Xiao Ming's Hope
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2109 Accepted Submission(s): 1428
Problem Description
Xiao Ming likes counting numbers very much, especially he is fond of counting odd numbers. Maybe he thinks it is the best way to show he is alone without a girl friend. The day 2011.11.11 comes. Seeing classmates walking with their girl friends, he coundn't help running into his classroom, and then opened his maths book preparing to count odd numbers. He looked at his book, then he found a question "C
(n,0)+C
(n,1)+C
(n,2)+...+C
(n,n)=?". Of course, Xiao Ming knew the answer, but he didn't care about that , What he wanted to know was that how many odd numbers there were? Then he began to count odd numbers. When n is equal to 1, C
(1,0)=C
(1,1)=1, there are 2 odd numbers. When n is equal to 2, C
(2,0)=C
(2,2)=1, there are 2 odd numbers...... Suddenly, he found a girl was watching him counting odd numbers. In order to show his gifts on maths, he wrote several big numbers what n would be equal to, but he found it was impossible to finished his tasks, then he sent a piece of information to you, and wanted you a excellent programmer to help him, he really didn't want to let her down. Can you help him?
Input
Each line contains a integer n(1<=n<=10
8)
Output
A single line with the number of odd numbers of C
(n,0),C
(n,1),C
(n,2)...C
(n,n).
Sample Input
Sample Output
首先给出这个Lucas定理:
A、B是非负整数,p是质数。AB写成p进制:A=a[n]a[n-1]...a[0],B=b[n]b[n-1]...b[0]。
则组合数C(A,B)与C(a[n],b[n])*C(a[n-1],b[n-1])*...*C(a[0],b[0]) modp同余
即:Lucas(n,m,p)=c(n%p,m%p)*Lucas(n/p,m/p,p)
For non-negative integers m and n and a prime p, the following congruence relationholds:
-
 表示的是同余,表示两个数对p取余,余数相同。
表示的是同余,表示两个数对p取余,余数相同。
where
-
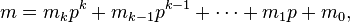
and
-
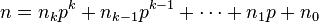
are the base p expansions of m and n respectively.
证明:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lucas%27_theorem
维基的意思是说在m中里面取n个%p来说,这样考虑:
将m划分成m0个1,m1个p,m2个p^2,……
将n划分成n0个1,n1个p,n2个p^2……
那是不是C(m,n)的总共的取法就是( 在m0个里面取n0个的方案数 * m1个里面取n1个的方案数 * m2个里面取n2个的方案数 ……)
证明就是这样。
之所以看lucas,是因为12年多校有Lucas定理的题。
咳咳,我们先来看看hdu3037.
意思是说将不少于m个球放在n个盒子里面。
做ACM做多了,把高中知识都忘了-------其实就是将m + n个球放在n个盒子当中有多少放法,就用Lucas来做呗。
其中,由于涉及到还有取模,需要运用求乘法逆元,求乘法逆元不一定要用欧几里德,还可以用欧拉定理。
欧拉定理求逆元简介: ---维基
在数论中,欧拉定理(也称费马-欧拉定理或欧拉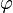 函数定理)是一个关于同余的性质。欧拉定理表明,若
函数定理)是一个关于同余的性质。欧拉定理表明,若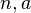 为正整数,且
为正整数,且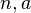 互素,
互素,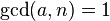 ,则
,则

其中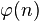 为欧拉函数,
为欧拉函数,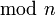 为同余关系。欧拉定理得名于瑞士数学家莱昂哈德·欧拉。
为同余关系。欧拉定理得名于瑞士数学家莱昂哈德·欧拉。
欧拉定理实际上是费马小定理的推广。
以下是 http://blog.csdn.net/wukonwukon/article/details/7341270 的代码,加上我的一点注释:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- using namespace std;
-
-
- #define N 100010
-
-
- long long mod_pow(int a,int n,int p)
- {
- long long ret=1;
- long long A=a;
- while(n)
- {
- if (n & 1)
- ret=(ret*A)%p;
- A=(A*A)%p;
- n>>=1;
- }
- return ret;
- }
-
-
- long long factorial[N];
-
-
- void init(long long p)
- {
- factorial[0] = 1;
- for(int i = 1;i <= p;i++)
- factorial[i] = factorial[i-1]*i%p;
- }
-
-
- long long Lucas(long long a,long long k,long long p)
-
- {
- long long re = 1;
- while(a && k)
- {
- long long aa = a%p;long long bb = k%p;
- if(aa < bb) return 0;
-
- re = re*factorial[aa]*mod_pow(factorial[bb]*factorial[aa-bb]%p,p-2,p)%p;
- a /= p;
- k /= p;
- }
- return re;
- }
- int main(){
- int a,b,c;
- while(cin >> a >> b >> c){
- cout << mod_pow(a,b,c)<< endl;
- }
- return 0;
- }
-
-
- int main()
- {
- int t;
- cin >> t;
- while(t--)
- {
- long long n,m,p;
- cin >> n >> m >> p;
- init(p);
- cout << Lucas(n+m,m,p) << "\n";
- }
- return 0;
- }
接着,再来看
Multi-University 05-1010hdu-4349
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4349
官方解题报告,懂了Lucas就非常非常非常好写代码了。
本题为Lucas定理推导题,我们分析一下 C(n,m)%2,那么由lucas定理,我们可以写
* 成二进制的形式观察,比如 n=1001101,m是从000000到1001101的枚举,我们知道在该定理中
* C(0,1)=0,因此如果n=1001101的0对应位置的m二进制位为1那么C(n,m) % 2==0,因此m对应n为0的
* 位置只能填0,而1的位置填0,填1都是1(C(1,0)=C(1,1)=1),不影响结果为奇数,并且保证不会
* 出n的范围,因此所有的情况即是n中1位置对应m位置0,1的枚举,那么结果很明显就是:2^(n中1的个数)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n)!=EOF)
{
int sum=1, num=0;
while(n!=0)
{
if(n&1)
{
num++;
}
n>>=1;
}
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
sum*=2;
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
 表示的是同余,表示两个数对p取余,余数相同。
表示的是同余,表示两个数对p取余,余数相同。
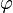 函数定理)是一个关于同余的性质。欧拉定理表明,若
函数定理)是一个关于同余的性质。欧拉定理表明,若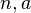 为正整数,且
为正整数,且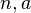 互素,
互素,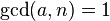 ,则
,则
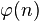 为欧拉函数,
为欧拉函数,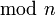 为同余关系。欧拉定理得名于瑞士数学家莱昂哈德·欧拉。
为同余关系。欧拉定理得名于瑞士数学家莱昂哈德·欧拉。







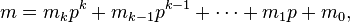
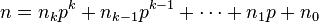














 517
517











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








