Johnson算法可以在O(V*V lgV + VE)的时间内找到所有节点对之间的最短路径,对于稀疏图来说,算法的渐进表现要由于重复平方法和FloydWarshall算法,如果图没有权值为负值的环路,则返回所有结点对的最短路径权重的矩阵,否则,报告图有权值为负的环
算法中运用Diskra、BellmanFord算法,使用的技术是重新赋予权重,
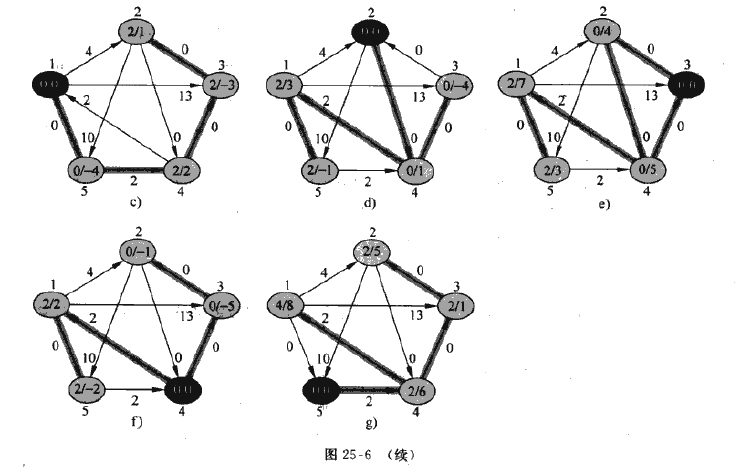
如果图G = (V, E)中权值全为非负值,则通过对所有结点运行一次dijkstra算法找出所有结点对的最短路径,
如果有非负值,但没有权重为负值的环路,那么只要计算出一组新的非负权重值,然后再用相同的方法即可。
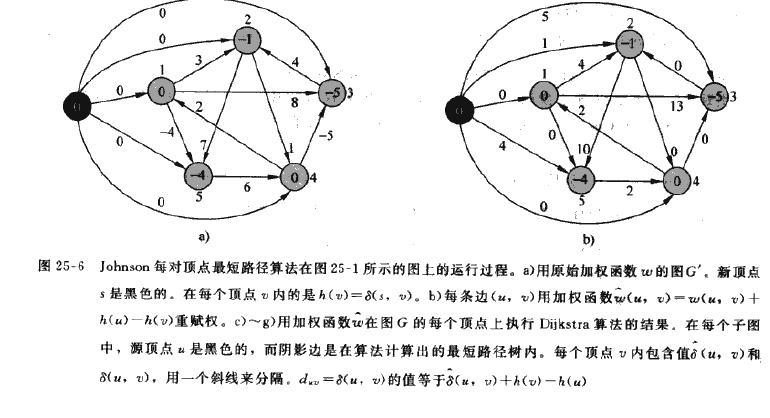
对于将负值权重转换为非负值使用的方法是,在原图上新加一个结点s,并将w(s, v) == 0, 然后对s运行BellmanFord函数计算出s到其他点的最短路径,
运用一个h[vexnum]数组存放这个值,h[i] = σ(s, v),即s到v的最短路径值。
这个值相当于将每个结点赋予一个一个值,这些值用于重新计算边的权重ww(u, v) = w(u, v) + h(u) - h(v),重新计算出来的权重即为非负值。
以下是代码的运行过程图,书410页:
以下为代码:
/************************************************************
Johnson.h: Johnson算法,存储为邻接表,
Date: 2014/1/5
Author: searchop
************************************************************/
#ifndef ALGRAPH_H
#define ALGRAPH_H
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
//邻接表的结构
struct ArcNode //表结点
{
int source; //图中该弧的源节点
int adjvex; //该弧所指向的顶点的位置
ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条弧的指针
int weight; //每条边的权重
};
template <typename VertexType>
struct VertexNode //头结点
{
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条依附于该顶点的弧的指针
int key; //Prim:保存连接该顶点和树中结点的所有边中最小边的权重;
//BellmanFord:记录从源结点到该结点的最短路径权重的上界
VertexNode *p; //指向在树中的父节点
int indegree; //记录每个顶点的入度
};
const int SIZE = 6;
//图的操作
template <typename VertexType>
class ALGraph
{
public:
typedef VertexNode<VertexType> VNode;
ALGraph(int verNum) : vexnum(verNum), arcnum(0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_VERTEX_NUM; i++)
{
vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
vertices[i].key = INT_MAX/2;
vertices[i].p = NULL;
vertices[i].indegree = 0;
}
}
//构造算法导论410页图(带权有向图)
void createWDG()
{
cout << "构造算法导论410页图(带权有向图)..." << endl;
int i;
for (i = 1; i < vexnum; i++)
vertices[i].data = 'a' + i - 1;
insertArc(1, 2, 3);
insertArc(1, 3, 8);
insertArc(1, 5, -4);
insertArc(2, 4, 1);
insertArc(2, 5, 7);
insertArc(3, 2, 4);
insertArc(4, 3, -5);
insertArc(4, 1, 2);
insertArc(5, 4, 6);
}
void createG()
{
cout << "构造图G'...." << endl;
vertices[0].data = 's';
insertArc(0, 1, 0);
insertArc(0, 2, 0);
insertArc(0, 3, 0);
insertArc(0, 4, 0);
insertArc(0, 5, 0);
}
