在数字化浪潮中,点云建模技术作为三维场景复刻的核心引擎,正推动着工业制造、建筑测绘、文物保护等领域的革新。通过激光雷达或深度相机采集的海量点云数据,能够以毫米级精度还原物理世界的细节特征。本文将以程序员视角,深入解析点云建模的技术原理,通过代码示例展示数据处理、特征提取与模型构建的关键环节,揭示数字世界复刻背后的技术实现路径。
数据采集与预处理:点云建模的基础工程
点云建模的质量始于数据采集的精度,而预处理则是提升建模效果的关键步骤。原始点云数据往往包含噪声、冗余点和缺失区域,需要通过滤波、去重、配准等预处理操作,为后续建模提供高质量的数据基础。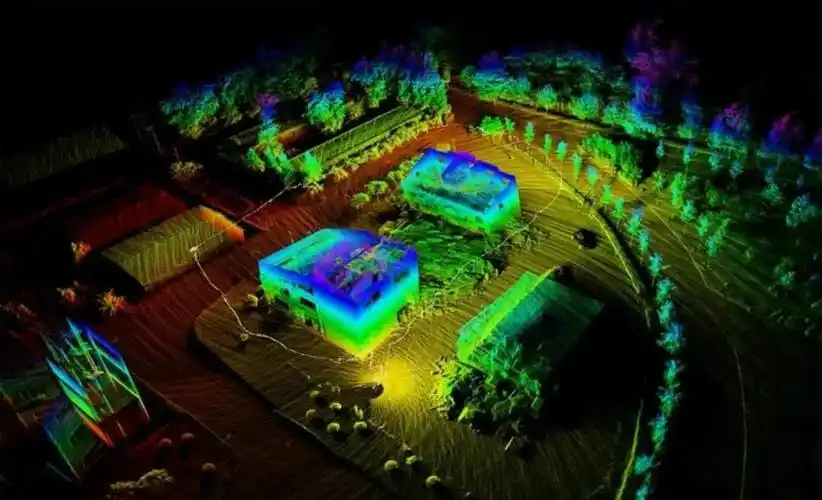
点云预处理核心代码:
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
from scipy.spatial import KDTree
class PointCloudPreprocessor:
def __init__(self):
self.voxel_size = 0.01 # 体素大小,控制下采样精度
self.statistical_params = {
"nb_neighbors": 50, # 统计滤波邻居数量
"std_ratio": 1.0 # 标准差阈值
}
def load_point_cloud(self, file_path):
"""加载点云数据"""
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(file_path)
print(f"原始点云点数: {len(pcd.points)}")
return pcd
def remove_outliers(self, pcd):
"""移除离群点噪声"""
# 统计滤波移除离群点
cl, ind = pcd.remove_statistical_outlier(
nb_neighbors=self.statistical_params["nb_neighbors"],
std_ratio=self.statistical_params["std_ratio"]
)
inlier_cloud = pcd.select_by_index(ind)
print(f"滤波后点云点数: {len(inlier_cloud.points)}")
return inlier_cloud
def down_sample(self, pcd):
"""点云下采样减少点数"""
# 体素格下采样,平衡精度与计算量
down_pcd = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size=self.voxel_size)
print(f"下采样后点云点数: {len(down_pcd.points)}")
return down_pcd
def estimate_normals(self, pcd):
"""估计点云法向量"""
# 估计法向量用于后续特征提取
pcd.estimate_normals(
search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.1, max_nn=30)
)
# 法向量方向一致化
pcd.orient_normals_consistent_tangent_plane(100)
return pcd
def remove_duplicates(self, pcd, tolerance=0.005):
"""移除重复点"""
points = np.asarray(pcd.points)
# 使用KDTree快速查找近邻点
kd_tree = KDTree(points)
# 查找距离小于 tolerance 的点对
pairs = kd_tree.query_pairs(tolerance)
# 标记需要保留的点索引
keep = np.ones(points.shape[0], dtype=bool)
for i, j in pairs:
if keep[i] and keep[j]:
# 保留其中一个点
keep[j] = False
# 筛选保留的点
unique_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
unique_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points[keep])
if pcd.has_normals():
