Problem A : Corn's new language
题目翻译:
Corn为了在校园里促进编程。他想增加一些有趣的主意使编程更加有吸引力。一个任务是它正在开发一门新的语言因为现存的任何一个语言对它来说都太简单了。这个语言的规则是:
(1)()是 valid 程序
(2) (P)如果P是一个valid程序,那么(P)就是一个valid程序
(3)P和Q都是valid程序,PQ才是valid程序
Corn想要一个语言的编译器。对于一个程序,编译器需要输出程序的最大深度,例如(())的深度是2,
((())())的深度是3.
答案求括号是否匹配,不匹配输出NO,匹配输出YES,并输出括号嵌套的深度。
解题思路:
括号匹配问题,简单模拟题目。
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[110];
while(~scanf("%s",str))
{
stack<char>st;
int len = strlen(str);
bool match = true;
int num = 0;
int mmax = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(str[i]=='(')
{
num++; ///嵌套层数加1
mmax = max(mmax,num);
st.push('(');
}
else ///是右括号
{
if(st.empty()) ///栈空
{
match = false;
break;
}
else if(st.top()!='(') ///栈顶不是左括号
{
match = false;
break;
}
else
{
num--; ///层数减1
mmax = max(mmax,num);
st.pop();
}
}
}
if(!st.empty()) ///最后栈不空
match = false;
if(match)
printf("YES %d\n",mmax);
else
printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
Problem B : Coach
在ACM训练营,教练把学生分成许多组,每个组都有三个学生,我们假设学生的编号是1~n,教练想让每个组都取得好成绩,因此他想按下面的条件组织,一个组有三个学生,他们是朋友,一个学生只能分到一个组,如果A和B是朋友,B和C是朋友,那么A和C也是朋友(也就是说朋友的朋友也是彼此是朋友)。
让计算是否能成功分队。
解题思路:
我用的广搜,用vector存图,对于一个未访问过的人,统计与它连通的人的人数,并标记这些人,如果人数对3取余有不是0的则输出No,否则输出Yes.
其实感觉题目有问题,一起做的小伙伴,都说开始的时候对人数进行模三判断会wa,我的开始也是先判断模三是否为0,而且还判断m是否为0.结果加
上这句,狂Wa十次,把一开始对三取余和对m的判断删除之后就对了。感觉题目特别有问题。好多人都被这样坑。
还可以用并查集写,好多人都用并查集写的。
让我狂Wa十次的代码,奔溃掉。
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5010;
vector<int>node[maxn];
int vis[maxn];
int n,m;
int bfs(int start)
{
queue<int>qu;
vis[start] = 1;
qu.push(start);
int num = 0;
int cur,nex;
while(!qu.empty())
{
cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
num++;
for(int i = 0; i < node[cur].size(); i++)
{
nex = node[cur][i];
if(vis[nex]==0)
{
vis[nex] = 1;
qu.push(nex);
}
}
}
return num;
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
///如果n根本不是3的倍数,或任何人之间无任何关系
if(n%3!=0 || m==0)
printf("No\n");
else
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(node,0,sizeof(node));
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
node[a].push_back(b);
node[b].push_back(a);
}
int ans;
bool flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(vis[i]==0)
{
ans = bfs(i);
if(ans%3)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
其实广搜都可以处理n不是3的倍数以及m=0的情况,但是觉得加上上面判断也不会错的,结果WA了十次,感觉WA的莫名其妙,现在也没想到错哪了。
下面是去掉第一句话的AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5010;
vector<int>node[maxn];
int vis[maxn];
int n,m;
int bfs(int start)
{
queue<int>qu;
vis[start] = 1;
qu.push(start);
int num = 0;
int cur,nex;
while(!qu.empty())
{
cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
num++;
for(int i = 0; i < node[cur].size(); i++)
{
nex = node[cur][i];
if(vis[nex]==0)
{
vis[nex] = 1;
qu.push(nex);
}
}
}
return num;
