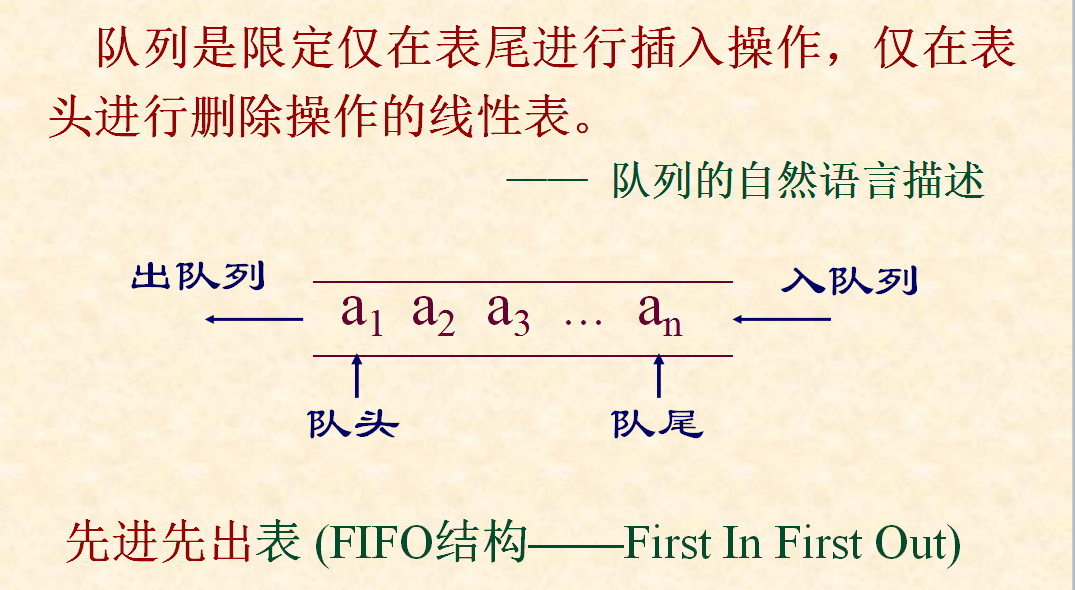
队列终于要上场了,等很久喽,那就闲言少叙,言归正传,何为队列?请看下图:
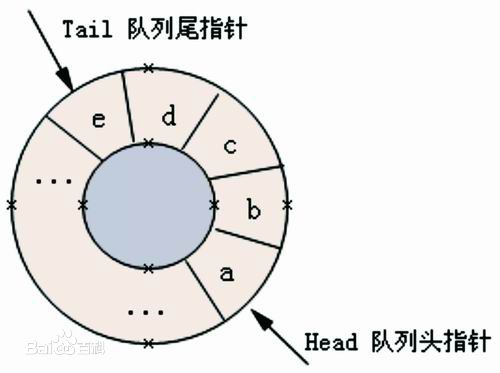
那何谓循环队列呢?这个,所谓一图胜千言,还是看图吧:
原来循环顺序表(线性表的顺序存储方式)的队列形式啊,懂了,兼具循环顺序表和队列两重特性,在实际中还是挺有用的,然后还是老规矩在代码和注释中看看循环队列的各种操作,接下来就是程序员与程序员之间的对话了:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//定义函数结果状态码
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
//定义循环队列空间大小
#define QUEUESIZE 20
//定义数据类型
typedef int ElemType ;
//定义程序返回状态类型
typedef int Status;
//循环队列存储结构
typedef struct _CircleQueue
{
ElemType data[QUEUESIZE]; //存储队列元素空间
int front; //队列头指针
int rear; //队列尾指针
int count; //队列元素个数
}CircleQueue;
/*************************************************
Function: InitQueue
Description: 初始化,构造空队列
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 成功返回OK
Others: 空队列 queue->front = queue->rear = 0
*************************************************/
Status InitQueue(CircleQueue *queue)
{
queue.data = (ElemType *)malloc(QUEUESIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
queue->front = queue->rear = 0;
queue->count = 0;
return OK;
}
//判断循环队列为空和满,一般来说有以下三种方法:
//1、使用计数器count,队列为空和满时,front都等于rear,本程序中采用的是这种方法。
//2、少用一个元素的空间,约定队列满时:(rear+1)%QUEUESIZE=front,为空时front=rear
// rear指向队尾元素的下一个位置,始终为空;队列的长度为(rear-front+QUEUESIZE)%QUEUESIZE。
// 强调一下,这种方法会保留一个元素空间。
//3、设置一个标志变量flag,当front == rear,且flag = 0 时为队列空,当front == rear,
// 且flag= 1时为队列满。
/*************************************************
Function: IsQueueEmpty
Description: 队列是否为空
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 为空返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE
Others:
*************************************************/
Status IsQueueEmpty(CircleQueue *queue)
{
if(queue->count == 0)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/*************************************************
Function: IsQueueFull
Description: 队列是否为满
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 为满返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE
Others:
*************************************************/
Status IsQueueFull(CircleQueue *queue)
{
if(queue->count == QUEUESIZE)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/*************************************************
Function: EnQueue
Description: 入队
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
数据元素 ElemType e
Output:
Return: 成功返回OK,失败返回ERROR
Others:
*************************************************/
Status EnQueue(CircleQueue *queue, ElemType e)
{
//验证队列是否已满
if(queue->count == QUEUESIZE)
{
printf("The queue is full");
return ERROR;
}
//入队
queue->data[queue->rear] = e;
//队尾指针后移
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % QUEUESIZE;
