在Java编程的世界里,异常处理、泛型和集合框架是构建高效、健壮应用的关键技术。通过掌握这些技术,我们可以更好地管理程序运行时的错误,提高代码的复用性和类型安全性。今天,我将通过一系列实验,分享如何在Java中使用异常处理、泛型和集合框架来解决实际问题。
实验背景
Java异常处理机制允许我们优雅地处理程序运行时的错误,泛型提供了类型安全的集合操作,而集合框架则为我们提供了丰富的数据结构来存储和管理数据。本次实验的目标是通过一系列实例,掌握Java异常处理、泛型和集合框架的基本使用方法。
实验设计
1. 验证部分:异常处理
异常处理基础
异常处理是Java中用于处理运行时错误的机制。以下是一个简单的异常处理示例,展示如何捕获和处理常见的异常:
public class TestExcept {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100 / 0; // ArithmeticException
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int[] a = new int[5];
try {
a[8] = 111; // ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int[] b = null;
try {
b[0] = 222; // NullPointerException
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Object str = "12345";
try {
int num = (int) str; // ClassCastException
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String x = "1111a";
try {
int n = Integer.parseInt(x); // NumberFormatException
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
自定义异常
自定义异常类允许我们创建具有特定行为的异常。以下是一个自定义异常类的示例:
class MyExcept extends Exception {
MyExcept(String info) {
super(info);
}
}
class MyFun {
void doWork(boolean isExcept) throws MyExcept {
System.out.println("doWork@MyFun0");
if (isExcept)
throw new MyExcept("出现异常!");
}
}
public class TestMyExcept {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFun mf = new MyFun();
try {
System.out.println("开始处理...");
mf.doWork(true);
} catch (MyExcept e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("完成异常处理!");
} finally {
System.out.println("完成收尾处理。");
}
System.out.println("结束处理。");
}
}输出结果:

2. 验证部分:泛型与集合框架
泛型基础
泛型提供了类型安全的集合操作。以下是一个使用泛型的示例:
class A {
public String toString() {
return "A";
}
}
class B extends A {
public String toString() {
return "B";
}
}
class C extends B {
public String toString() {
return "C";
}
}
class MyTest<E, F> {
E x;
F y;
MyTest(E x, F y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
void show() {
System.out.println("结果:x=" + x + "; y=" + y);
}
}
public class GenericClass {
static void checkMyTest1(MyTest<?, ?> test) {
System.out.print("测试->");
test.show();
}
static void checkMyTest2(MyTest<? super B, ? extends B> test) {
System.out.print("测试->");
test.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTest<String, Double> test1 = new MyTest<>("Hello!", 111.0);
test1.show();
MyTest<A, C> test2 = new MyTest<>(new A(), new C());
test2.show();
checkMyTest1(test1);
checkMyTest1(test2);
checkMyTest2(test2);
}
}
输出结果:

集合框架基础
集合框架提供了丰富的数据结构来存储和管理数据。以下是一个使用集合框架的示例:
import java.util.*;
class Apple {
int id;
double price;
Apple(int id, double price) {
this.id = id;
this.price = price;
}
public String toString() {
return "apple id=" + id + "; price=" + price;
}
}
public class TestQueue1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Apple> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new Apple(6, 4.3));
queue.add(new Apple(11, 5.5));
queue.add(new Apple(6, 8.2));
queue.addFirst(new Apple(23, 7.3));
queue.removeLast();
queue.add(new Apple(6, 9.6));
System.out.println("队列长度:" + queue.size());
for (Apple a : queue)
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println("------------------");
queue.pollLast();
while (!queue.isEmpty())
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}输出结果:

3. 设计部分:综合应用
自定义异常处理
以下是一个自定义异常处理的示例,展示如何创建和使用自定义异常类:
class MyException extends Exception {
String message;
public MyException(int m) {
message = "温度为" + m + "度,已超出范围!";
}
public String toString() {
return message;
}
}
class DataInput {
public void check(int m) throws MyException {
if (m > 500 || m < 100) {
throw new MyException(m);
} else {
System.out.println("合理的温度范围。");
}
}
}
public class TestTemperature {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataInput p = new DataInput();
try {
p.check(1400);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
集合框架应用
以下是一个使用集合框架的示例,展示如何管理图书信息:
import java.util.*;
class Book {
private String isbn;
private String title;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String isbn, String title, String author, double price) {
this.isbn = isbn;
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
public String getIsbn() {
return isbn;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
}
class BookList {
private LinkedList<Book> list = new LinkedList<>();
public void addBook(Book book) {
list.add(book);
}
public void deleteBook(String isbn) {
list.removeIf(book -> book.getIsbn().equals(isbn));
}
public Book findBookByIsbn(String isbn) {
for (Book book : list) {
if (book.getIsbn().equals(isbn)) {
return book;
}
}
return null;
}
public void updateBook(String isbn, Book newBook) {
for (ListIterator<Book> it = list.listIterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Book book = it.next();
if (book.getIsbn().equals(isbn)) {
it.set(newBook);
break;
}
}
}
public Book findMostExpensiveBook() {
double maxPrice = Double.MIN_VALUE;
Book mostExpensiveBook = null;
for (Book book : list) {
if (book.getPrice() > maxPrice) {
maxPrice = book.getPrice();
mostExpensiveBook = book;
}
}
return mostExpensiveBook;
}
}
public class TestBookStore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookList list = new BookList();
list.addBook(new Book("9999", "aa", "nnn", 23.5));
}
}
泛型与集合框架综合应用
以下是一个使用泛型和集合框架的示例,展示如何管理商品信息:
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Product implements Comparable<Product> {
private String name;
private double price;
public Product(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Product other) {
return Double.compare(other.price, this.price);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
public class ProductStore {
private TreeSet<Product> products;
public ProductStore() {
this.products = new TreeSet<>();
}
public ProductStore(Comparator<? super Product> comparator) {
this.products = new TreeSet<>(comparator);
}
public void addProduct(Product product) {
products.add(product);
}
public void deleteProduct(Product product) {
products.remove(product);
}
public void modifyProduct(Product oldProduct, Product newProduct) {
products.remove(oldProduct);
products.add(newProduct);
}
public void printProducts() {
System.out.println("Product List:");
for (Product product : products) {
System.out.println(product);
}
}
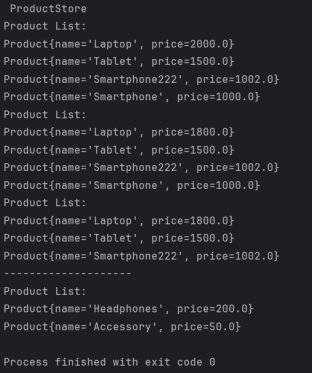
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductStore store = new ProductStore();
store.addProduct(new Product("Laptop", 2000.0));
store.addProduct(new Product("Smartphone", 1000.0));
store.addProduct(new Product("Tablet", 1500.0));
store.addProduct(new Product("Smartphone111", 1000.0));
store.addProduct(new Product("Smartphone222", 1002.0));
store.printProducts();
Product laptop = new Product("Laptop", 1800.0);
store.modifyProduct(new Product("Laptop", 2000.0), laptop);
store.printProducts();
store.deleteProduct(new Product("xxxx", 1000.0));
store.printProducts();
System.out.println("--------------------");
ProductStore storeWithComparator = new ProductStore(new Comparator<Product>() {
@Override
public int compare(Product o1, Product o2) {
return Double.compare(o2.getPrice(), o1.getPrice());
}
});
storeWithComparator.addProduct(new Product("Accessory", 50.0));
storeWithComparator.addProduct(new Product("Headphones", 200.0));
storeWithComparator.printProducts();
}
}输出结果:
单词计数器
以下是一个使用集合框架的示例,展示如何统计单词出现的次数:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class WordCounter {
private Map<String, Integer> wordCounts;
private Scanner scanner;
public WordCounter() {
wordCounts = new HashMap<>();
scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
}
public void addWord(String word) {
if (wordCounts.containsKey(word)) {
wordCounts.put(word, wordCounts.get(word) + 1);
} else {
wordCounts.put(word, 1);
}
}
public void printWordCounts() {
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : wordCounts.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
WordCounter counter = new WordCounter();
System.out.println("请输入单词(输入'EXIT'结束):");
String input;
while (!(input = counter.scanner.nextLine()).equalsIgnoreCase("EXIT")) {
counter.addWord(input);
counter.printWordCounts();
}
counter.scanner.close();
}
}输出结果:

实验使用环境
- 开发工具:IntelliJ IDEA
- 运行环境:Java SE Development Kit (JDK)
实验小结
在本次实验中,我遇到了一些挑战,尤其是在处理自定义异常和泛型时。通过不断调试和查阅文档,我学会了如何正确处理异常,并在代码中添加适当的异常处理逻辑。同时,我也对泛型的类型擦除机制有了更深入的理解。
通过这次实验,我不仅掌握了Java异常处理、泛型和集合框架的基本操作,还学会了如何在实际应用中使用这些技术。这些技能为我未来开发更复杂的应用程序打下了坚实的基础。同时,我也认识到了在编程中细节处理的重要性,一个小的疏忽可能会导致程序无法正常运行。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








