Day 04
文章目录
链表 Part 02
5. 两两交换链表中的节点(力扣24)
- 题目描述:两两交换链表中的结点
- 思路:题目中说不改变结点的内容,只进行交换,意思就是只 对链表指针的指向进行修改。
- 要用虚拟头结点,这样可以对所有节点一视同仁的操作。
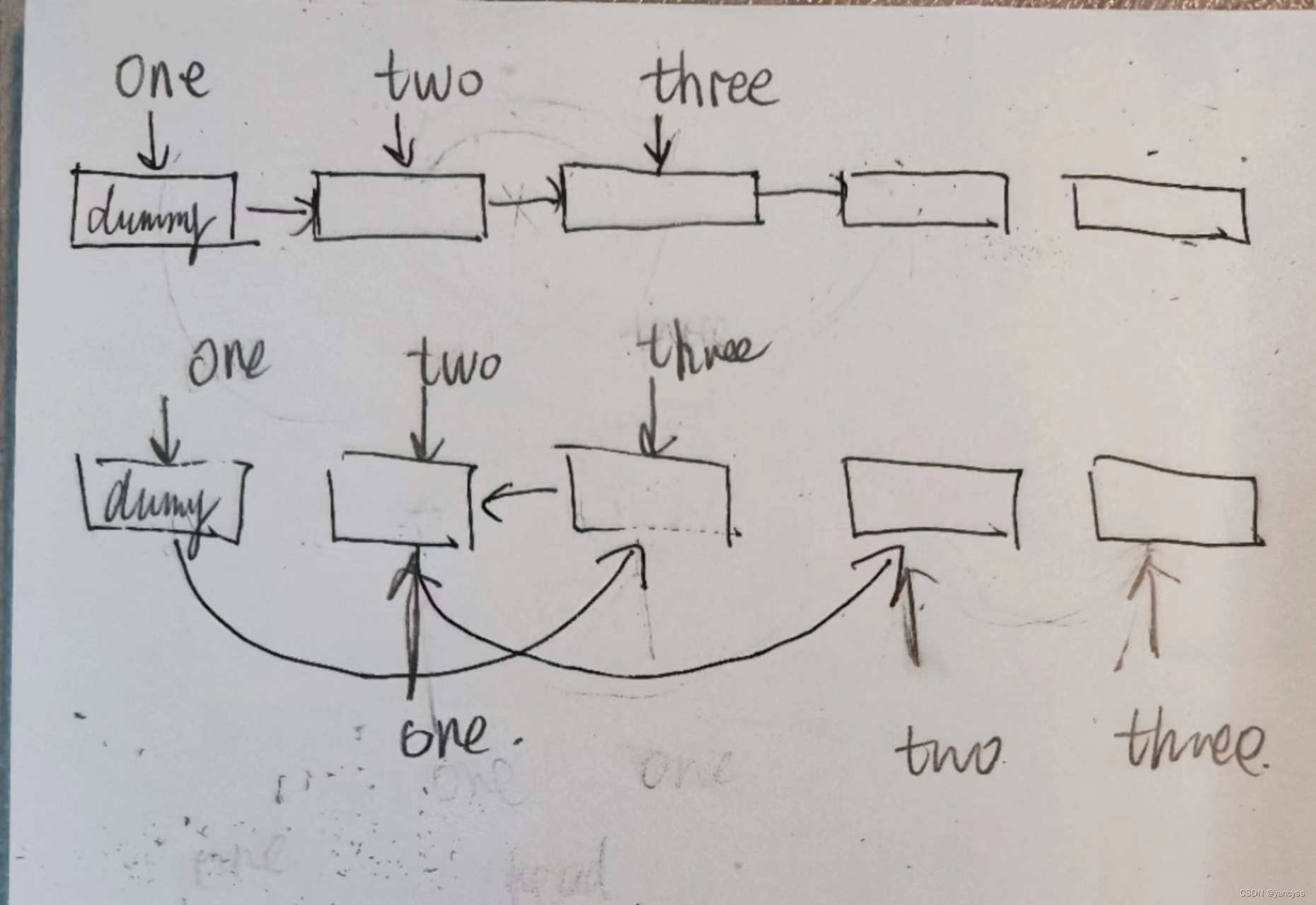
- 因为涉及到三个节点的指针改变指向,所以这里设计三个指针,one two three。然后,想象将箭头拔下来,再插到预想的位置(下面那个图,把线扯平就是调换后的顺序啦~)。顺序上,因为有了one two three三个指针,这三个节点我们都能随时找得到,但是three的下一个节点需要three.next来指示,因此需要先把two的箭头插到three.next节点上。其余两个箭头拔插的顺序随意。
- 一轮拔插后,再移动one two three三个节点向后,可以使用while循环,也可以用递归的方法。
- Python 语法细节
- python 逻辑求值的短路规则:因为这需要判断one 的下一个节点,和下下个节点是否有值,但是当one.next为空时,使用one.next.next会报错。而短路规则可以实现如果one.next为空,逻辑短路,不再向下求值。
while one.next and one.next.next

- 写递归调用的时候,最后一行不能只写调用函数,要加return
- Python实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
## 三个指针交换法
# dummy_head = ListNode(next=head)
# one = dummy_head
# while one.next and one.next.next:
# two = one.next
# three = two.next
# two.next = three.next
# one.next = three
# three.next = two
# one = two
# return dummy_head.next
## 递归法
dummy_head = ListNode(next=head)
one = dummy_head
return self.swap(one,dummy_head)
def swap(self,one,dummy_head):
if not one.next or not one.next.next:
return dummy_head.next
two = one.next
three = two.next
two.next = three.next
one.next = three
three.next = two
one = two
return self.swap(one,dummy_head)
- C++语法细节
- 在一个成员函数中定义的局部变量其他成员函数无法访问
- C++实现
class Solution {
private:
ListNode* one = nullptr, *two = nullptr, *three = nullptr;
ListNode* result = nullptr;
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
// //三指针法
// ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
// ListNode* one = dummy;
// ListNode* two = nullptr;
// ListNode* three = nullptr;
// while (one->next and one->next->next){
// two = one->next;
// three = two->next;
// two->next = three->next;
// one->next = three;