//Johnson算法,先使用BellmanFord算法,使所有的边的权重变为非负值,
//然后运用dijkstra算法求出结点对的最短路径
int **Johnson()
{
createG(); //构造G’
displayGraph();
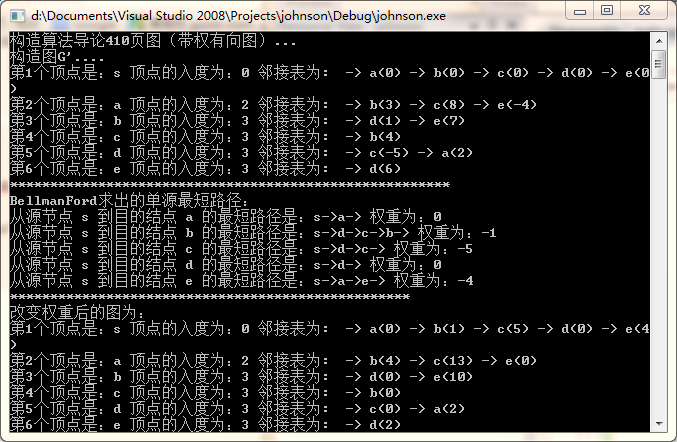
if (!BellmanFord(1))
cout << "the input graph contains a negative-weight cycle" << endl;
else
{
int h[SIZE];
int i, j, k;
//将数组h[]的值设为运行BellmanFord后取得的值,h[i]为结点s到其他点的最短路径
for (i = 0; i < vexnum; i++)
h[i] = vertices[i].key;
//遍历所有的边,将边的权值重新赋值,即将所有的边的权值改为负值
for (i = 0; i < vexnum; i++)
{
ArcNode *arc = vertices[i].firstarc;
for (; arc != NULL; arc = arc->nextarc)
arc->weight = arc->weight + h[arc->source] - h[arc->adjvex];
}
以下为代码:
cout << "改变权重后的图为:" << endl; displayGraph();
int **d = new int *[SIZE];
for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++)
d[j] = new int[SIZE];
//对每个结点运行dijkstra算法,求出每个点到其他点的最短路径,保存在key中
for (k = 1; k < SIZE; k++)
{
Dijkstra(k+1);
for (i = 1; i < SIZE; i++)
d[k][i] = vertices[i].key + h[i] - h[k];
}
cout << "最后计算出的结点对的最短距离:" << endl;
displayTwoDimArray(d);
return d;
}
}
//输出一个二维数组
void displayTwoDimArray(int **p)
{
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++)
cout << p[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" << endl;
}
//打印邻接链表
virtual void displayGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < vexnum; i++)
{
cout << "第" << i+1 << "个顶点是:" << vertices[i].data
<< " 顶点的入度为:" << vertices[i].indegree << " 邻接表为: ";
ArcNode *arcNode = vertices[i].firstarc;
while (arcNode != NULL)
{
cout << " -> " << vertices[arcNode->adjvex].data
<< "(" << arcNode->weight << ")";
arcNode = arcNode->nextarc;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "*******************************************************" << endl;
}
//PVnode排序准则
class PVNodeCompare
{
public:
bool operator() (VNode *pvnode1, VNode *pvnode2)
{
return pvnode1->key > pvnode2->key;
}
};
//对每个结点的最短路径估计和前驱结点进行初始化,最短路径初始化为INT_MAX, p初始化为NULL
//并将源节点的key初始化为0
void InitalizeSingleSource(int index)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_VERTEX_NUM; i++)
{
vertices[i].key = INT_MAX>>2;
vertices[i].p = NULL;
}
vertices[index].key = 0;
}
//对边(u, v)进行松弛,将目前s到v的最短路径v.key与s到u的最短路径加上w(u, v)的值进行比较
//如果比后面的值还大,则进行更新,将v.key缩短,并且将p置为u
void relax(ArcNode *arc)
{
//竟然溢出了!!
