {
// ... private members omitted
IMqttClient client;
public static final String TOPIC = "testTopic1/003";
public EngineTemperatureSensor(IMqttClient client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
public Void call() throws Exception {
if ( !client.isConnected()) {
return null;
}
Random rnd = null;
//double temp = 80 + rnd.nextDouble() * 20.0;
double temp = 10 + 1.1 * 20.0;
byte[] payload = String.format("T:%04.2f",temp)
.getBytes();
MqttMessage msg2= new MqttMessage(payload);
msg2.setQos(0);
msg2.setRetained(true);
client.publish(TOPIC,msg2);
//print out the message
System.out.println("Published message: " + msg2);
return null;
}
}import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttConnectOptions;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class mainc3 {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
String publisherId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
try {
IMqttClient publisher = new MqttClient("tcp://127.0.0.1:1883", publisherId);
MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions();
options.setAutomaticReconnect(true);
options.setCleanSession(true);
options.setConnectionTimeout(10);
publisher.connect(options);
// 调用EngineTemperatureSensor
EngineTemperatureSensor sensor = new EngineTemperatureSensor(publisher);
executor.submit(sensor); // 提交任务,但不阻塞主线程
// 这里可以添加代码来等待用户输入或者其他信号来安全地关闭程序
// 例如,你可以使用System.in.read()来等待用户输入
System.out.println("Press Enter to exit...");
new Scanner(System.in).nextLine(); // 等待用户输入
} catch (Exception e) {
//print e message
//print seperator line
System.out.println("))))))))))))))))))))))))");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 确保最后关闭ExecutorService和MQTT客户端
executor.shutdown(); // 提交的任务将不再被接受
try {
// 等待任务完成(可选,取决于你是否需要确保所有任务都完成)
if (!executor.awaitTermination(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
executor.shutdownNow(); // 取消正在执行的任务
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
executor.shutdownNow(); // 当前线程被中断,需要关闭ExecutorService
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 保留中断状态
}
// 关闭MQTT客户端(如果有必要的话)
// 注意:这里可能需要额外的逻辑来处理MQTT客户端的关闭,具体取决于你的实现
}
}
}





















 1021
1021

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