normals = np.asarray(pcd.normals)
unique_pcd.normals = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(normals[keep])
print(f"去重后点云点数: {len(unique_pcd.points)}")
return unique_pcd
def complete_pipeline(self, file_path):
"""完整预处理流程"""
pcd = self.load_point_cloud(file_path)
pcd = self.remove_outliers(pcd)
pcd = self.remove_duplicates(pcd)
pcd = self.down_sample(pcd)
pcd = self.estimate_normals(pcd)
return pcd
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
preprocessor = PointCloudPreprocessor()
# 处理示例点云文件
processed_pcd = preprocessor.complete_pipeline("raw_scan.ply")
# 保存预处理结果
o3d.io.write_point_cloud("processed_scan.ply", processed_pcd)
点云预处理的核心目标是在保留关键特征的前提下优化数据质量与规模。上述代码实现了完整的预处理流程:通过统计滤波去除因设备噪声产生的离群点;利用体素下采样在保持空间结构的同时减少数据量,通常可将点数降低 50%-80%;采用 KDTree 实现高效的重复点检测与移除;通过法向量估计为后续建模提供几何特征基础。预处理后的点云数据将显著提升后续建模算法的效率与精度,是实现毫米级复刻的基础工程。
三维建模核心算法:从点集到表面重构
点云建模的核心挑战在于如何从离散的三维点集中重建出连续的表面模型。表面重构算法需要处理点云密度不均、边界模糊等问题,同时保证模型的拓扑正确性与细节还原度。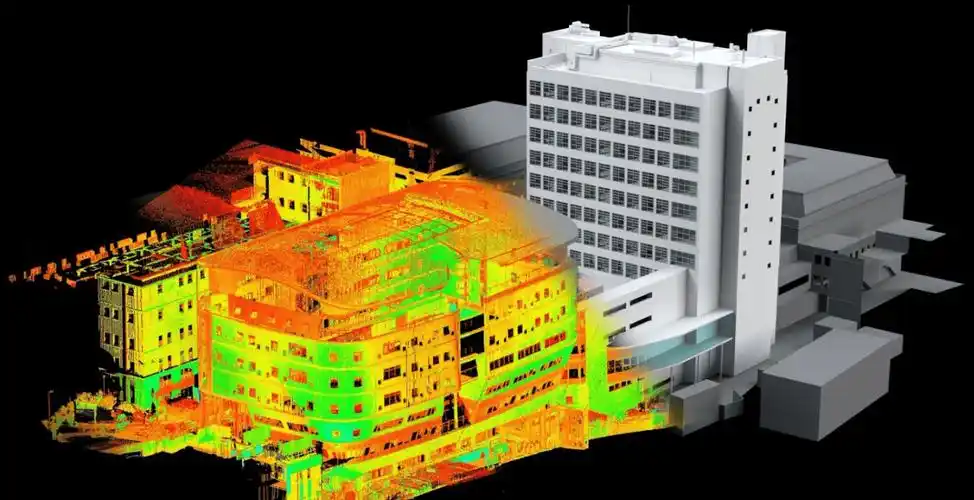
表面重构算法实现:
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
class SurfaceReconstructor:
def __init__(self):
# 泊松重建参数
self.poisson_params = {
"depth": 9, # 重建深度,控制细节级别
"width": 0, # 体素宽度
"scale": 1.1, # 尺度因子
"linear_fit": True # 线性拟合优化
}
# Alpha Shapes参数
self.alpha = 0.03 # 控制表面复杂度
def poisson_reconstruction(self, pcd):
"""泊松表面重建算法"""
# 确保点云有法向量
if not pcd.has_normals():
pcd.estimate_normals(
search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.1, max_nn=30)
)
# 执行泊松重建
print("执行泊松表面重建...")
mesh, densities = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_from_point_cloud_poisson(
pcd,
depth=self.poisson_params["depth"],
width=self.poisson_params["width"],
scale=self.poisson_params["scale"],
linear_fit=self.poisson_params["linear_fit"]
)
# 根据密度过滤低置信度三角形
vertices_to_keep = densities > np.quantile(densities, 0.01)
mesh = mesh.select_by_index(np.where(vertices_to_keep)[0])
return mesh
def alpha_shapes_reconstruction(self, pcd):
"""Alpha Shapes表面重建"""
print("执行Alpha Shapes表面重建...")