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(node,0,sizeof(node));
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
node[a].push_back(b);
node[b].push_back(a);
}
int ans;
bool flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(vis[i]==0)
{
ans = bfs(i);
if(ans%3)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}
Problem C : Frog
题目翻译:
有一只叫Matt的小青蛙,一天他来到了一条河。河可以看成是一个轴,Matt站在最左岸(0位置)。它想过河并到达右河岸(N位置).但是Matt只能跳L个单位长度,例如从0到L,河里面有N-1块石头(等间距的放置)石头的大小可以忽略,因此每块石头可以看成坐标轴上的一个点,Matt可以从左河岸调到其他石头上,他可以从一块石头上跳到右河岸,或者从左岸跳到右岸,现在Matt想知道它有多少种过河方案,当然Matt只能向前跳。
输入:
测试数据不超过100组,每组测试数据包括两个整数N和L,代表右河岸的位置,和Matt能跳的最长的长度。
输出:
对于每组测试数据,输出过河方案对10^9+7的模。
解题思路:
和斐波那契数列相似的递推。
设F[i]为到达地 i 块石头的方案数。
当 i <= L 时
F[0] = 1;
F[1] = F[0] = 1;
F[2] = F[1] + F[0] = 1+1 = 2;
F[3] = F[2] + (F[1]+F[0]) = 2*F[2]
此处可以推得。当 i >= 2 && i <= L时。
F[i] = 2*F[i-1]
不信的话可以拿数据 5 4 去推,一定是这样的。
当 i > L 时,先定义sum = F[L] = (F[L-1] + F[L-2] +。。。+F[1] + F[0]);
因此 i > L 时:
sum = sum - F[i-L-1] + F[i-1];
意思就是当i = L +1 的时候,sum 是0~L-1项的和,然而当前我要的是1~L这些项的和,所以让sum-F[0]+F[L] 就是从 sum - F[i-L-1] + F[i-1]
然后让 F[i] = sum%mod,但是sum是不能这样一直推下去的,因为后面数太大了,所以sum也需要对题目给定的数取模,取模后就会面临一个问题,sum一旦大于mod,取模后
变成较小的数,而F[i-L-1]其实还是很大的数,这样减法后,sum值会成负数。所以出现这种情况的时候,a[i] = sum + mod。否则a[i] = sum%mod。
当然如果sum成了负数,我们要加上mod使它在成为正数。如果它本身是正数,为了不超过mod,要对mod取余。这题目算是运气好,乱写出来了。
想想为什么要这样,可以想为什么sum会变成负数,一定是sum加到一定值了然后大于mod值了,然后对mod取模,sum变小了,在下次循环减去F[i-L-1]时,F[i-L-1]还是很大的
数,因此sum会变成负值,但是可别忘了,要是不取mod,sum一定是大于F[i-L+1]的,所以sum如果小于0了就要加上mod.
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100003;
const long long mod = 1e9+7;
long long a[maxn];
int main()
{
int N,L;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&N,&L))
{
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 1;
long long sum;
for(int i = 2; i <= L; i++)
{
a[i] = (2*a[i-1])%mod;
}
sum = a[L]; ///sum = a[l-1]+a[l-2]+..a[0];
for(int i = L+1; i <= N; i++)
{
sum = sum - a[i-L-1] + a[i-1];
if(sum < 0)
a[i] = sum+mod;
else
a[i] = sum%mod;
if(sum<0)
sum = sum + mod;
else
sum = sum%mod;
}
printf("%lld\n",a[N]);
}
return 0;
}
ACM's Posters
ACM海报:有N张海报,其高度与墙的高度是相同的,任何人可以往任何地方粘贴海报(意思就是可以覆盖别人的),给出N张海报的宽度范围,给出
海报墙的长度,求未被粘贴的区间,如果整个墙被粘满海报,直接输出Crazy ACM!。
解题思路:
粗略一看觉得是线段树,以n构造线段树,确发现n是海报张数,并不是墙的长度,墙的长度是R,并且高达66亿。
其实很简单的。输入若干海报覆盖的区间后,按照左边界从小到大排序,左边界相等的时候,按右边界从小到大排序。
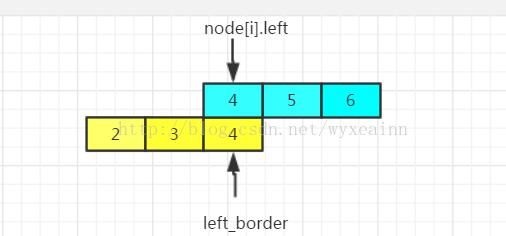
设置变量left_border来表示前i-1张海报所延伸到的最右侧(就是前i-1张海报覆盖范围的最右侧)。
则对于第 i 张海报,与left_border有三种情形。
情形一:恰好衔接型
像区间【2,4】【5,6】这样恰好衔接住的,left_border+1 == node[i].left.则海报所覆盖到的最右侧要更新。
情形二:区间相交型
这种情况是node[i].left<=left_border。图上是相等情况,当前区间一个是【2,4】一个是【3,5】就是小于号成立的情形了。这种情况海报所覆盖的最右边界需要更新。
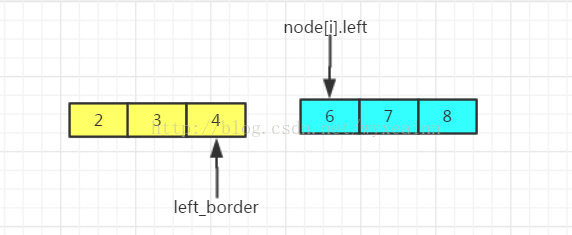
情形三:区间相离型。
如图所示类型,这种类型就是区间未被覆盖,输出【left_border+1,node[i].left-1】,然后还是要更新left_border的值,从node[i].right开始。
考虑完所有的海报后,这题没有完,还要看看最终的left_border和R的关系,如果left_border+1<R。则区间left_border+1到R也未被覆盖。