//更新队列长度
queue->count++;
return OK;
}
/*************************************************
Function: DeQueue
Description: 出队
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 成功返回数据元素,失败程序退出
Others:
*************************************************/
ElemType DeQueue(CircleQueue *queue)
{
//判断队列是否为空
if(queue->count == 0)
{
printf("The queue is empty!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//保存返回值
ElemType e = queue->data[queue->front];
//更新队头指针
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % QUEUESIZE;
//更新队列长度
queue->count--;
return e;
}
/*************************************************
Function: GetHead
Description: 取队头元素
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 成功返回数据元素,否则程序退出
Others:
*************************************************/
ElemType GetHead(CircleQueue *queue)
{
//判断队列是否为空
if(queue->count == 0)
{
printf("The queue is empty!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return queue->data[queue->front];
}
/*************************************************
Function: TraverseQueue
Description: 遍历整个队列
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 无
*************************************************/
void TraverseQueue(CircleQueue *queue)
{
int i = queue.front; //首先获取队列头指针
while(i != queue.rear) //以是否到尾指针来进行判断
{
printf("%d ",queue.data[i]);
i = (i+1) % QUEUESIZE; //这一步很重要,自己体会,嘿嘿!
}
printf("\n");
}
/*************************************************
Function: ClearQueue
Description: 清空队列
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 成功返回OK
Others:
*************************************************/
Status ClearQueue(CircleQueue *queue )
{
queue->front = queue->rear = 0;
queue->count = 0;
return OK;
}
/*************************************************
Function: GetLength
Description: 取得队列的长度
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 返回队列的长度
Others:
*************************************************/
int GetLength(CircleQueue *queue)
{
return queue->count;
}
/*************************************************
Function: DestroyQueue
Description: 销毁队列
Input: 队列指针 CircleQueue *queue
Output:
Return: 成功返回OK
Others:
*************************************************/
Status DestroyQueue(CircleQueue *queue )
{
ClearQueue( queue ); //首先清空队列
if(queue.data)
{
free(queue.data); //然后销毁存储队列元素的数组空间
queue.data = NULL; //因为数组在内存里本质上就是指针,所以这一步是防止野指针的出现
}
free(queue); //最后销毁循环队列结构体
return OK;
}和栈一样,队列的时间复杂度也是O(1);空间的话就是一个固定的数组长度了,一谈到固定,弊端就出来了,很多时候无法固定的,所以固定了很容易溢出,怎么办,这时候可以考虑链队列,链队列就下期见喽!






















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








