鸿蒙NEXT开发实战往期必看文章:
一分钟了解”纯血版!鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next应用开发!
“非常详细的” 鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next应用开发学习路线!(从零基础入门到精通)
HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发案例实践总结合(持续更新......)
HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发性能优化实践总结(持续更新......)
1. HTTP上传文件简介
在上一篇文章使用HttpRequest下载文件到本地示例中,我们使用HttpRequest下载了文件,同样,使用HttpRequest也可以上传文件,假设我们有一个网站,其文件上传地址为http://192.168.100.101:8081/upload,为简单起见,该网站不需要登录既可以上传文件,当然,需要的登录话也没什么,参考上一篇文章即可。本文将模拟文件上传的功能,开发鸿蒙应用客户端把文件上传到服务端,为减少复杂性,假设上传的是文本类型的小文件,其他类型的或者更大的文件,也可以参考本文修改。
2. 客户端上传示例
本示例运行后的界面如图所示:

单击选择按钮,从本地选择文件后,然后单击上传按钮即可上传文件到服务端。
下面详细介绍创建该应用的步骤。
步骤1:创建Empty Ability项目。
步骤2:在module.json5配置文件加上对权限的声明:
"requestPermissions": [
{
"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"
}
]这里添加了访问互联网的权限。
步骤3:在Index.ets文件里添加如下的代码:
import http from '@ohos.net.http';
import util from '@ohos.util';
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs';
import picker from '@ohos.file.picker';
import systemDateTime from '@ohos.systemDateTime';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
//连接、通讯历史记录
@State msgHistory: string = ''
//上传地址
@State uploadUrl: string = "http://192.168.100.101:8081/upload"
//要上传的文件
@State uploadFilePath: string = ""
//是否允许上传
@State canUpload: boolean = false
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text("模拟上传示例")
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.padding(10)
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.Start, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text("上传的文件:")
.fontSize(14)
