1 示例2:Hello Node
这个例子将介绍Nodes, Bounding Volumes, Sphere, Colors, Translation(平移) and Scaling(缩放)。
1.1 源代码
package jmetest.TutorialGuide;import com.jme.app.SimpleGame;import com.jme.bounding.BoundingBox;import com.jme.bounding.BoundingSphere;import com.jme.math.Vector3f;import com.jme.renderer.ColorRGBA;import com.jme.scene.Node;import com.jme.scene.Spatial;import com.jme.scene.shape.Box;import com.jme.scene.shape.Sphere;/*** Started Date: Jul 20, 2004<br><br>
*
* Simple Node object with a few Geometry manipulators.** @author Jack Lindamood
*/public class HelloNode extends SimpleGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {HelloNode app = new HelloNode();app.setConfigShowMode(ConfigShowMode.AlwaysShow);app.start();
}
protected void simpleInitGame() {Box b=new Box("My Box",new Vector3f(0,0,0),new Vector3f(1,1,1));
// Give the box a bounds object to allow it to be culledb.setModelBound(new BoundingSphere());
// Calculate the best bounds for the object you gave itb.updateModelBound();// Move the box 2 in the y direction upb.setLocalTranslation(new Vector3f(0,2,0));
// Give the box a solid color of blue.b.setDefaultColor(ColorRGBA.blue.clone());
Sphere s=new Sphere("My sphere",5,5,1f);
// Do bounds for the sphere, but we'll use a BoundingBox this times.setModelBound(new BoundingBox());
s.updateModelBound();
// Give the sphere random colorss.setRandomColors();// Make a node and give it childrenNode n=new Node("My Node");
n.attachChild(b);
n.attachChild(s);
// Make the node and all its children 5 times larger.n.setLocalScale(5);// Remove lighting for rootNode so that it will use our basic colors.rootNode.setLightCombineMode(Spatial.LightCombineMode.Off);
rootNode.attachChild(n);
}
}
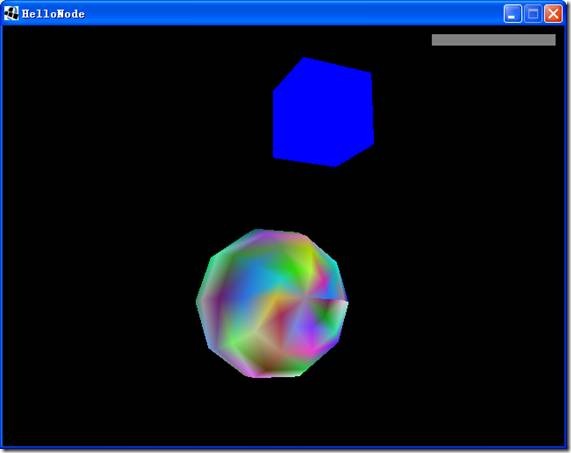
首先来预览一下结果
// Give the box a bounds object to allow it to be culled
b.setModelBound(new BoundingSphere());
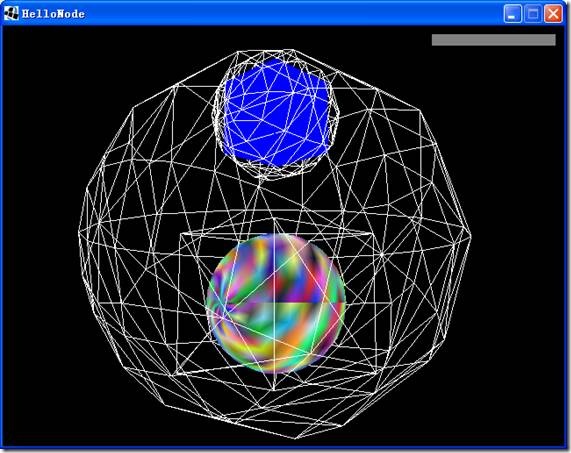
用一个球把这个box的边界包围起来。包围盒(Bounding Volumes)例如BoundingSphere、BoundingBox、BoundingCapsule是jME中用来加速的关键。通常一个物体是不规则的。对一个不规则的物体,计算起来自然要麻烦一些。如果把这个物体用一个规则的简单的形状包围起来,那么就可以提高计算速度,也可以很简单地测试这个物体是否可见。比如我们可以把一个非常复杂的人用一个球包起来。如果这个球不可见,咱们也用不着花那么大的力气去画一个非常复杂的人。本例中我们用一个球来包一个立方体。
这里只是一个空的边界,需要调用
// Calculate the best bounds for the object you gave it
以使球正确无缝地包起立方体。用一个半径1米的球做宽只有1厘米的立方体显然是没什么意义的。updateModelBound()会计算最佳的边界。
// Move the box 2 in the y direction up
b.setLocalTranslation(new Vector3f(0,2,0));
是将这个box向上平移2个单元格。因为它的初始坐标是(0,0,0),现在设成了(0,2,0)。
// Give the box a solid color of blue.
b.setDefaultColor(ColorRGBA.blue.clone());
把球的颜色着为蓝色。ColorRGBA的四元素为Red/Green/Blue/Alpha(透明度)。取值范围是[0-1],0为完全透明的,0.5意味着半透明。
Sphere s=new Sphere("My sphere",10,10,1f);
这里我们新构造了一个球。jME只会画三角形,不会画曲线。用三角形来画圆形是非常困难的,所以只能是无限接近圆。中间两个参数表示了近似度,值越大越近似圆。但是值越大的话所画的三角形也越多,太多的三角形也会降低帧率(FPS)。最后一个参数是球的半径,float型。
s.setModelBound(new BoundingBox());
s.updateModelBound();
我们用一个立方体把这个球包起来。再将球设为随机颜色:
// Give the sphere random colors
s.setRandomColors();
// Make a node and give it children
Node n=new Node("My Node");
n.attachChild(b);
n.attachChild(s);
把box和球加到节点中。再把这个节点加到场景的根节点中:rootNode.attachChild(n);
要将节点n的所有子对象同步放大5倍怎么做呢:
// Make the node and all its children 5 times larger.
n.setLocalScale(5);
同理,想平移的话用setLocalTranslation,旋转用setLocalRotation。
// Remove lighting for rootNode so that it will use our basic colors.
rootNode.setLightCombineMode(Spatial.LightCombineMode.Off);
最后加这行代码使我们设置的颜色生效。否则就是灰色的。
场景图如下:
| rootNode | |
| “My Node” made 5x bigger | |
| “My box” moved 2 up. | “My sphere” |
运行时可以按“B”看下边界效果:
按“T”数一下有多少三角形:








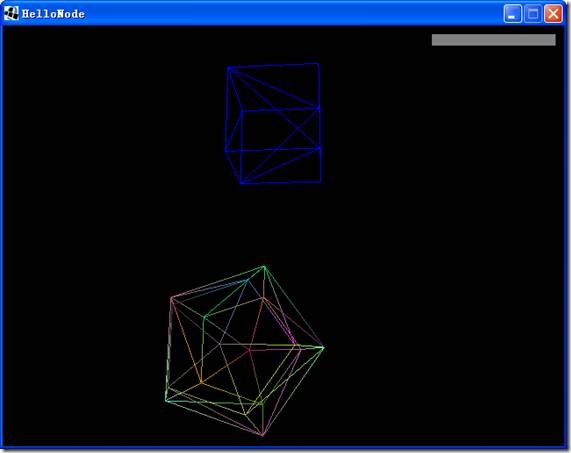














 4324
4324

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








