| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 21794 | Accepted: 10098 |
Description
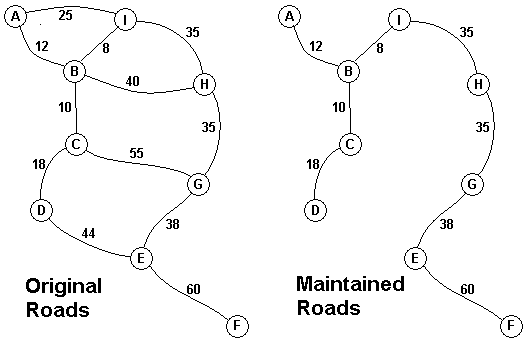
The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.
Input
Output
Sample Input
9
A 2 B 12 I 25
B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8
C 2 D 18 G 55
D 1 E 44
E 2 F 60 G 38
F 0
G 1 H 35
H 1 I 35
3
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20
0
Sample Output
216
30
Source
问题描述:
题目大意在相通n个岛屿的所有桥都坏了,要重修,重修每一个桥所用的时间不同,求重修使每个岛屿都间接或直接与其他岛屿相同时所用的的最短时间(只有修完一个桥后才可修下一个桥)。简言之就是求最小生成树。对于数据,数据输入的第一行n代表岛屿的个数,当为0是结束程序,接着n-1行开始时为这岛屿的编号,用大写字母表示,接着是一个整数m,表示与该岛屿连接的字典序大于该岛屿编号的个数,然后该行输入m对数据,每对数据的第一个字母表示与该岛屿连通的岛屿的编号,第二个数字表示要重修两岛屿之间桥所需要的时间,输出数据见样例及原题。该题图为稀疏图,用Kruskal算法比较好
Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法的基本思想:
假设WN=(V,{E})是一个含有n个顶点的连通网,则按照克鲁斯卡尔算法构造最小生成树的过程为:
1. 先构造一个只含n个顶点,而边集为空的子图,
2. 若将该子图中各个顶点看成是各棵树上的根结点,则它是一个含有n棵树的一个森林。
3. 之后,从网的边集E中选取一条权值最小的边,若该条边的两个顶点分属不同的树,则将其加入子图,
4. 也就是说,将这两个顶点分别所在的两棵树合成一棵树;
5. 反之,若该条边的两个顶点已落在同一棵树上,则不可取,而应该取下一条权值最小的边再试之。
6. 依次类推,直至森林中只有一棵树,也即子图中含有n-1条边为止。
eg:
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20
组成的图就是三个顶点A,B,C分别相连组成三角形,AB=10,BC=20,AC=40,最小生成树为ABC,权值和为30。每次查找的节点是不是在已经生成的连通分量中,如果没有则加入并加权如果已经在连通分量中,则舍弃该点,不加权。这是关键点,是在生成树中查找并归并的核心。
代码实现如下:
/***********************************************************************
Copyright (c) 2015,wangzp
All rights no reserved.
Name: 《Jungle Roads》In PEKING UNIVERSITY ACM
ID: PROBLEM 1251
问题简述: 题目大意在相通n个岛屿的所有桥都坏了,要重修,重修每一个桥所用的时间不同,
求重修使每个岛屿都间接或直接与其他岛屿相同时所用的的最短时间
(只有修完一个桥后才可修下一个桥)。简言之就是求最小生成树。
对于数据,数据输入的第一行n代表岛屿的个数,当为0是结束程序,
接着n-1行开始时为这岛屿的编号,用大写字母表示,
接着是一个整数m,表示与该岛屿连接的字典序大于该岛屿编号的个数,
然后该行输入m对数据,每对数据的第一个字母表示与该岛屿连通的岛屿的编号,
第二个数字表示要重修两岛屿之间桥所需要的时间,输出数据见样例及原题。
该题图为稀疏图,用Kruskal算法比较好
Date: SEP 14, 2015
***********************************************************************/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std; //A到Z,用0-25表示,初始化顶点,26棵只有根节点的树 int p[26]; //并查集,用于判断两点是否直接或间接连通,关键点 struct prog{ int u; int v; int w; }map[80];//存储边的信息,包括起点/终点/权值 //排序函数,将边根据权值从小到大排 bool cmp (prog a,prog b) { return a.w < b.w; } //并查集的find,关键递归函数,非常难理解,用一个输入可以很快理解: //3 //A 2 B 10 C 40 //B 1 C 20 /*组成的图就是三个顶点A,B,C分别相连组成三角形, AB=10,BC=20,AC=40,最小生成树为ABC,权值和为30 每次查找的节点是不是在已经生成的连通分量中,如果没有则加入并加权 如果已经在连通分量中,则舍弃该点,不加权*/ int find(int x) { if (x == p[x]) { return x; } else { p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } } int main() { int n; while (cin>>n ,n) { int i , j ; for(i = 0;i < 26;i ++ ) { p[i] = i ;//并查集初始化 } int k = 0 ; for (i = 0;i < n - 1;i ++ ) {//构造边的信息 char str[3]; int m; cin>>str>>m; for (j = 0;j < m;j++,k++) { char str2[3]; int t; cin>>str2>>t; map[k].u = (str[0]-'A'); map[k].v = (str2[0]-'A'); map[k].w = t; } } //注意:排序函数,是按照你自己写的cmp函数的规律对map进行排序 sort (map,map + k,cmp);//将边从小到大排序 int ans = 0; //所要求的答案 for (i = 0;i < k;i++) { int x = find(map[i].u); int y = find(map[i].v); if(x != y) {//如果两点不在同一连通分量里,则将两点连接,并存储该边 ans += map[i].w; p[x] = y; } } cout<
<

























 1262
1262











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








