一、Chapter1——Introduction
(一)Introduction of real-time rendering
1、what is "real-time rendering" ?
——not individual image, rather dynamic process.
2、FPS & Hz
3、display rate & refresh rate
A shutter that illuminates the frame three times has a 72 Hz refresh rate, which shows frames at 24 FPS.
4、real-time rendering & interactivity.
real-time rendering always means showing the 3D image on the screen , not just interactivity.
5、three point of real-time rendering
interactivity, 3D and graphics acceleration hardware.
6、About the content of the book
We will focus on providing methods to increase speed and improve image quality, while also describing the features and limitations of acceleration algorithms and graphics APIs.
(二)Notation and Definition
略过
二、Chapter2——The Graphics Rendering Pipeline.
(一)Concept
the main function of the graphics rendering pipeline is to generate a 2D image given a virtual camera , 3D objects ,light sources and more.
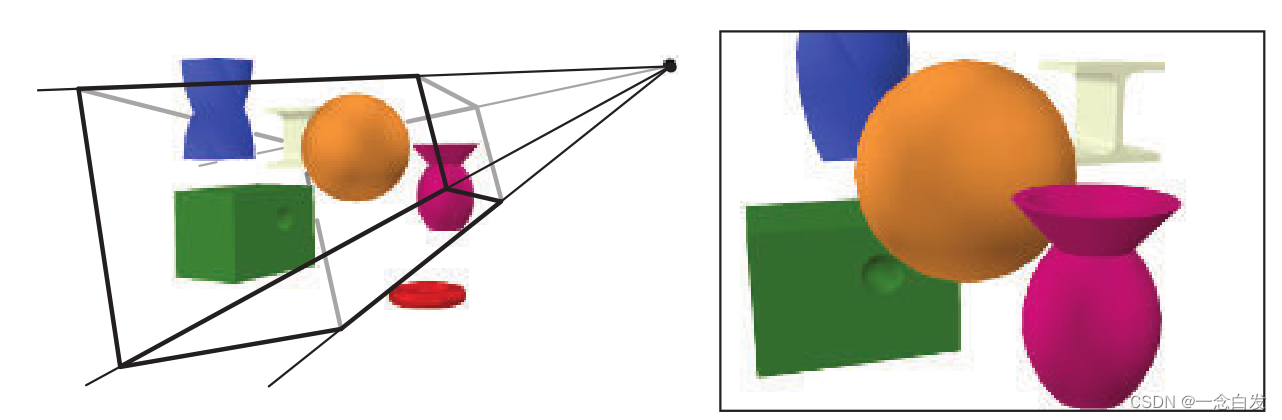
The locations and shapes of the objects in the image are determined by their geometry, the characteristics of the environment, and the placement of the camera in that environment.
The appearance of the objects is affected by material properties, light sources, textures (images applied to surfaces), and shading equations.
(二)、Architecture
1、Pipeline
A pipeline consists of several stages , each of which performs part of a larger task.
The pipeline stages execute in parallel, with each stage dependent upon the result of the previous stage. ——so they are stalled until the slowest stage has finished its task.
2、4 main stages of graphics rendering pipeline
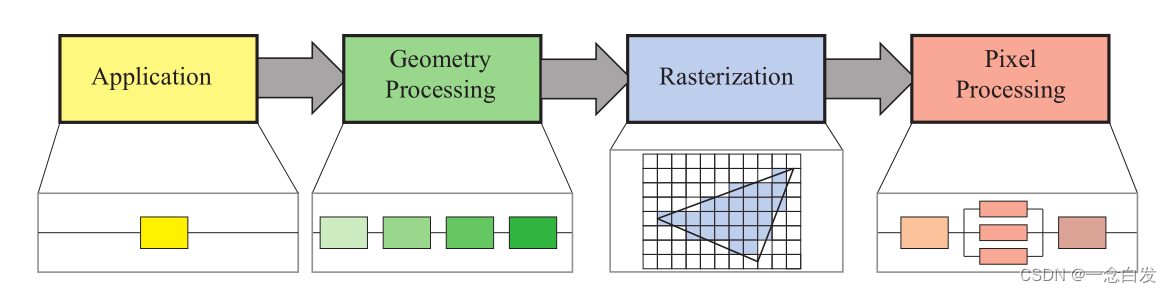
3、functional stages & the structure of their implementation.
A functional stage has a certain task to perform but does not specify the way that task is executed in the pipeline. A given implementation may combine two functional stages into one unit or execute using programmable cores, while it divides another, more time-consuming, functional stage into several hardware units.
4、FPS & Hz
Frames per second is used to express either the rate for a particular frame, or the average performance over some duration of use. Hertz is used for hardware, such as a display, which is set to a fixed rate.
5、The responsibility of every stage
Application : collision detection, global acceleration algorithms, animation, physics simulation, and many others, depending on the type of application. runing on CPUs.
Geometry Processing : transforms, projections, and all other types of geometry handling. This stage computes what is to be drawn, how it should be drawn, and where it should be drawn. Runing on the GPU.
Rasterization : takes as input three vertices, forming a triangle, and finds all pixels that are considered inside that triangle, then forwards these to the next stage.Runing on the GPU.
Pixel Processing : executes a program per pixel to determine its color and may perform depth testing to see whether it is visible or not.Runing on the GPU.
(三)、The Application Stage.
1、some application work can be performed by the GPU, using a seperate mode called a compute shader, which treat GPU as a highly parallel general processor, ignoring its special functionality meant specifically for rendering graphics.
