这是我参加全国信息安全大赛的设计的加密系统中的一个加密算法,虽然比赛的结果不是非常理想但是,我还是学到了很多东西,现在和大家分享一下,比赛收获的东西。
基于口令加密
PBE(Password Based Encryption,基于口令加密)算法是一种基于口令的加密算法,其特点在于口令是由用户自己掌握的,采用随机数杂凑多重加密等方法保证数据的安全性。
PBE算法没有密钥的概念,密钥在其它对称加密算法中是经过算法计算得出来的,PBE算法则是使用口令替代了密钥。
密钥的长短直接影响了算法的安全性,但不方便记忆。即便是我们将密钥经过Base64编码转换为一个可见字符,长密钥一样不容易记忆。因此,在这种情况下密钥是需要存储的,但是口令则不然。比如一般人天天开关电脑,进入操作系统的唯一途径就是输入口令。口令是我们便于记忆的一种凭证,基于这一点,PBE算法使用口令替代了密钥。
PBE算法并没有真正构建新的加密/解密算法,而是对我们已经知道的对称加密算法(如DES算法)做了包装。使用PBE算法对数据做加密/解密操作的时候,其实是使用了DES或者是AES等其它对称加密算法做了相应的操作。
既然PBE算法使用我们较为常用的对称加密算法,那就无法回避密钥的问题。口令并不能替代密钥,密钥是经过加密算法计算得来的,但是口令本身不可能很长看,单纯的口令很容易通过穷举攻击方式破译,这就引入了“盐”。盐能阻止字典攻击或预先计算的攻击,它本身是一个随机信息,相同的随机信息极不可能使用两次。将盐附加在口令上,通过消息摘要算法经过迭代计算获得构建密钥/初始化向量的基本材料,使得破译的难度加大。
基于PBE算法的消息传递模型如下图3-13所示:甲乙双方作为消息传递双方(甲方为发送方,也就是甲方是本系统的服务器,乙方作为接收方,也就是本系统客户端的使用者),假定甲乙双方在消息传递前已经商定加密算法迭代的次数,与完成一次消息传递需要经过如下步骤:
1) 由消息传递双方约定口令,这里由甲方构建口令。
2) 由口令构建者发布口令,即本系统的服务器将口令发送给系统的客户端使用者
3) 由口令构建者构建本次消息传递使用的盐,这里由甲方(本系统)构建盐
4) 由消息发送方使用口令、盐对数据加密,这里由甲方对数据加密
5) 由消息发送者将盐、加密数据放松给消息接收者,这里由甲方将盐、加密数据发送给乙方
6) 由消息接收方使用盐、口令对加密数据解密,这里由乙方完成数据解密
图3-13 基于PBE算法的消息通讯模型
基于PBE算法的消息传递模型理解起来并不是十分复杂。对于上述单项消息传递而言,如果乙方想要恢复甲方消息,甲方并不需要重复步骤1、2,仅仅想要由乙方执行3、4、5,由甲方执行步骤6即可。
同时,甲乙双方也可以在消息传递过程中传递迭代次数。
“盐”本身就是一种可以由消息传递双方按一定规律约定的消息,比如时间。也可以是某个不可变物理硬件的编号,比如U盘的自身唯一标识,而本系统则采用“手机的唯一标识”,WIM 是一个防篡改硬件,在安全层和应用层执行安全功能,保存处理用户的ID 和权限等功能。
甲乙双方可以通过约定消息传递的时间,这里是由本系统直接决定时间,并将其作为基本消息,根据预定的算法(如MD5算法) 对其处理,最终获取真正的“盐”,这样一来,“盐”就无需传递,提高了安全性。
假设一个场景:由这样的一个系统,用户使用者需要通过手机访问一个系统,同同时需要输入口令方能登录系统,那么手机本身就是“盐”的提供者!即使手机丢失,加密的信息也未必能被窃取!即“盐”与口令就像两把不可分离的钥匙。
PBE实现方案:
Java 6 和Bouncy Castle都提供了PBE系列算法的相关实现,差别在于对各种消息摘要算法和对称加密算法的组合。常用的消息摘要算法包括MD5和SHA算法,常用的对称加密算法包括DES、RC2等。PBE系列算法就死将这些算法进行合理组合,其密钥长度均以PBE具体的算法中的对称加密算法为准。
有关PBE算法的Java6 和Bouncy Castle实现细节如下表3-11。
表3-11 PBE算法
| 算法 | 密钥长度 | 密钥默认长度 | 工作方式 | 填充方式 | 备注 |
| PBEWithMD5AndDES | 56 | 56 |
CBC |
PKCS5Padding | Java6实现 |
| PBEWithMD5AndTripeDES | 112、168 | 168 | Java7实现 | ||
| PBEWithSHA1AndDESede | 112、168 | 168 | java8实现 | ||
| PBEWithSHA1AndRC2_40 | 40至1024 | 128 | java9实现 | ||
| PBEWithMD5AndDES | 64 | 64 |
CBC |
PKCS5Padding, PKCS7Padding, ISO10126Padding, ZeroBytePadding |
BouncyCastle实现 |
| PBEWithMD5AndRC2 | 128 | 128 | |||
| PBEWithSHA1AndDES | 64 | 64 | |||
| PBEWithSHA1AndRC2 | 128 | 128 | |||
| PBEWithSHAAndIDEA-CBC | 128 | 128 | |||
| PBEWithSHAAnd2- KeyTripleDES-CBC | 128 | 128 | |||
| PBEWithSHAAnd3- KeyTripleDES-CBC | 192 | 192 | |||
| PBEWithSHA- And128BitRC2-CBC | 128 | 128 | |||
| PBEWithSHA- And40BitRC2-CBC | 40 | 40 | |||
| PBEWithSHA- And128BitRC4 | 128 | 128 | |||
| PBEWithSHA- And40BitRC4 | 40 | 40 | |||
| PBEWithSHA- AndTwofish-CBC | 256 | 256 |
/*
* Copyright 2013 WeCode authors
*
* Licensed under the WeCode, Version 1.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License from ydonghao2@gmail.com
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.wecode.database.secure;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory;
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEKeySpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEParameterSpec;
/**
* PBE安全编码组件
*
* @author WeCode ( ydonghao2 )
* @version 1.0
*/
public class PBECoder {
