什么是观察者模式
当一个对象中的数据被多个对象所依赖,并且当被依赖发生变化的时候,会通知所有的依赖项。我们称这种模式为观察模式,被依赖的对象我们称之为目标,依赖项我们称之为观察者。
观察者模式与订阅发布者模式的区别
1、观察者模式
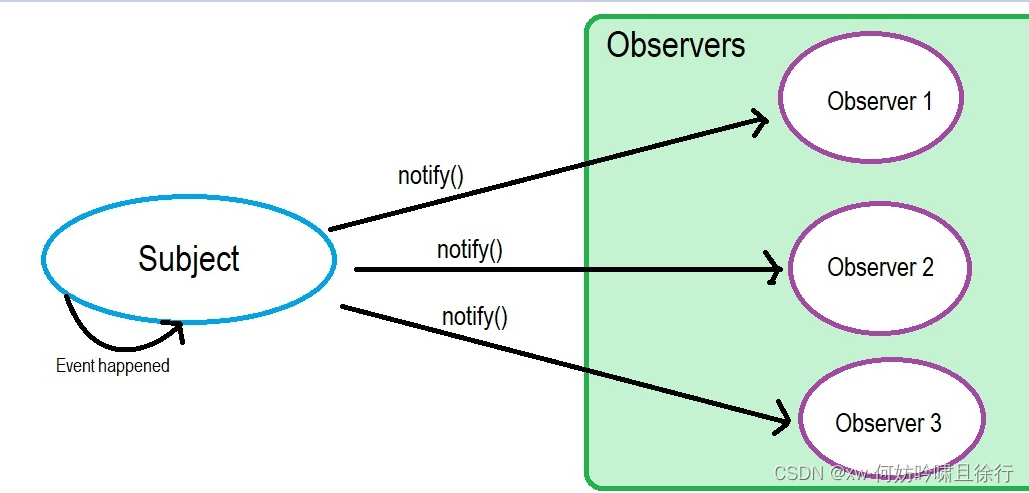
在观察者模式中,目标与观察者是直接通信的。他们知道彼此的存在,当被依赖项发生变化时,是目标直接通知观察者的。
观察者模式里面,changed()方法所在的实例对象,就是被观察者(Subject,或者叫Observable),它只需维护一套观察者(Observer)的集合,这些Observer实现相同的接口,Subject只需要知道,通知Observer时,需要调用哪个统一方法就好了。
2、订阅发布者模式
而在订阅与发布者模式中,订阅者与发布者之间是通过统一的调度中心来实现数据的通信(比如兄弟组件通信中的eventBus就是信息的中间传递着),他们彼此并不知道对方的存在。当发布者发布信息的时候,是先传到统一的调度中心,再由调度中心统一传递给所有订阅者。
在发布订阅模式里,发布者,并不会直接通知订阅者,发布者和订阅者,彼此互不相识,完全解耦。
订阅者与发布者通过第三者,也就是在消息队列里面,我们常说的经纪人Broker。

发布者只需告诉Broker,我要发的消息,topic是AAA;
订阅者只需告诉Broker,我要订阅topic是AAA的消息;
于是,当Broker收到发布者发过来消息,并且topic是AAA时,就会把消息推送给订阅了topic是AAA的订阅者。
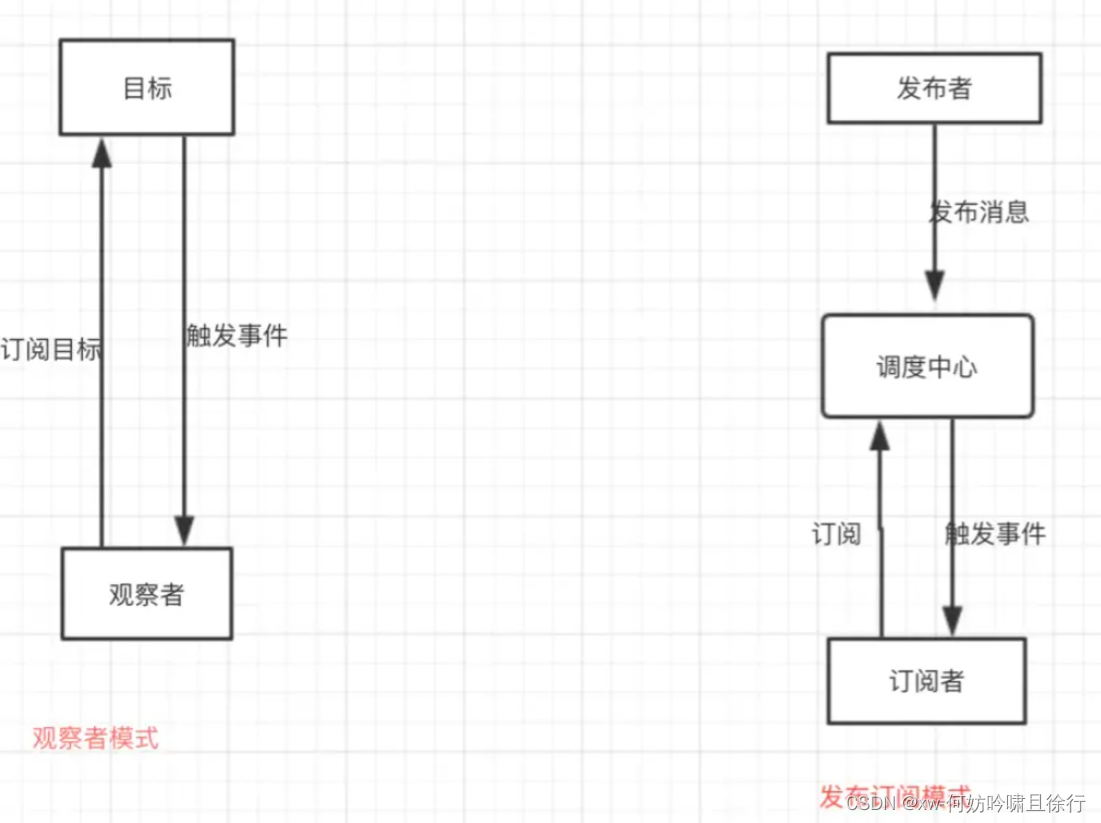
这两个模式的区别,如下简图所示:

总结
从表面上看:
- 观察者模式里,只有两个角色 —— 观察者 + 被观察者
- 而发布订阅模式里,却不仅仅只有发布者和订阅者两个角色,还有一个经常被我们忽略的 —— 经纪人Broker
往更深层次讲:
- 观察者和被观察者,是松耦合的关系
- 发布者和订阅者,则完全不存在耦合
从使用层面上讲:
- 观察者模式,多用于单个应用内部
- 发布订阅模式,则更多的是一种跨应用的模式(cross-application pattern),比如我们常用的消息中间件
参考:
观察者模式 vs 发布订阅模式 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
面试官:Vue中的观察者模式 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
------------------------------------------------- 代码实现:发布订阅 ---------------------------------------------------
//subject.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mutex>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CObserver
{
public:
CObserver(int nType);
virtual ~CObserver() {};
virtual void OnNotify(int nEvent, const char* pMsg, int nLen) {};
virtual void SetType(int nType);
virtual int GetType() const;
private:
int m_nType;
};