2、not divided into substages. so to increase performance, this stage is often executed in parallel on several processor cores.
3、receive the input of keyboard ,mouse and so on.
(四)、Geometry Processing
1、The geometry processing stage divided into a pipeline of functional stages.
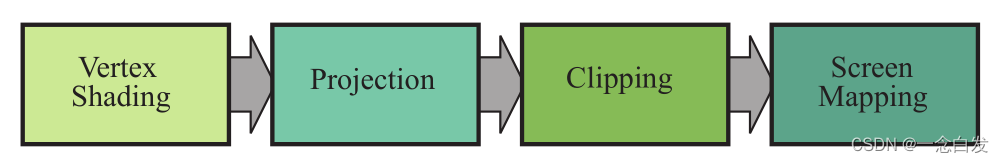
2、Vertex Shading
two main tasks : compute the position of vertices and whatever programmer need to output about vertices.
2.1、the position of the models have some space or coordinate system.
①model transformation : to generate locations,orientations, and sizes of models.
model space --> world space
②view transform : To facilitate projection and clipping, the camera will be put at the origin and aim special direction.
world space --> view space
2.2 、Materials and lights could render the appearance of the models.
This operation of determining the effect of a light on a material is known as shading. It involves computing a shading equation at various points on the object.
2.3、As part of vertex shading, rendering systems perform projection and then clipping.
Projection transforms the view volume into a unit cube with its extreme points at (−1,−1,−1) and (1,1,1).
there are two main ways of projection : orthographic and perspective projection.
view space --> clip space
orthographic projection : The main characteristic of orthographic projection is that parallel lines remain parallel after the transform. the model will be transformed into a unit cube directly.
perspective projection : the farther away an object lies from the camera, the smaller it appears after projection. the models will be transformed into a frustum and then a unit cube.
and then devide by w for the next stage clipping.
3、Optional Vertex Processing
optional stages that can take place on the GPU, in this order: tessellation, geometry shading, and stream output.
3.1、tessellation stage
①the processed vertices could make some patches, and a set of patches could form curved surfaces. the tessellation stage will convert sets of patch vertices into larger sets of vertices that are then used to make new sets of triangles. The camera for the scene can be used to determine how many triangles are generated: many when the patch is close, few when it is far away.
②The tessellation stage consists of a series of stages itself—hull shader, tessellator, and domain shader.
3.2、 geometry shader
It takes in primitives of various sorts and can produce new vertices.
An example of particle generation.
3.3、stream output
Instead of sending our processed vertices down the rest of the pipeline to be rendered to the screen, at this point we can optionally output these to an array for further processing.
4、Clipping
It is the primitives that are partially inside the view volume that require clipping.
In addition to the six clipping planes of the unit cube, the user can define additional clipping planes to visibly chop objects.
The clipping step uses the 4-value homogeneous coordinates produced by projection to perform clipping. Values do not normally interpolate linearly across a triangle in perspective space. The fourth coordinate is needed so that data are properly interpolated and clipped when a perspective projection is used. Finally, perspective division is performed, which places the resulting triangles’ positions into three-dimensional normalized device coordinates.
Question : why interpolate there ?
the order : clipping --> perspective division --> culling.
5、Screen Mapping
Then the screen mapping is a translation followed by a scaling operation. The new x- and y- coordinates are said to be screen coordinates. The z-coordinate is also mapped to [z1 ,z2 ], with z1 = 0 and z2 = 1 as the default values.
The Pixel Representation : integer and floating point. the transform of them :
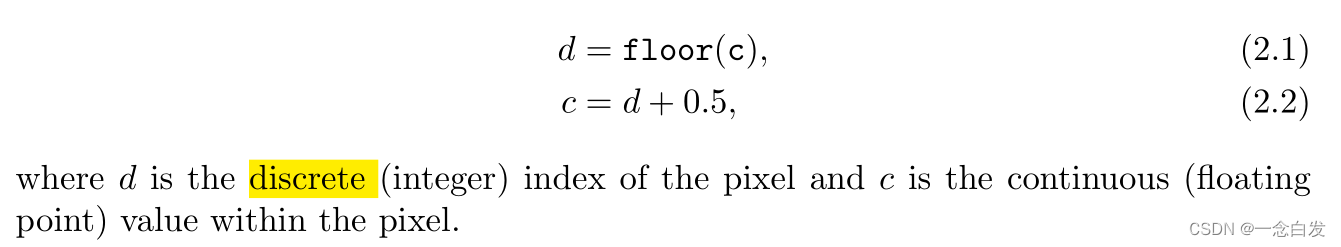
(五)、Rasterization
contain two substage : triangle setup and triangle traversal.
1、triangle setup
the differentials, edge equations, and other data for the triangle are computed.
2、triangle traversal
check if the center of vertices cover the triangle --> if covered, generate a fragment by interpolating.
(六)、Pixel Processing
two substage : pixel shading and merging.
1、pixel shading
the end product is a color value for each fragment. A large variety of techniques can be employed here, one of the most important of which is texturing.
2、merging
combine the fragment color produced by the pixel shading stage with the color currently stored in the buffer.
This stage is also responsible for resolving visibility.—— z-buffer, which allow any order to be rendered. but the transparency is one of the major weaknesses of the basic z-buffer.
more : alpha channel, stencil buffer. front buffer & back buffer.
(七)、Through the Pipeline
略
reference : 《real-time rendering》(fourth edition)























 5391
5391











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