# 转换为numpy数组
points = np.asarray(pcd.points)
# 使用DBSCAN聚类处理可能的多物体场景
clustering = DBSCAN(eps=0.05, min_samples=10).fit(points)
labels = clustering.labels_
unique_labels = set(labels)
meshes = []
# 对每个聚类单独重建
for label in unique_labels:
if label == -1: # 噪声点
continue
cluster_points = points[labels == label]
cluster_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
cluster_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(cluster_points)
# 执行Alpha Shapes重建
mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_from_point_cloud_alpha_shape(
cluster_pcd, self.alpha
)
meshes.append(mesh)
# 合并所有聚类的网格
if meshes:
combined_mesh = meshes[0]
for mesh in meshes[1:]:
combined_mesh += mesh
return combined_mesh
return None
def mesh_simplification(self, mesh, target_triangles=50000):
"""网格简化减少三角形数量"""
print(f"原始网格三角形数量: {len(mesh.triangles)}")
# 计算需要简化的比例
triangle_count = len(mesh.triangles)
if triangle_count <= target_triangles:
return mesh
# 执行简化
simplify_ratio = target_triangles / triangle_count
simplified_mesh = mesh.simplify_quadric_decimation(target_triangles)
# 移除简化后可能产生的退化三角形
simplified_mesh.remove_degenerate_triangles()
# 移除重复顶点
simplified_mesh.remove_duplicated_vertices()
# 修复网格拓扑
simplified_mesh.remove_non_manifold_edges()
print(f"简化后网格三角形数量: {len(simplified_mesh.triangles)}")
return simplified_mesh
def mesh_refinement(self, mesh):
"""网格细化提升细节质量"""
# 执行拉普拉斯平滑
mesh = mesh.filter_smooth_laplacian(number_of_iterations=10)
# 法线一致性检查与修复
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
return mesh
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 加载预处理后的点云
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("processed_scan.ply")
# 初始化重建器
reconstructor = SurfaceReconstructor()
# 选择泊松重建(适合密集点云)
mesh = reconstructor.poisson_reconstruction(pcd)
# 网格优化
mesh = reconstructor.mesh_simplification(mesh, target_triangles=100000)
mesh = reconstructor.mesh_refinement(mesh)
# 保存结果
o3d.io.write_triangle_mesh("reconstructed_model.ply", mesh)
主流的表面重构算法主要分为两类:泊松重建和 Alpha Shapes 重建。泊松算法通过构建隐式函数的梯度场来生成连续表面,适合处理密集且均匀分布的点云,能生成平滑完整的模型,但对边界处理能力较弱;Alpha Shapes 算法基于 Delaunay 三角剖分,通过控制 alpha 参数调节表面复杂度,更适合处理具有明显边界的物体,但对噪声较敏感。
代码实现中加入了针对复杂场景的优化策略:通过 DBSCAN 聚类处理多物体场景;采用网格简化在保证视觉效果的前提下降低模型复杂度;使用拉普拉斯平滑提升表面质量。这些技术组合使得重建模型既能保持毫米级的细节精度,又能控制数据规模以适应不同应用场景的需求。
实践应用与技术优化:点云建模的工程落地
点云建模技术的价值最终体现在实际应用中,不同领域的需求差异要求建模流程进行针对性优化。从工业检测到数字孪生,点云模型的工程落地需要解决精度控制、效率平衡与格式适配等关键问题。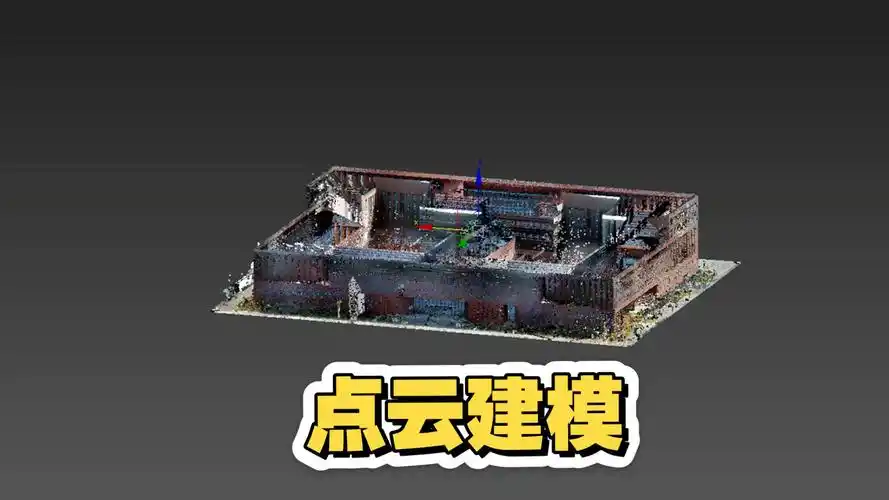
工程化应用代码示例:
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import trimesh
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation as R
class PointCloudApplication:
def __init__(self):
self.reference_model_path = "reference_model.ply"
self.tolerance = 0.005 # 5毫米精度 tolerance
def model_alignment(self, source_pcd, target_pcd):
"""点云配准与对齐"""
# 粗配准:使用FPFH特征
source_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
source_pcd,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.25, max_nn=100)
)
target_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