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000010;
int N;
long long R;
struct Node
{
long long left;
long long right;
}node[maxn];
bool cmp(struct Node n1,struct Node n2)
{
if(n1.left==n2.left)
return n1.right < n2.right;
else
return n1.left<n2.left;
}
long long Max(long long a,long long b)
{
if(a>b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%lld",&N,&R))
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%lld%lld",&node[i].left,&node[i].right);
sort(node,node+N,cmp);
long long left_border = 0;
bool flag = true;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
///恰好衔接型
if(left_border+1==node[i].left)
{
left_border = Max(left_border,node[i].right);
}
///区间相交型
else if(node[i].left<=left_border)
{
left_border = Max(left_border,node[i].right);
}
else ///除了上面两种后,就是区间相离型
{
printf("[%lld, %lld]\n",left_border+1,node[i].left-1);
left_border = node[i].right;
flag = false;
}
}
///易错点,忘记考虑最终海报覆盖到的最右边界可能没有延伸到墙的最右侧
if(left_border+1<R)
{
flag = false;
printf("[%lld, %lld]\n",left_border+1,R);
}
if(flag)
printf("Crazy ACM!\n");
}
return 0;
}
Festival
题目翻译:
在过去的DHU节日聚乐会,xiangTang得到许多瓶饮料,但是每一瓶都是一种不同的口味,而且他们不是the same concentration。有时太多的选择会造成困惑,xiaotang打算把他们都混合在一起创造一种极其独特的味道,请你帮助他,给出每种饮料的concentration(c1,c2,cn),每次你都可以用x瓶饮料而且混合他们。保证在混合后concentration会变成这些数的平均数,例如,如果你选择3,4,8,则你会得到5,继续混合知道只有一瓶剩下,你的目的是让最后的concentration最大。输入:多组测试数据,第一行是一个数字N,第二行是N个数字Ci.每瓶饮料的concentration。输出:最后合成一瓶后最大的concentration。解题思路:贪心。采取两两相合的思想,每次取两个最小的相合,直到合完所有的。两两相合后C趋近与较大的了。然后在相合,又向较大的靠拢了。所以先排序,然后两个最小的相合。
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[103];
int main()
{
int N;
while(~scanf("%d",&N))
{
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a+1,a+1+N);
for(int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
a[i] = (a[i]+a[i-1])/2;
}
printf("%d\n",a[N]);
}
}Problem J : Raising Bacteria
你是一个bacteria的爱好者,因此他想去在盒子里增加一些bacteria.起初,盒子是空的,每天早上,你可以在盒子里放置任意数量的bacteria。每天晚上每一个bacterium会分裂成两个bacteria。在某些时刻你希望看到盒子里面有x个bacteria。那么
你放入盒子的最小细菌数量是多少。
解题思路:
如果当前有t个细菌,那么过一夜会分裂,变成2*t个,因此对于任何偶数x,它由x/2个细菌繁殖过来就好,对于任何奇数y,可以由y-1/2个细菌繁殖过来后在放一个细菌,
因此此题目可以转换成统计2进制数中1的个数。
例如计算繁殖14个细菌,所要放置的最小细菌数,化为2进制:1110
二进制一位是0,是偶数,右移一位变成111 = 7 ;也就是说14可以由7个细菌经过一夜分裂而来;
二进制最后一位是1,是奇数,右移一位变成11,也就是说7可以是3个细菌经过一夜分裂后,在放入一个得来;
二进制最后一位是1,是奇数,右移一位变成1,也就是说3可以是1个细菌经过一夜分裂后,在放入一个得来;
二进制最后一位是1,是奇数,右移一位是0,说明是在第一天最初放进去的1个。
则答案就是3.
分别是第一天放1个,经过一夜繁殖后第二天放入一个,1*2+1 = 3;,然后再经过一夜繁殖后第三天放入一个,3*2+1 = 7,然后经过一夜繁殖,第四天达到要求数目7*2=14
所以答案可以变成统计一个数化为2进制后,统计01串中1的个数就是答案。
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
while(~scanf("%d",&x))
{
int ans = 0;
while(x)
{
if(x&1) ans++;
x >>= 1;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
























 581
581

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