public static final String ALGORUTHM = "PBEWITHMD5andDES";
/**
* 迭代次数
*/
public static final int ITERATION_COUN = 100;
/**
* "盐"初始化<br>
* 盐长度必须为8字节
* @return byte[] 盐
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] initSalt() throws Exception {
//实例化安全随机数
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
//产出盐
return random.generateSeed(8);
}
/**
* 转换密钥
* @param password 密码
* @return Key密钥
* @throws Exception
*
*/
private static Key toKey(String password) throws Exception {
//密钥材料转换
PBEKeySpec keySpec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray());
//实例化
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORUTHM);
//生成密钥
SecretKey secretkey = keyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec);
return secretkey;
}
/**
* 加密
* @param data 数据
* @param password 密钥
* @param salt 盐
* @return byte[] 加密数据
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, String password, byte[] salt) throws Exception{
//转换密钥
Key key = toKey(password);
//实例化PBE参考数据
PBEParameterSpec parameterSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, ITERATION_COUN);
//实例化
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORUTHM);
//初始化
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, parameterSpec);
//执行操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
/**
* 解密
* @param data 数据
* @param password 密码
* @param salt 盐
* @return byte[] 解密数据
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, String password, byte[] salt) throws Exception{
//转换密钥
Key key = toKey(password);
//实例化PBE参数材料
PBEParameterSpec parameterSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, ITERATION_COUN);
//实例化
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORUTHM);
//初始化
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, parameterSpec);
//执行操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
}
PBE算法是实现过程中需要关注的环节,包括“盐”的初始化,密钥材料的转化和加密/解密的时间。
在初始化“盐”时,必须使用随机的方式构造“盐”,最终要得到一个8字节的字节数组。鉴于安全性的要求,这里的随机数生成器只能使用SecureRandom类,如下所示:
//实例化安全性随机数
SecureRandomrandom = new SecureRandom();
//产出“盐”
byte[]b = random.generateSeed(8);字节数组b[]就是我们要的“盐”。
密钥材料转换部分不同于其他对称加密算法,这里使用的是PBEKeySpec类,如下所示:
//密钥材料转换
PBEKeySpeckeySpec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toChatArray());其他对称加密算法的密钥材料实现类的构造方法要求输入字节数组形式的变量,而PBEKeySpec类构造方法则要求输入字符数组变量。
为什么不是字符串(String)而是字符数组(char[])呢?这是因为字符串是可序列化的封装类,可在程序调用时被序列化到文件中,而字符数组只能以内存变量的形式保留在内存中。
在加密/解密实现时,需要注意使用参数材料PBEParameterSpec类,同时注意迭代次数。构建PBE参数材料后就可以转交给Cipher类完成加密/解密操作,如下所示:
//实例化PBE参数材料
PBEParameterSpecparamSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, ITERATION_COUNT);
//实例化
Cipher= cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
//初始化
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,key, paramSpec);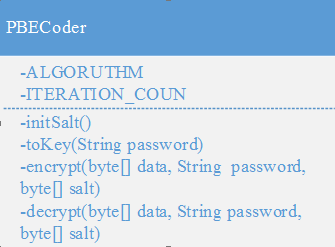
- KEY_ALGORITHM 指明加密算法,这里是PBEWITHMD5andDES加密算法。
- ITERATION_COUN迭代的次数。
+initSalt()PBE加密方式的初始化盐返回的是byte[] 盐,盐长度必须为8字节。
+ toKey(Stringpassword) 转换密钥,password是密码,返回Key类型密钥。
+encrypt(byte[]data, String password, byte[] salt) 加密方法。Data是数据,password是密钥,salt是盐,返回byte[]类型,是加密以后的数据。
+decrypt(byte[]data, String password, byte[] salt)解密方法,data是数据,password的密码,salt是盐,返回byte[]类型,是解以后的数据。