if (vertices[arc->adjvex].key > vertices[arc->source].key + arc->weight)
{
vertices[arc->adjvex].key = vertices[arc->source].key + arc->weight;
vertices[arc->adjvex].p = &vertices[arc->source];
}
}
//BellmanFord, index为实际第几个点
bool BellmanFord(int index)
{
InitalizeSingleSource(index-1);
for (int i = 1; i < vexnum; i++) //循环共进行vexnum-1次
{
//遍历所有的边,并对每个边进行一次松弛
for (int j = 0; j < vexnum; j++)
{
for (ArcNode *arc = vertices[j].firstarc; arc != NULL; arc = arc->nextarc)
relax(arc);
}
}
//再次遍历所有的边,检查图中是否存在权重为负值的环路,如果存在,则返回false
for (int j = 0; j < vexnum; j++)
{
for (ArcNode *arc = vertices[0].firstarc; arc != NULL; arc = arc->nextarc)
{
if (vertices[arc->adjvex].key > vertices[arc->source].key + arc->weight)
return false;
}
}
cout << "BellmanFord求出的单源最短路径:" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < vexnum; i++)
{
printPath(index-1, i);
}
cout << "**************************************************" << endl;
return true;
}
void Dijkstra(int index)
{
InitalizeSingleSource(index-1);
vector<VNode> snode; //保存已经找到最短路径的结点
vector<VNode *> que; //保存结点的指针的数组,用这个数组执行堆的算法
//将结点指针进队列,形成以key为关键值的最小堆
for (int i = 0; i < vexnum; i++)
que.push_back(&(vertices[i]));
//使que按照pvnodecompare准则构成一个最小堆
make_heap(que.begin(), que.end(), PVNodeCompare());
while (que.empty() == false)
{
//将队列中拥有最小key的结点出队
VNode *node = que.front();
pop_heap(que.begin(), que.end(), PVNodeCompare()); //从堆中删除最小的结点,只是放到了vector的最后
que.pop_back(); //将vector中的这个结点彻底删除,因为后面还要再排序一次,以免影响后面的堆排序,pop算法。
snode.push_back(*node);
for (ArcNode *arc = node->firstarc; arc != NULL; arc = arc->nextarc)
relax(arc);
make_heap(que.begin(), que.end(), PVNodeCompare());
}
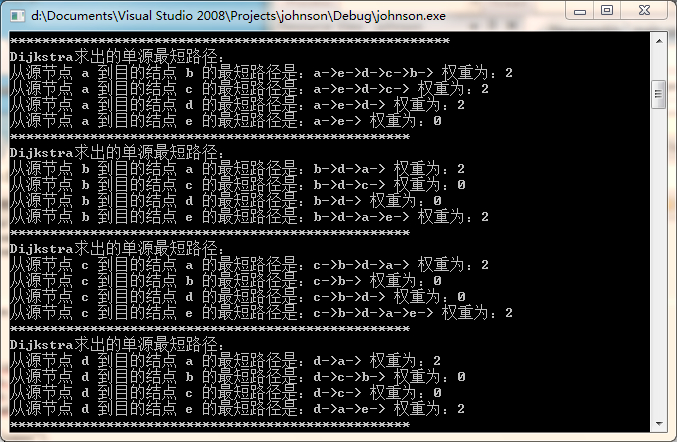
cout << "Dijkstra求出的单源最短路径:" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < vexnum; i++)
{
if (i != index-1)
printPath(index-1, i);
}
cout << "**************************************************" << endl;
}
protected:
//插入一个表结点
void insertArc(int vHead, int vTail, int weight)
{
//构造一个表结点
ArcNode *newArcNode = new ArcNode;
newArcNode->source = vHead;
newArcNode->adjvex = vTail;
newArcNode->nextarc = NULL;
newArcNode->weight = weight;
//arcNode 是vertics[vHead]的邻接表
ArcNode *arcNode = vertices[vHead].firstarc;
if (arcNode == NULL)
vertices[vHead].firstarc = newArcNode;
else
{
while (arcNode->nextarc != NULL)
{
arcNode = arcNode->nextarc;
}
arcNode->nextarc = newArcNode;
}
arcnum++;
vertices[vTail].indegree++; //对弧的尾结点的入度加1
}
//打印源节点到i的最短路径
void printPath(int i, int j)
{
cout << "从源节点 " << vertices[i].data << " 到目的结点 "
<< vertices[j].data << " 的最短路径是:" /*<< endl*/;
__printPath(&vertices[i], &vertices[j]);
cout << " 权重为:" << vertices[j].key << endl;
}
void __printPath(VNode* source, VNode* dest)
{
if (source == dest)
cout << source->data << "->";
else if (dest->p == NULL)
cout << " no path!" << endl;
else
{
__printPath(source, dest->p);
cout << dest->data << "->";
}
}
private:
//const数据成员必须在构造函数里初始化
static const int MAX_VERTEX_NUM = 20; //最大顶点个数
VNode vertices[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //存放结点的数组
int vexnum; //图的当前顶点数
int arcnum; //图的弧数
};
#endif#include "johnson.h"
int main()
{
ALGraph<char> wdgGraph(6);
wdgGraph.createWDG();
wdgGraph.Johnson();
/*wdgGraph.displayGraph();*/
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行时间分析:
BellmanFord的运行时间为O(V*E)
Dijkstra运用斐波那契堆来实现的话为O(VlgV + E),总共运行V次,则为O(V*VlgV + VE)
所以Johnson算法运行时间为以下为代码:O(V*VlgV + VE)






















 6186
6186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