CObserver::CObserver(int nType) :m_nType(nType)
{
//TODU
}
void CObserver::SetType(int nType)
{
m_nType = nType;
}
int CObserver::GetType() const
{
return m_nType;
}
class CSubject
{
public:
CSubject();
virtual ~CSubject();
virtual void Add(CObserver* po);
virtual void Del(CObserver* po);
virtual void Notify(CObserver* pSender, int nEvent, const char* pMsg, int dwLen);
void ClearObserver();
std::list<CObserver*>* GetObservers();
CObserver* GetObserver(int nType);
private:
list<CObserver*>* m_pListObserver;
mutex* m_pListLock;
};
CSubject::CSubject() :m_pListObserver(NULL), m_pListLock(NULL)
{
m_pListObserver = new list<CObserver*>;
m_pListLock = new mutex;
}
CSubject::~CSubject()
{
if(m_pListObserver)
{
m_pListObserver->clear();
delete m_pListObserver;
m_pListObserver = NULL;
}
if (m_pListLock)
{
delete m_pListLock;
m_pListLock = NULL;
}
}
void CSubject::Add(CObserver* po)
{
if (m_pListObserver == NULL)
{
return;
}
m_pListLock->lock();
if (find(m_pListObserver->begin(), m_pListObserver->end(), po) == m_pListObserver->end())
{
m_pListObserver->push_back(po);
}
m_pListLock->unlock();
}
void CSubject::Del(CObserver* po)
{
if (NULL == m_pListObserver)
{
return;
}
m_pListLock->lock();
if (find(m_pListObserver->begin(), m_pListObserver->end(), po) != m_pListObserver->end())
{
m_pListObserver->remove(po);
}
m_pListLock->unlock();
}
void CSubject::Notify(CObserver* pSender, int nEvevt, const char* pMsg, int dwLen)
{
if (NULL == m_pListObserver)
{
return;
}
m_pListLock->lock();
list<CObserver*>::iterator ite;
ite = m_pListObserver->begin();
while (ite != m_pListObserver->end())
