二维整型矩阵Table [m][n]. 满足
Table[i][j] ≤ Table[i][j + 1],
Table[i][j] ≤ Table[i + 1][j]
在此中进行查找元素。
1.阶梯搜索
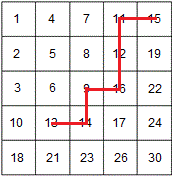
从右上角或者左下角开始,如下图红线所示的查找13的过程
bool stepWise(int mat[][N_MAX], int N, int target,
int &row, int &col) {
if (target < mat[0][0] || target > mat[N-1][N-1]) return false;
row = 0;
col = N-1;
while (row <= N-1 && col >= 0) {
if (mat[row][col] < target)
row++;
else if (mat[row][col] > target)
col--;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}时间复杂度O(m+n)。
2.分治法
取矩阵的中心,将其划分成如下四个部分
如果查21,由于21》9,所以黄色部分排除。
复杂度推导
T(n) = 3T(n/2) + c, = 3 [ 3T(n/4) + c ] + c = 3 [ 3 [ 3T(n/8) + c ] + c ] + c = 3k T(n/2k) + c (3k - 1)/2 = 3k ( T(n/2k) + c ) - c/2 Setting k = lg n, T(n) = 3lg n ( T(1) + c ) - c/2 = O(3lg n) = O(nlg 3) <== 3lg n = nlg 3 = O(n1.58)
代码:
bool quadPart(int mat[][N_MAX], int M, int N, int target, int l, int u, int r, int d, int &targetRow, int &targetCol) {
if (l > r || u > d) return false;
if (target < mat[u][l] || target > mat[d][r]) return false;
int col = l + (r-l)/2;
int row = u + (d-u)/2;
if (mat[row][col] == target) {
targetRow = row;
targetCol = col;
return true;
} else if (l == r && u == d) {
return false;
}
if (mat[row][col] > target) {
return quadPart(mat, M, N, target, col+1, u, r, row, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, l, row+1, col, d, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, l, u, col, row, targetRow, targetCol);
} else {
return quadPart(mat, M, N, target, col+1, u, r, row, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, l, row+1, col, d, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, col+1, row+1, r, d, targetRow, targetCol);
}
}
bool quadPart(int mat[][N_MAX], int N, int target, int &row, int &col) {
return quadPart(mat, N, N, target, 0, 0, N-1, N-1, row, col);
}3.二分查找
用下面的方法可以将查找范围缩小到剩余的两部分。
ai < s < ai+1 , where ai is the ith traversed cell.
If the target element equals one of the traversed cells, we immediately return the element as found. Otherwise we partition the matrix into two sub-matrices following the partition point we found. As it turns out, we need cn time (linear time) to find such partition point, since we are essentially performing a linear search. Therefore, the complexity could be written as the following recurrence relation: (Note: I omitted the proof, as it is left as an exercise to the reader. )
复杂度:
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + cn = O(n lg n)
bool binPart ( int mat [ ] [ N_MAX ] , int M , int N , int target , int l , int u , int r , int d , int & targetRow , int & targetCol ) {if ( l > r || u > d ) return false ;if ( target < mat [ u ] [ l ] || target > mat [ d ] [ r ] ) return false ;int mid = l + ( r - l ) / 2 ;int row = u ;while ( row <= d && mat [ row ] [ mid ] <= target ) {if ( mat [ row ] [ mid ] == target ) {targetRow = row ;targetCol = mid ;return true ;}row ++ ;}return binPart ( mat , M , N , target , mid + 1 , u , r , row - 1 , targetRow , targetCol ) ||binPart ( mat , M , N , target , l , row , mid - 1 , d , targetRow , targetCol ) ;}bool binPart ( int mat [ ] [ N_MAX ] , int N , int target , int & row , int & col ) {return binPart ( mat , N , N , target , 0 , 0 , N - 1 , N - 1 , row , col ) ;}




























 644
644

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








