(1)定义一个名为CPerson的类,有以下私有成员:姓名、身份证号、性别和年龄,成员函数:构造函数、析构函数、输出信息的函数。并在此基础上派生出CEmployee类,派生类CEmployee增加了两个新的数据成员,分别用于表示部门和薪水。要求派生类CEmployee的构造函数显示调用基类CPerson的构造函数,并为派生类CEmployee定义析构函数,定义输出信息的函数。
class CPerson
{
protected:
string m_szName;
string m_szId;
int m_nSex;//0:women,1:man
int m_nAge;
public:
CPerson(string name,string id,int sex,int age);
void Show1();
~CPerson();
};
class CEmployee:public CPerson
{
private:
string m_szDepartment;
double m_Salary;
public:
CEmployee(string name,string id,int sex,int age,string department,double salary);
void Show2();
~CEmployee();
};
int main()
{
string name,id,department;
int sex,age;
double salary;
cout<<"input employee's name,id,sex(0:women,1:man),age,department,salary:\n";
cin>>name>>id>>sex>>age>>department>>salary;
CEmployee employee1(name,id,sex,age,department,salary);
employee1.Show2();
return 0;
}
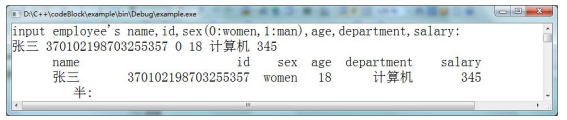
下面的运行结果供参考:
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
class CPerson
{
protected:
string m_szName;
string m_szId;
int m_nSex;//0:women,1:man
int m_nAge;
public:
CPerson(string name,string id,int sex,int age);
void Show1();
~CPerson();
};
CPerson::CPerson(string name,string id,int sex,int age)
{
m_szName=name;
m_szId=id;
m_nSex=sex;
m_nAge=age;
}
void CPerson::Show1()
{
cout<<setw(10)<<m_szName<<setw(25)<<m_szId;
if(m_nSex==1)
cout<<setw(7)<<"man";
else
cout<<setw(7)<<"women";
cout<<setw(5)<<m_nAge<<endl;
}
CPerson::~CPerson() { }
class CEmployee:public CPerson
{
private:
string m_szDepartment;
double m_Salary;
public:
CEmployee(string name,string id,int sex,int age,string department,double salary);
void Show2();
~CEmployee();
};
CEmployee::CEmployee(string name,string id,int sex,int age,string department,double salary):CPerson(name,id,sex,age)
{
m_szDepartment=department;
m_Salary=salary;
}
void CEmployee::Show2()
{
cout<<setw(10)<<"name"<<setw(25)<<"id"<<setw(7)<<"sex"<<setw(5)<<"age"<<setw(12)<<"department"<<setw(10)<<"salary"<<endl;
Show1();
cout<<setw(12)<<m_szDepartment<<setw(10)<<m_Salary<<endl;
}
CEmployee::~CEmployee() {}
int main()
{
string name,id,department;
int sex,age;
double salary;
cout<<"input employee's name,id,sex(0:women,1:man),age,department,salary:\n";
cin>>name>>id>>sex>>age>>department>>salary;
CEmployee employee1(name,id,sex,age,department,salary);
employee1.Show2();
return 0;
}
总结:
由于基类CPerson的成员变量采用了protected属性,所以可以直接运用基类的数据成员但是也可以调用成员函数,若基类CPerson的成员变量采用了privated属性,则只能使用CPerson::Show();实现
(2)字符串除了用C++扩充的string类型外,按C语言的传统,还可以用char *表示。请将类声明中的string全部改为char *后,重新写一遍程序(此时的区别是,类中有指针成员,构造和析构函数需要考虑深复制的问题了。)
class CPerson
{
protected:
char *m_szName;
char *m_szId;
int m_nSex;//0:women,1:man
int m_nAge;
public:
CPerson(char *name,char *id,int sex,int age);
void Show1();
~CPerson();
};
private:
char *m_szDepartment;
float m_Salary;
public:
CEmployee(char *name,char *id,int sex,int age,char *department,float salary);
void Show2();
~CEmployee();
};
int main()
{
char name[10],id[19],department[10];
int sex,age;
float salary;
cout<<"input employee's name,id,sex(0:women,1:man),age,department,salary:\n";
cin>>name>>id>>sex>>age>>department>>salary;
CEmployee employee1(name,id,sex,age,department,salary);
employee1.Show2();
return 0;
}
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
class CPerson
{
protected:
char *m_szName;
char *m_szId;
int m_nSex;//0:women,1:man
int m_nAge;
public:
CPerson(char *name,char *id,int sex,int age);
void Show1();
~CPerson();
};
CPerson::CPerson(char *name,char *id,int sex,int age)
{
m_szName=new char[strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(m_szName,name);
m_szId=new char[strlen(id)+1];
strcpy(m_szId,id);
m_nSex=sex;
m_nAge=age;
}
void CPerson::Show1()
{
cout<<setw(10)<<m_szName<<setw(25)<<m_szId;
if(m_nSex==1)
cout<<setw(7)<<"man";
else
cout<<setw(7)<<"women";
cout<<setw(5)<<m_nAge<<endl;
}
CPerson::~CPerson()
{
delete [ ]m_szName;
delete [ ]m_szId;
}
class CEmployee:public CPerson
{
private:
char *m_szDepartment;
double m_Salary;
public:
CEmployee(char *name,char *id,int sex,int age,char *department,double salary);
void Show2();
~CEmployee();
};
CEmployee::CEmployee(char *name,char *id,int sex,int age,char *department,double salary):CPerson(name,id,sex,age)
{
m_szDepartment=new char[strlen(department)+1];
strcpy(m_szDepartment,department);
m_Salary=salary;
}
void CEmployee::Show2()
{
cout<<setw(10)<<"name"<<setw(25)<<"id"<<setw(7)<<"sex"<<setw(5)<<"age"<<setw(12)<<"department"<<setw(10)<<"salary"<<endl;
Show1();
cout<<setw(12)<<m_szDepartment<<setw(10)<<m_Salary<<endl;
}
CEmployee::~CEmployee() {delete [ ]m_szDepartment; }
int main()
{
char name[10],id[19],department[10];
int sex,age;
double salary;
cout<<"input employee's name,id,sex(0:women,1:man),age,department,salary:\n";
cin>>name>>id>>sex>>age>>department>>salary;
CEmployee employee1(name,id,sex,age,department,salary);
employee1.Show2();
return 0;
}






















 675
675

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