.width(100)
.flexGrow(0)
TextInput({ text: this.uploadFilePath })
.enabled(false)
.width(100)
.fontSize(11)
.flexGrow(1)
Button("选择")
.onClick(() => {
this.selectFile()
})
.width(70)
.fontSize(14)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(10)
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.Start, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text("上传地址:")
.fontSize(14)
.width(80)
.flexGrow(0)
TextInput({ text: this.uploadUrl })
.onChange((value) => {
this.uploadUrl = value
})
.width(110)
.fontSize(11)
.flexGrow(1)
Button("上传")
.onClick(() => {
this.uploadFile()
})
.enabled(this.canUpload)
.width(70)
.fontSize(14)
.flexGrow(0)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(10)
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Text(this.msgHistory)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
.padding(10)
.width('100%')
.backgroundColor(0xeeeeee)
}
.align(Alignment.Top)
.backgroundColor(0xeeeeee)
.height(300)
.flexGrow(1)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical)
.scrollBar(BarState.On)
.scrollBarWidth(20)
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)
.height('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
//构造上传文本文件的body内容
buildBodyContent(boundary: string, fileName: string, content: string) {
let body = `--${boundary}\r\n`
body = body + `Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="${fileName}"\r\n`
body = body + `Content-Type: text/plain\r\n`
body = body + '\r\n'
body = body + content
body = body + '\r\n'
body = body + `--${boundary}`
body = body + '--\r\n'
return body
}
//上传文件
async uploadFile() {