// three->next = two;
// one = one->next->next;
// }
// return dummy->next;
// // 递归法
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
one = dummy;
result = dummy;
return swap(one);
}
ListNode* swap(ListNode* one){
if(not one->next or not one->next->next){
return result->next;
}
two = one->next;
three = two->next;
two->next = three->next;
one->next = three;
three->next = two;
return swap(one->next->next);
}
};
6. 删除链表的倒数第n个节点(力扣19)
- 题目描述:删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 思路:先遍历得到链表长度,再遍历导待删除的结点的前一个,让他直接指向后一个的后一个。如果想实现一次遍历就实现,用快慢指针。快慢指针就像从dummy发车的两趟列车,让快车比慢车早n+1站出发,这样当快车到达终点的时候,慢车正好到达倒数第n站再向前一站。
- python语法细节
- Python实现
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(0,head)
one = dummy
two = dummy
num = 0
while num<n:
num = num+1
one = one.next
while one.next :
one = one.next
two = two.next
two.next = two.next.next
return dummy.next
- C++语法细节
- C++中while循环写法:while后面条件要写括号
-while (condition) { // 循环体 // 这里是代码块,会在条件为真时重复执行 }
- C++实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode* one = dummy;
ListNode* two = dummy;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
one = one->next;
}
while (one->next){
one = one->next;
two = two->next;
}
two->next = two->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
7.两链表相交(力扣 面试题02.07.链表相交)
- 题目描述:两链表相交
- 思路:根据示例,如果两链表有相交的地方,一定是在两链表的尾部。而且此题,相交的点不仅仅是值相同,而且相交的是同一个节点(不能根据值来判断是否是同一个节点,而要判指针指向的是同一个节点)。
- python语法细节
- 当错误信息提示,cura 类型为NoneType时,不仅要检查是否为空指针,而且要检查是否被正确的初始化
- 在 Python 中,通常用 None 表示空值,而不是 null。所以在函数中返回空值时,应该使用 None
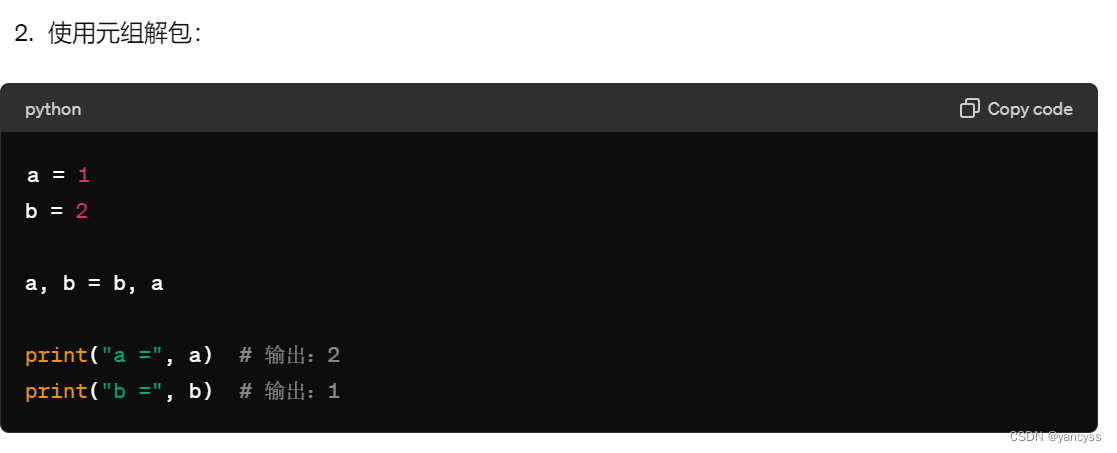
- Python中交换两个变量的值,不需要加一个中间变量,可以使用解包的方法直接交换。
- Python实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
lena = 0
cur = headA
while cur:
lena += 1
cur = cur.next
lenb = 0
cur = headB
