Foreword
既然今天把莫队算法给复习了,又要准备AC糖果公园,那么就把树上莫队也给再写一遍先吧……
Overview
You are given a tree with N nodes. The tree nodes are numbered from 1 to N. Each node has an integer weight.
We will ask you to perfrom the following operation:
u v : ask for how many different integers that represent the weight of nodes there are on the path from u to v.
Input
In the first line there are two integers N and M.(N<=40000,M<=100000)
In the second line there are N integers.The ith integer denotes the weight of the ith node.
In the next N-1 lines,each line contains two integers u v,which describes an edge (u,v).
In the next M lines,each line contains two integers u v,which means an operation asking for how many different integers that represent the weight of nodes there are on the path from u to v.
Output
For each operation,print its result.
Example
Input:
8 2
105 2 9 3 8 5 7 7
1 2
1 3
1 4
3 5
3 6
3 7
4 8
2 5
7 8
Output:
4
4
Analysis
1. 树上莫队
首先我们想到的是离线算法,这里可以使用莫队算法,也就是把链上的莫队推广到树上。
通过求一个欧拉序列即可,记录序列 lis[2N] ,每个点的第一个位置 in[N] ,每个点的第二个位置 out[N] 。
类似的题解很多很多,此处不在赘述,只是重点讲一下如何确定所求的区间。
对于
x
,
①
{x,y}={lis[l],lis[r]}
②
∀i∈[l,r]
,
lis[i]∉{x,y}
也就是把 [in[x],out[x]] , [in[y],out[y]] 当成两条线段,考虑情况。
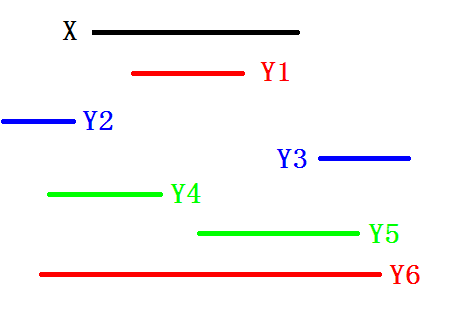
我们通过分类讨论线段间的关系,两条线段的情况有以下
6
种:
①对于
性质,不可能成立。
②对于
Y1
和
Y6
的包含关系,应该取区间
[min(in[x],in[y]),max(in[x],in[y])]
。
③对于
Y2
和
Y3
的相离关系,应该取区间
[min(out[x],out[y]),min(in[x],in[y])]
。
还要注意:情况②的区间即最近公共祖先是
x
和
还有就是这道题要用异或值来搞,这里不讲了。
时间复杂度: O(nn−√)
2. 可持久化线段树
记录当点到根的路径的上一个权值相同的坐标。
以坐标建立可持久化线段树。
区间减法解决问题。
时间复杂度: O(nlogn)
Code
树上莫队。
实测 2420 MS。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=65536;
const int S=131072;
const int M=131072;
const int U=20;
int n,a[N];
struct D
{
int w,id;
friend inline int operator < (D da,D db)
{
return da.w<db.w;
}
}d[N];
int num;
int rt=1;
struct G
{
int v,nxt;
}mp[N<<1];
int tt,hd[N];
inline int read(void)
{
int x=0,f=1; char c=getchar();
for (;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if (c=='-') f=-1;
for (;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) x=x*10+c-'0';
return x*f;
}
inline void ins(int u,int v)
{
mp[++tt].v=v;
mp[tt].nxt=hd[u];
hd[u]=tt;
}
int vis[N];
int in[N],out[N];
int lis[S],len;
int unit;
int dep[N];
int pre[U][N];
void dfs(int now,int ht)
{
vis[now]=1,dep[now]=ht;
lis[in[now]=++len]=now;
for (int k=hd[now];k;k=mp[k].nxt)
if (!vis[mp[k].v]) pre[0][mp[k].v]=now,dfs(mp[k].v,ht+1);
lis[out[now]=++len]=now;
}
int m,unit1;
struct Ques
{
int fl,fr,anc;
int l,r;
int id;
inline void getlr(void)
{
if (anc==fl||anc==fr)
{
l=min(in[fl],in[fr]);
r=max(in[fl],in[fr]);
}
else
{
l=min(out[fl],out[fr]);
r=max(in[fl],in[fr]);
}
}
friend inline int operator < (Ques qa,Ques qb)
{
return qa.l/unit1!=qb.l/unit1?qa.l/unit1<qb.l/unit1:qa.r<qb.r;
}
}q[M];
int ans[M];
inline int LCA(int x,int y)
{
if (dep[x]<dep[y]) swap(x,y);
for (int i=unit;i>=0;i--)
if (dep[x]-(1<<i)>=dep[y]) x=pre[i][x];
if (x==y) return x;
for (int i=unit;i>=0;i--)
if (pre[i][x]!=pre[i][y]) x=pre[i][x],y=pre[i][y];
return pre[0][x];
}
int l,r;
int cnt[N],sta[N];
int res;
inline void upd(int loc)
{
res-=cnt[a[loc]]>0;
cnt[a[loc]]+=sta[loc]?-1:1;
sta[loc]^=1;
res+=cnt[a[loc]]>0;
}
int main(void)
{
n=read(),m=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) d[i].w=read(),d[i].id=i;
sort(d+1,d+n+1);
a[d[1].id]=num=1;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if (d[i].w!=d[i-1].w) num++;
a[d[i].id]=num;
}
int u,v;
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
u=read(),v=read();
ins(u,v),ins(v,u);
}
unit=(int)(log(n)/log(2));
pre[0][rt]=rt;
dfs(rt,1);
for (int i=1;i<=unit;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=n;j++)
pre[i][j]=pre[i-1][pre[i-1][j]];
unit1=(int)sqrt(len);
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
q[i].id=i;
q[i].fl=read(),q[i].fr=read();
q[i].anc=LCA(q[i].fl,q[i].fr);
q[i].getlr();
}
sort(q+1,q+m+1);
l=1,r=0;
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
for (;l<q[i].l;l++) upd(lis[l]);
for (;l>q[i].l;l--) upd(lis[l-1]);
for (;r<q[i].r;r++) upd(lis[r+1]);
for (;r>q[i].r;r--) upd(lis[r]);
if (q[i].fl==q[i].anc||q[i].fr==q[i].anc)
ans[q[i].id]=res;
else
{
upd(q[i].anc);
ans[q[i].id]=res;
upd(q[i].anc);
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}小结
1. 静态调试
反正家里的电脑暂时不能动态调试,那就要使用静态调试,这里总结一下静态调试的几个技巧。
【技巧1】我们把某些过程打上注释符号,运行程序。
①若RE,那么没有打上注释符号的地方有问题;
②若没有RE,那么没有打上注释符号的地方没有问题。
通常可以从头到尾逐渐缩小注释符号的范围,一段一段的处理检查错误。
【技巧2】运行程序没有出现RE也不一定正确呀,可以输出值看看正不正确。
弄得像找电路故障一样......
2. 树上莫队
【注意点1】在把树的路径转到线段上时,通过分类讨论两条线段的位置情况能更好地找到对应区间。
【注意点2】考虑LCA:包含情况不用考虑LCA,相交情况要考虑LCA。
【注意点3】特别注意莫队算法用于排序的重载运算符”
<
<script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-29"><</script>”的写法。
(PS:一天连续写错2次QAQ)

























 1177
1177











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