target_pcd,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.25, max_nn=100)
)
# RANSAC粗配准
result_ransac = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_pcd, target_pcd, source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
mutual_filter=True,
max_correspondence_distance=0.1,
estimation_method=o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(False),
ransac_n=3,
checkers=[
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(0.1)
],
criteria=o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999)
)
# 精配准:ICP算法
result_icp = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source_pcd, target_pcd, 0.02,
result_ransac.transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane()
)
print(f"配准误差: {result_icp.inlier_rmse}")
return result_icp.transformation
def dimensional_measurement(self, mesh, points):
"""基于点云模型的尺寸测量"""
# 转换点为numpy数组
points_np = np.asarray(points)
if len(points_np) < 2:
raise ValueError("至少需要两个点进行测量")
# 计算点之间的欧氏距离
distances = []
for i in range(len(points_np)-1):
dist = np.linalg.norm(points_np[i] - points_np[i+1])
distances.append(dist)
# 计算总面积(如果是闭合模型)
area = mesh.get_surface_area() if mesh.is_closed() else None
return {
"distances": distances,
"surface_area": area,
"unit": "meter"
}
def model_quality_inspection(self, scan_mesh, reference_mesh):
"""模型质量检测与偏差分析"""
# 将参考模型采样为点云
reference_pcd = reference_mesh.sample_points_uniformly(number_of_points=100000)
# 将扫描模型采样为点云
scan_pcd = scan_mesh.sample_points_uniformly(number_of_points=100000)
# 配准扫描模型到参考模型
transformation = self.model_alignment(scan_pcd, reference_pcd)
scan_pcd.transform(transformation)
scan_mesh.transform(transformation)
# 计算点到面的距离
distances = scan_pcd.compute_point_cloud_distance(reference_mesh)
distances = np.asarray(distances)
# 统计偏差
stats = {
"max_deviation": np.max(distances),
"min_deviation": np.min(distances),
"mean_deviation": np.mean(distances),
"std_deviation": np.std(distances),
"pass_rate": np.mean(distances < self.tolerance) * 100 # 合格率
}
# 可视化偏差分布
plt.hist(distances, bins=50)
plt.xlabel("偏差 (m)")
plt.ylabel("点数")
plt.title("模型偏差分布直方图")
plt.savefig("deviation_histogram.png")
return stats
def export_for_application(self, mesh, format_type="web"):
"""根据应用场景导出不同格式的模型"""
if format_type == "web":
# 为WebGL优化的轻量模型
simplified = mesh.simplify_quadric_decimation(10000)
o3d.io.write_glb(simplified, "model_web.glb")
return "model_web.glb"
elif format_type == "cad":
# 高精度CAD交换格式
o3d.io.write_step(mesh, "model_cad.step")
return "model_cad.step"
elif format_type == "ar":
# AR应用的轻量化模型
simplified = mesh.simplify_quadric_decimation(5000)
# 压缩纹理坐标
o3d.io.write_glb(simplified, "model_ar.glb")
return "model_ar.glb"
return None
# 应用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = PointCloudApplication()
# 加载重建模型和参考模型
scan_mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh("reconstructed_model.ply")
ref</doubaocanvas>























 884
884

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