while cur:
lenb += 1
cur = cur.next
# 让a 是长的那个,如果不是,使用元组解包交换二者的位置
if lenb > lena:
lena,lenb = lenb,lena
headA,headB = headB,headA
cura = headA
curb = headB
for i in range(lena-lenb):
cura = cura.next
while cura:
if(cura==curb):
return cura
else:
cura = cura.next
curb = curb.next
return None
- C++语法细节
- C++实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int lenA = getlength(headA) ,lenB = getlength(headB);
if(lenB > lenA){
int tmp = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmp;
ListNode* temp=headA;
headA = headB;
headB = temp;
}
ListNode* curA = headA;
for(int i=0;i<lenA-lenB;i++){
curA = curA->next;
}
ListNode* curB = headB;
while (curA){
if(curA == curB){
return curA;
}
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
int getlength(ListNode* cur){
int length = 0;
while(cur){
length += 1;
cur = cur->next;
}
return length;
}
};
8. 环形链表2 (力扣142)
-
题目描述:环形链表2
-
思路:很难,人脑很难想到…当一条路不知道什么位置开始遇到鬼打墙,我们发射两个指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果有环,他俩一定会相遇,如果相遇,那么从相遇那个点和起始点在发射两个一次一步的指针,相遇点就是环入口。推导如下图,插入详细解释

-
python语法细节
写代码时候要考虑无环的情况 -
Python实现
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
fast ,slow = head,head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast == slow:
another = head
while slow!=another:
slow = slow.next
another = another.next
return another
return None
- C++语法细节
- 要先让快慢指针跑起来,再判断相遇时刻。不然就在头结点判断相遇了…
- C++实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast and fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast==slow){
slow = head;
cout<<fast->val<<endl;
while (fast){
if(fast==slow){
return fast;
}
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};





















 629
629











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








