I/O流
- File类——创建或删除文件等操作
-
- 初始化:File f=new File("d:\\test.txt"); 反斜杠可用File.separator常量代替,会根据不同环境而选择
- 创建:f.creatNewFile(); 需要try catch处理异常
- 删除:f.delete(); 最好用 f.exists()判断是否存在文件
- 文件夹:f.mkdir();
- 列出目录全部文件:String str[]= f.list();
- 列出带路径的目录下的文件:File files[]=f.listFiles();
- 判断文件是否是目录: f.isDirectory()
-
- RandomAccessFile类——随机读取文件指定位置的数据
-
- 写入数据
-
RandomAccessFile rdf=new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw"); //rw为读写,若不存在文件,则新建
rdf.writeBytes("zhangsan");
rdf.writeInt(10);
rdf.close(); //关闭文件- 读取数据
RandomAccessFile rdf=new RandomAccessFile(file,"r"); //以只读形式打开文件
byte b[]=new byte[8];
//rdf.skipBytes(12); //跳过字节
for(int i=0;i<b.length();i++)
b[i]=rdf.readByte(); //循环读取前8个内容
String name=new String(b);
rdf.close();- 字节流——主要操作byte数据
- OutputStream——抽象类
- 多态性实例化:OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file);
- 写入数据:out.write(byte b[]);
- 关闭输出流:out.close();
- 追加新内容:OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file,true); 使用"\r\n“增加换行
- InputStream
- 多态性实例化:InputStream input=new FileInputStream(file);
- 读入数据:byte b[]=new byte[(int)file.length()]; 开辟足够的空间 input.read(b);
- 判断文件是否读到末尾:temp=input.read()!=-1 若为-1则已到尾
- OutputStream——抽象类
- 字符流——一个字符=2个字节
- Writer
- 实例化:Writer out= new FileWriter(file);
- 输出:out.write(str);
- 追加内容:Writer out=new FileWriter(file,true);
- 可使用:out.flush() 来直接将缓存区的数据写入
- Reader
- 实例化:Reader in = new Reader(file);
- 读取:char[] c=new char[1024]; 一个一个字符来读取
- Writer
- 转换流——字符流与字节流的转换
- OutputStreamWriter:Writer的子类,将输出的字符流转为字节流
- InputStreamReader:Reader的子类,将输入的字节转为字符流
- 转换步骤
- 内部操作流——将内容写入内存中,主要是字节流,主要是都在内存中操作
- ByteArrayOutputStream:将内存的数据输出
- ByteArrayInputStream:将数据输入到内存
- 管道流——两个线程之间的通信
- 管道输出流(PipedOutputStream)
- 管道输入流(PipedInputStream)
- 如果需要管道输出,必须将输出流连在输入流上,PipedOutputStream pos=new PipedOutputStream(); pos.connect(pis);
- 打印流——打印任何数据
- 字节打印
- PrintStream:OutputStream的子类
- 装饰设计模式:PrintStream可接受OutputStream对象
- 字节打印
- System类对IO的支持
- 常量的命名不规范是java历史发展的产物
- System.out:是PrintStream的对象,所以能直接调用print()'println();
- System.err:如果程序出现错误,则可以输出,跟out有一样的功能,但在概念上最好分开使用
- System.in:从键盘获取输入流,是InputStream的对象
- 问题存在:输入数据不能超过所指定的数组长度 | 如果数组长度为奇数,则会导致中文乱码
- 输入输出重定向
- setOut\setErr:接受PrintStream对象
- setIn:接受InputStream对象
- BufferedReader:只能接受字符流的缓冲区,对于上面的System.in的问题给出如下解决方案
-
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String str=br.readLine();System.out.println(str);
- Scanner类——可以接受任意的输入流
- 分隔符默认为空格,可以使用useDelimiter("\n")设置为回车
- 从文件中获取数据
-
Scanner scan=new Scanner(file); StringBuffer str=new StringBuffer(); while(scan.hasNext()){ //判断是否还有内容 str.append(scan.next()).append("\n"); //去除内容 } System.out.println(str); - 数据操作流——与平台无关的数据操作流