//上传文件使用的分隔符
let boundary: string = '----ShandongCaoxianNB666MyBabyBoundary' + (await systemDateTime.getCurrentTime(true)).toString()
//选择要上传的文件的内容
let fileContent: string = buf2String(this.readContentFromFile(this.uploadFilePath))
let segments = this.uploadFilePath.split('/')
//文件名称
let fileName = segments[segments.length-1]
//上传请求的body内容
let bodyContent = this.buildBodyContent(boundary, fileName, fileContent)
let textEncoder = new util.TextEncoder();
let contentBuf = textEncoder.encodeInto(bodyContent)
//http请求对象
let httpRequest = http.createHttp();
let opt: http.HttpRequestOptions = {
method: http.RequestMethod.POST,
header: { 'Content-Type': `multipart/form-data; boundary=${boundary}`,
'Content-Length': contentBuf.length.toString()
},
extraData: bodyContent
}
//发送上传请求
httpRequest.request(this.uploadUrl, opt)
.then((resp) => {
this.msgHistory += "响应码:" + resp.responseCode + "\r\n"
this.msgHistory += "上传成功\r\n"
})
.catch((e) => {
this.msgHistory += "请求失败:" + e.message + "\r\n"
})
}
//选择文件,为简单起见,选择一个不太大的文本文件
selectFile() {
let documentPicker = new picker.DocumentViewPicker();
documentPicker.select().then((result) => {
if (result.length > 0) {
this.uploadFilePath = result[0]
this.msgHistory += "select file: " + this.uploadFilePath + "\r\n";
this.canUpload = true
}
}).catch((e) => {
this.msgHistory += 'DocumentViewPicker.select failed ' + e.message + "\r\n";
});
}
//从文件读取内容
readContentFromFile(fileUri: string): ArrayBuffer {
let buf = new ArrayBuffer(1024 * 4);
let file = fs.openSync(fileUri, fs.OpenMode.READ_ONLY);
let readLen = fs.readSync(file.fd, buf, { offset: 0 });
