相信接触Android久一点的朋友对于LayoutInflater一定不会陌生,都会知道它主要是用于加载布局的。而刚接触Android的朋友可能对LayoutInflater不怎么熟悉,因为加载布局的任务通常都是在Activity中调用setContentView()方法来完成的。其实setContentView()方法的内部也是使用LayoutInflater来加载布局的,只不过这部分源码是internal的,看不到而已。那么今天我们就来把LayoutInflater的工作流程仔细地剖析一遍,也许还能解决掉某些困扰你心头多年的疑惑。
Button在界面上显示出来了!说明我们确实是借助LayoutInflater成功将button_layout这个布局添加到LinearLayout中了。LayoutInflater技术广泛应用于需要动态添加View的时候,比如在ScrollView和ListView中,经常都可以看到LayoutInflater的身影。
Layoutflater原理分析:
当然,仅仅只是介绍了如何使用LayoutInflater显然是远远无法满足大家的求知欲的,知其然也要知其所以然,接下来我们就从源码的角度上看一看LayoutInflater到底是如何工作的。
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext;
View result = root;
try {
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("merge can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
rInflate(parser, root, attrs);
} else {
View temp = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
rInflate(parser, temp, attrs);
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp;
}
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} catch (IOException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(
parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": " + e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
}
return result;
}
}
private void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
}
parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
} else {
final View view = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
}
}
parent.onFinishInflate();
} 这样的话,把整个布局文件都解析完成后就形成了一个完整的DOM结构,最终会把最顶层的根布局返回,至此inflate()过程全部结束。
inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)第三个参数attachToRoot又是什么意思呢?其实如果你仔细去阅读上面的源码应该可以自己分析出答案,这里我先将结论说一下吧,感兴趣的朋友可以再阅读一下源码,校验我的结论是否正确。
1. 如果root为null,attachToRoot将失去作用,设置任何值都没有意义。
2. 如果root不为null,attachToRoot设为true,则会给加载的布局文件的指定一个父布局,即root。
3. 如果root不为null,attachToRoot设为false,则会将布局文件最外层的所有layout属性进行设置,当该view被添加到父view当中时,这些layout属性会自动生效。
4. 在不设置attachToRoot参数的情况下,如果root不为null,attachToRoot参数默认为true。
好了,现在对LayoutInflater的工作原理和流程也搞清楚了。
杂谈:
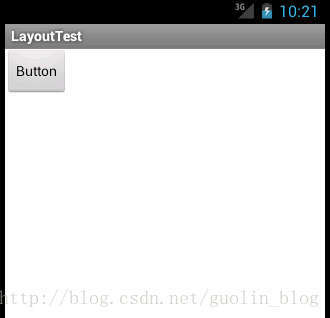
这个例子中的按钮看起来有点小,想要调大一些?那简单的呀,修改button_layout.xml中的代码,如下所示:
<Button xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="Button" >
</Button> 这里我们将按钮的宽度改成300dp,高度改成80dp,这样够大了吧?现在重新运行一下程序来观察效果。咦?怎么按钮还是原来的大小,没有任何变化!是不是按钮仍然不够大,再改大一点呢?还是没有用!
解析:其实这里不管你将Button的layout_width和layout_height的值修改成多少,都不会有任何效果的,因为这两个值现在已经完全失去了作用。平时我们经常使用layout_width和layout_height来设置View的大小,并且一直都能正常工作,就好像这两个属性确实是用于设置View的大小的。而实际上则不然,它们其实是用于设置View在布局中的大小的,也就是说,首先View必须存在于一个布局中,之后如果将layout_width设置成match_parent表示让View的宽度填充满布局,如果设置成wrap_content表示让View的宽度刚好可以包含其内容,如果设置成具体的数值则View的宽度会变成相应的数值。这也是为什么这两个属性叫作layout_width和layout_height,而不是width和height。
再来看一下我们的button_layout.xml吧,很明显Button这个控件目前不存在于任何布局当中,所以layout_width和layout_height这两个属性理所当然没有任何作用。那么怎样修改才能让按钮的大小改变呢?解决方法其实有很多种,最简单的方式就是在Button的外面再嵌套一层布局,如下所示:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="Button" >
</Button>
</RelativeLayout>
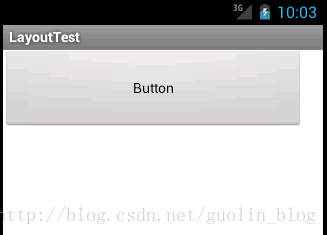
结论:这里我们又加入了一个RelativeLayout,此时的Button存在与RelativeLayout之中,layout_width和layout_height属性也就有作用了。当然,处于最外层的RelativeLayout,它的layout_width和layout_height则会失去作用。现在重新运行一下程序,结果如下图所示:
OK!按钮的终于可以变大了。
看到这里,也许有些朋友心中会有一个巨大的疑惑。不对呀!平时在Activity中指定布局文件的时候,最外层的那个布局指定大小是生效的呀。确实,这主要是因为,在setContentView()方法中,Android会自动在布局文件的最外层再嵌套一个FrameLayout,所以layout_width和layout_height属性才会有效果。那么我们来证实一下吧,修改MainActivity中的代码,如下所示:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private LinearLayout mainLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mainLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.main_layout);
ViewParent viewParent = mainLayout.getParent();
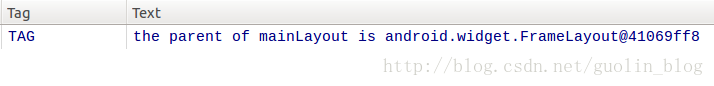
Log.d("TAG", "the parent of mainLayout is " + viewParent);
}
}
可以看到,这里通过findViewById()方法,拿到了activity_main布局中最外层的LinearLayout对象,然后调用它的getParent()方法获取它的父布局,再通过Log打印出来。现在重新运行一下程序,结果如下图所示:
非常正确!LinearLayout的父布局确实是一个FrameLayout,而这个FrameLayout就是由系统自动帮我们添加上的。
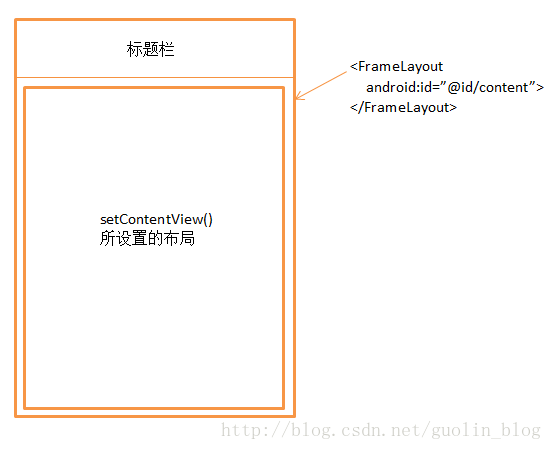
说到这里,虽然setContentView()方法大家都会用,但实际上Android界面显示的原理要比我们所看到的东西复杂得多。任何一个Activity中显示的界面其实主要都由两部分组成,标题栏和内容布局。标题栏就是在很多界面顶部显示的那部分内容,比如刚刚我们的那个例子当中就有标题栏,可以在代码中控制让它是否显示。而内容布局就是一个FrameLayout,这个布局的id叫作content,我们调用setContentView()方法时所传入的布局其实就是放到这个FrameLayout中的,这也是为什么这个方法名叫作setContentView(),而不是叫setView()。
最后再附上一张Activity窗口的组成图吧,以便于大家更加直观地理解:
OK,暂时讲到这里。






















 2021
2021

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