- DataOutputStream
- 此类继承自FilterOutputStream,OutputStream的子类,同时也实现了DataOutput接口
- DataInputStream
- InputStream的子类
- 实例化:public DataInputStream(InputStream in)
- DataOutputStream
- 合并流——将两个文件的内容合并成一个文件
- SequenceInputStream
-
InputStream in1=new FileInputStream(new File("D:"+File.separator+"d.txt")); InputStream in2=new FileInputStream(new File("D:"+File.separator+"b.txt")); SequenceInputStream sis=new SequenceInputStream(in1,in2); //实例化合并流 OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(new File("D:"+File.separator+"c.txt")); int temp=0; while((temp=sis.read())!=-1){ os.write(temp); //写入新文本 } sis.close(); in1.close(); in2.close(); os.close();
- 压缩流——可将文件或文件夹压缩成ZIP、JAR、GZIP等
- ZipOutputStream类
- 能将一个文件或文件夹压缩
- ZipFile类
- 用来解压缩一个ZipEntry,不能解压缩文件夹
- ZipInputStream类——方便读取ZIP的压缩文件
-
File file=new File("d:"+File.separator+"c.zip"); File outFile=null; ZipFile zipFile=new ZipFile(file); ZipInputStream zipInput=new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); ZipEntry entry=null; InputStream input=null; OutputStream out=null; while((entry=zipInput.getNextEntry())!=null){ //可解压多个实体 System.out.println("解压缩"+ entry.getName()+"文件"); outFile=new File("d:"+File.separator+entry.getName()); input=zipFile.getInputStream(entry); out=new FileOutputStream(outFile); int temp=0; while((temp=input.read())!=-1){ out.write(temp); } input.close(); out.close(); }
- ZipOutputStream类
- 回退流——把读取进来的某些数据重新退回到输入流的缓冲区
- PushbackInputStream
-
String str="what,are,you,doing"; PushbackInputStream push=new PushbackInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes())); int temp=0; while((temp=push.read ())!=-1){ if(temp==','){ push.unread(temp); push.read(); }else{ System.out.print((char)temp); } }
- 字符编码
-
- ISO8859-1:属于单字节编码,只能表示0-255的字符范围,主要用与英文
- GBK/GB2321:中文的国标编码,专门用来表示汉字,可表示简体和繁体,GB2321只能表示简体
- unicode:最标准的16进制编码,不兼容ISO8859-1编码
- UTF:对于unicode的不方便,兼容ISO8859-1编码,每一个字符长度为1-6个字节不等,中文网站使用
- 乱码的产生:输出内容的编码与接受内容的编码不一致
-
- 对象序列化——把一个对象变为2进制的数据流
-
- Serializable接口:对象即可序列化,就是一个标志性的接口
- ObjectOutputStream:序列化操作,
- ObjectInputStream:反序列化操作
- 一个对象被序列化的只有属性
- 不可以让所有类都实现Serializble接口: 随着JDK的发展,可能会在此接口增加方法
- Externalizable接口——指定对象的内容可序列化
- 实现的类必须得有一个无参的构造方法,因为反序列化的时候会默认调用无参构造方法,否则将会出现异常
- 需覆写;
- public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException{}; 根据需要读取的内容,反序列化使用
- Serializable接口:对象即可序列化,就是一个标志性的接口
-
- public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException{}' 根据需要保存属性或具体内容,序列化使用
- transient关键字——某些属性不希望被序列化
- 可在属性前加:private transient String name;
-
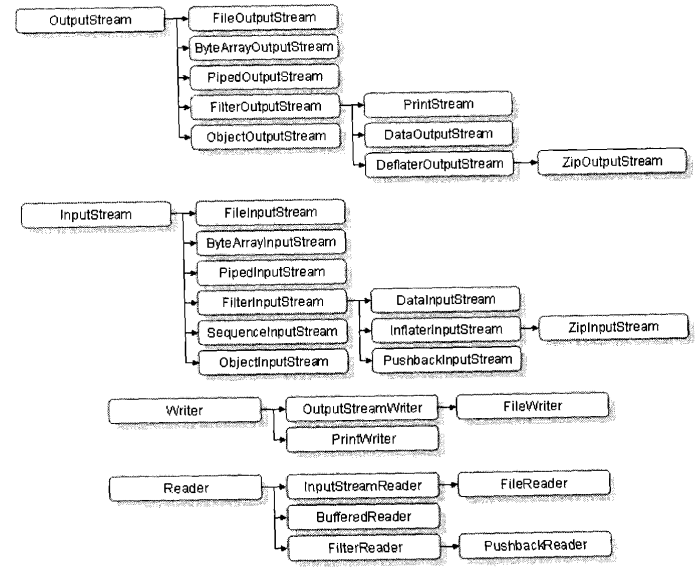
- 本章知识点

























 445
445

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