let result = buf.slice(0, readLen)
fs.closeSync(file);
return result
}
}
//ArrayBuffer转utf8字符串
function buf2String(buf: ArrayBuffer) {
let msgArray = new Uint8Array(buf);
let textDecoder = util.TextDecoder.create("utf-8");
return textDecoder.decodeWithStream(msgArray)
}
步骤4:编译运行,可以使用模拟器或者真机。
步骤5:单击“选择”按钮,弹出文件选择窗口,如图所示:。
步骤6:选择要上传的文件,这里选择"harmonyos.txt",返回应用后的截图如下所示:
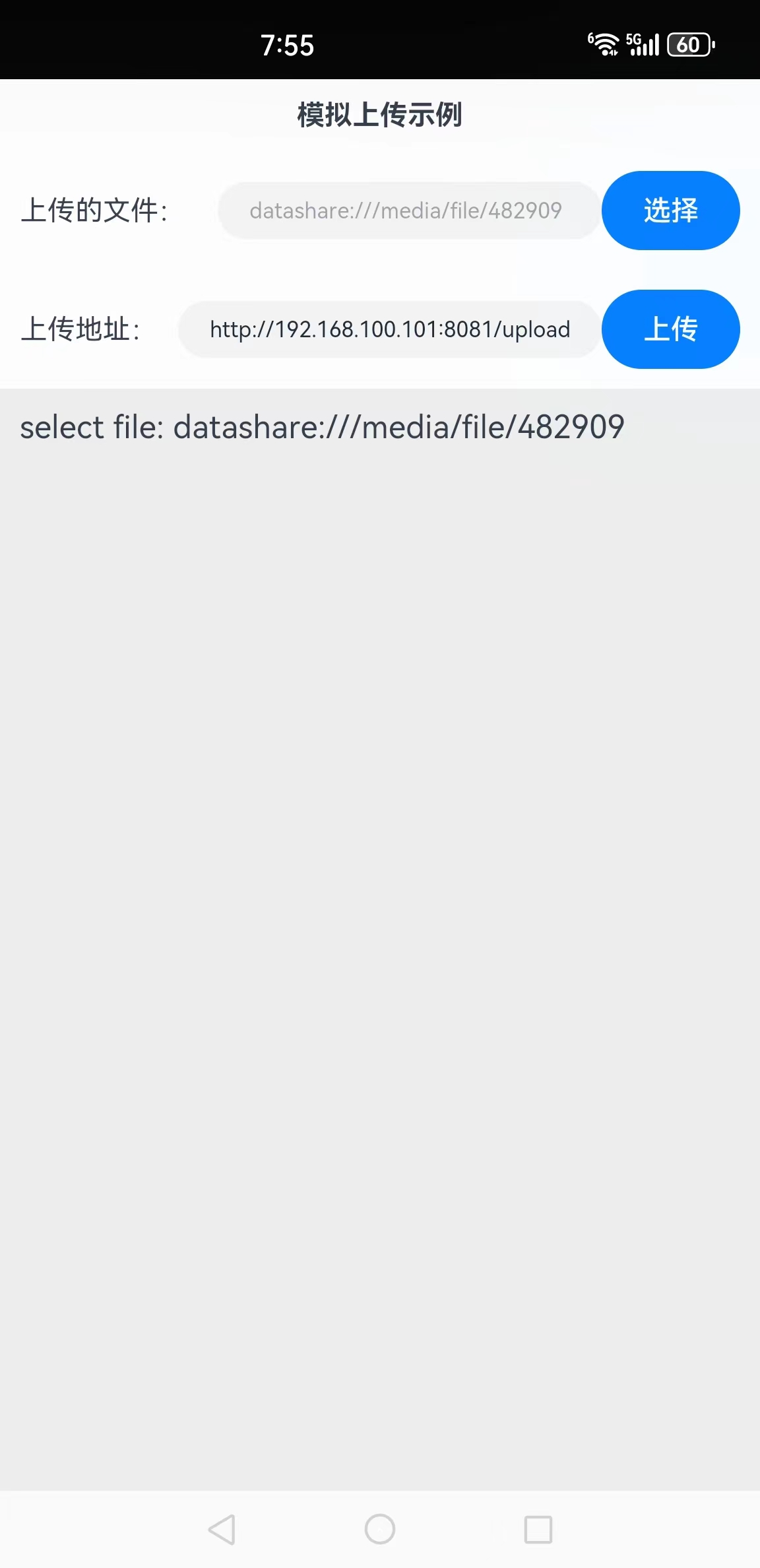
因为鸿蒙系统对物理文件和沙箱文件作了隔离,在应用看来,这个文件的路径是file: datashare:///media/file/482909
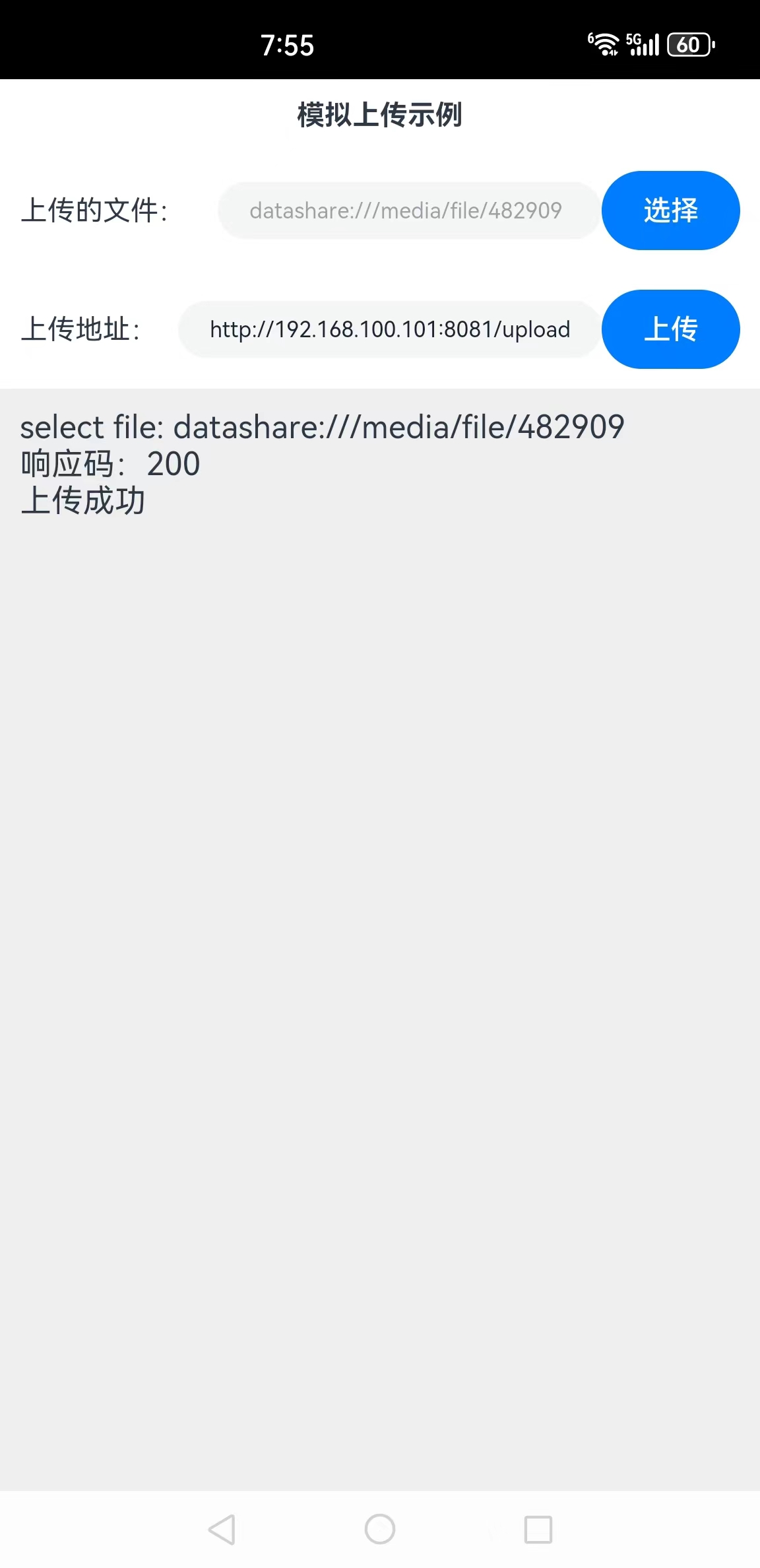
步骤7:单击“上传”按钮,上传文件到服务端,截图如下所示:
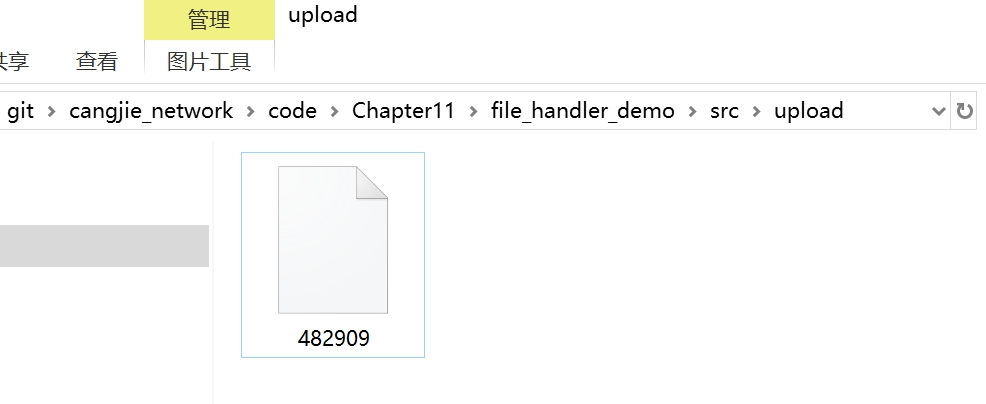
步骤8:在服务端可以看到上传后的文件(具体路径和服务端有关):
使用记事本打开该文件,可以看到文件内容:
这样就完成了文件的上传。
3. 上传功能分析
要实现上传功能,关键点在如下方面:
首先,构造HTTP请求的body部分,代码如下:
//构造上传文本文件的body内容
buildBodyContent(boundary: string, fileName: string, content: string) {
let body = `--${boundary}\r\n`
body = body + `Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="${fileName}"\r\n`
body = body + `Content-Type: text/plain\r\n`
body = body + '\r\n'
body = body + content
body = body + '\r\n'
body = body + `--${boundary}`
body = body + '--\r\n'
return body
}特别注意的是Content-Disposition和Content-Type,另外就是参数boundary,它是分隔符,要保证不和文件内容重复。
其次,就是请求的Header部分,代码如下:
//http请求对象
let httpRequest = http.createHttp();
let opt: http.HttpRequestOptions = {
method: http.RequestMethod.POST,
header: { 'Content-Type': `multipart/form-data; boundary=${boundary}`,
'Content-Length': contentBuf.length.toString()
},
extraData: bodyContent
}比较容易犯错的是Content-Length,它是内容的字节长度。




























 1272
1272

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