PBE算法实现和AES算法有很多类似的地方,相似的地方下面代码不具体介绍。
PBE的主要代码如下:
本系统在这里采用的是PBEWITHMD5andDES算法。
public static final String ALGORUTHM ="PBEWITHMD5andDES";
迭代次数
public static final int ITERATION_COUN = 100;
"盐"初始化
盐长度必须为8字节
返回:
byte[]盐
抛出:
java.lang.Exception
public static byte[] initSalt() throws Exception {
//实例化安全随机数
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
//产出盐
return random.generateSeed(8);
}转换密钥
参数:
password-密码
返回:
Key密钥
抛出:
java.lang.Exception
PBE算法定义并继承了SecretKey接口。
private static Key toKey(String password) throws Exception {
//密钥材料转换
PBEKeySpec keySpec = newPBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray());
//实例化
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory =SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORUTHM);
//生成密钥
SecretKey secretkey =keyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec);
return secretkey;
}加密方法
参数:
data- 数据
password- 密钥
salt- 盐
返回:
byte[]加密数据
抛出:
java.lang.Exception
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, String password, byte[] salt) throws Exception{
//转换密钥
Key key = toKey(password);
//实例化PBE参考数据
PBEParameterSpec parameterSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt,ITERATION_COUN);
//实例化
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORUTHM);
//初始化
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, parameterSpec);
//执行操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}解密方法
参数:
data- 数据
password- 密码
salt- 盐
返回:
byte[]解密数据
抛出:
java.lang.Exception
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, String password,byte[] salt) throws Exception{
//转换密钥
Key key = toKey(password);
//实例化PBE参数材料
PBEParameterSpec parameterSpec = newPBEParameterSpec(salt, ITERATION_COUN);
//实例化
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORUTHM);
//初始化
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, parameterSpec);
//执行操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}PBE算法实例验证PBECoder.java:
/** Licensed under the WeCode, Version 1.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License from ydonghao2@gmail.com
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.wecode.database.secure;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* PBE 检验
*
* @author WeCode ydonghao2
* @version 1.0
*/
public class PBECoderTest {
/**
* 测试
*
* @throws Exception
*/
/**
* 测试的时候人工可以引入junit.jar包
* @throws Exception
*/
//@Test
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String inputStr = "PBE";
System.err.println("原文:\t" + inputStr);
byte[] input = inputStr.getBytes();
String pwd = "ydonghao";
System.err.println("密码:\t" + pwd);
// 初始化盐
byte[] salt = PBECoder.initSalt();
System.err.println("盐:\t" + Base64.encodeBase64String(salt));
// 加密
byte[] data = PBECoder.encrypt(input, pwd, salt);
System.err.println("加密后\t" + Base64.encodeBase64String(data));
// 解密
byte[] output = PBECoder.decrypt(data, pwd, salt);
String outputStr = new String(output);
System.err.println("解密后\t" + outputStr);
}
}
这个加密算法的实现需要一些环境的搭建,参考这里: http://blog.csdn.net/ydonghao2/article/details/11046635























 3436
3436

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