{
CObserver* po = *(ite);
//pSender != NULL 点对点通知 通知pSender
//pSender == NULL 广播 通知到所有Observer
if ((pSender == NULL || po == pSender) && (po != NULL))
{
po->OnNotify(nEvevt, pMsg, dwLen);
}
ite++;
}
m_pListLock->unlock();
}
void CSubject::ClearObserver()
{
m_pListLock->lock();
m_pListObserver->clear();
m_pListLock->unlock();
}
list<CObserver*>* CSubject::GetObservers()
{
return m_pListObserver;
}
CObserver* CSubject::GetObserver(int nType)
{
m_pListLock->lock();
list<CObserver*>::iterator ite;
ite = m_pListObserver->begin();
while (ite != m_pListObserver->end())
{
CObserver* po = *(ite);
if (po != NULL && po->GetType() == nType)
{
return po;
}
ite++;
}
m_pListLock->unlock();
return NULL;
}
//派生类
class CMyObserver : public CObserver
{
public:
CMyObserver(int nType);
void OnNotify(int nEvent, const char* pMsg, int nLen);
};
CMyObserver::CMyObserver(int nType) : CObserver(nType) {}
void CMyObserver::OnNotify(int nEvent, const char* pMsg, int nLen)
{
cout << nEvent << endl;
cout << pMsg << endl;
cout << nLen << endl;
}
//测试例
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Observer.h"
int main()
{
/****************** 观察者模式验证 **********************/
CObserver* po1 = new CMyObserver(1);
CObserver* po2 = new CMyObserver(2);
CSubject* psub = new CSubject();
psub->Add(po1);
psub->Add(po2);
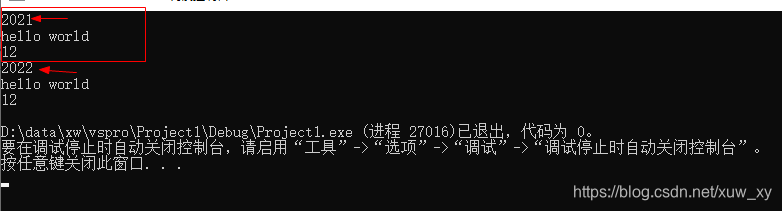
psub->Notify(po1,2021,"hello world",12);
psub->Notify(po2, 2022, "hello world", 12);
}
//测试结果截图 消息通知成功
注:观察者模式 vs 发布订阅模式 介绍可参考下述链接
参考:























 1531
1531











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










