CGAL笔记之形状重建——泊松表面重建
1 介绍
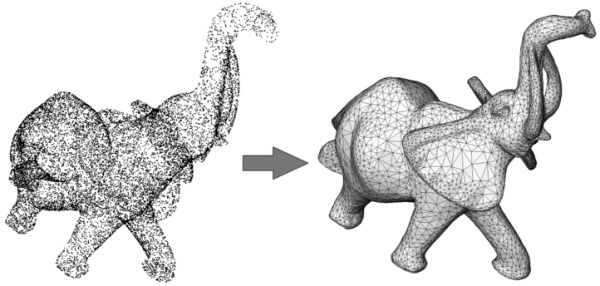
该 CGAL 组件实现了一种表面重建方法,该方法将具有定向法线的输入点集作为输入并计算隐式函数。我们假设输入点不包含异常值且噪声很小。输出表面网格是通过使用 CGAL 表面网格生成器或可能使用任何其他表面轮廓算法提取此函数的等值面来生成的。左图:使用 Minolta 激光扫描仪在大象雕像上采样的 17K 个点。右:重建的表面网格。
更具体地说,核心表面重建算法包括计算一个隐函数,该函数是推断实体的近似指示函数(Poisson Surface Reconstruction - 简称泊松)。泊松是一个两步过程:它需要在函数评估之前求解隐函数。
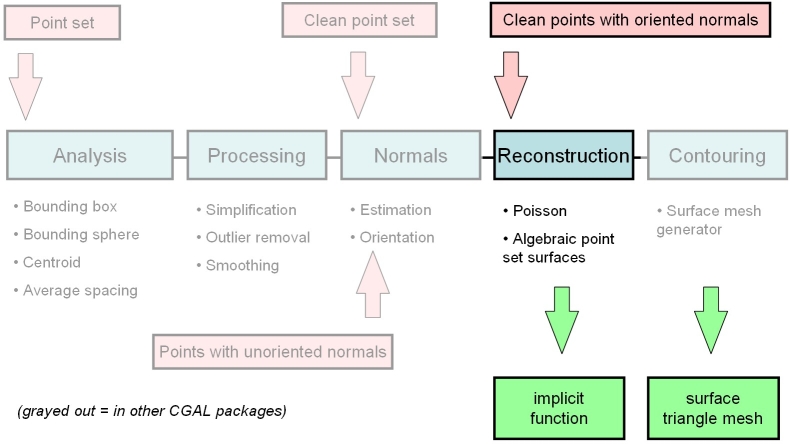
2 公共重建管道
从点集重建表面通常是一个顺序过程,包括以下步骤:1)扫描和扫描对齐产生一组点或具有法线的点;2)异常值去除;3) 简化以减少输入点数;4)平滑以减少输入数据中的噪声;5) 当采集设备尚未提供法线时的法线估计和定向;和 6) 表面重建。
CGAL 为上面列出的除对齐之外的所有步骤提供算法。
Point Set Processing描述了在重建之前对点集进行预处理的算法,这些算法具有专门用于简化、异常值去除、平滑、法线估计和法线定向的功能。
3 泊松
给定一组在 3D 实体边界上采样的具有定向法线的 3D 点(在后续中表示为定向点),泊松曲面重建方法求解推断实体的近似指示函数,其梯度最匹配输入法线。以自适应八叉树表示的输出标量函数然后使用自适应行进立方体等高线。
CGAL 实现了该算法的一个变体,它在 3D Delaunay 三角剖分上求解分段线性函数而不是自适应八叉树。该算法将一组 3D 定向点作为输入。它从这些点构建 3D Delaunay 三角剖分,并通过 Delaunay 细化对其进行细化,以移除所有形状不良(非各向同性)的四面体并细分输入定向点的松散边界框。在细化过程中添加的每个 Steiner 点的法线设置为零。然后,它求解标量指示函数,表示为精细三角剖分上的分段线性函数。更具体地说,它在三角剖分的每个顶点上使用稀疏线性求解器求解泊松方程Δf=div(n)。最终,CGAL曲面网格生成器提取出一个等值面,其函数值默认设置为f在所有输入点的中值。
4 重构函数
poisson_surface_reconstruction_delaunay()提供了全局函数。它以法线点作为输入并处理整个重建管道:
- 它计算隐函数
- 它使用基于 Delaunay 细化的 CGAL 表面网格生成器以给定的精度重建表面
- 它以多边形网格输出结果。
此功能旨在为泊松重建提供快速且用户友好的 API。高级用户可能对使用允许他们使用其他表面网格器或不同输出结构的类。
4.1 例子
以下示例读取点集并使用泊松重建重建曲面。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/poisson_surface_reconstruction.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/read_points.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
// Types
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;
typedef Kernel::Vector_3 Vector;
typedef std::pair<Point, Vector> Pwn;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<Kernel> Polyhedron;
int main(void)
{
std::vector<Pwn> points;
if(!CGAL::IO::read_points(CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/kitten.xyz"), std::back_inserter(points),
CGAL::parameters::point_map(CGAL::First_of_pair_property_map<Pwn>())
.normal_map(CGAL::Second_of_pair_property_map<Pwn>())))
{
std::cerr << "Error: cannot read input file!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
Polyhedron output_mesh;
double average_spacing = CGAL::compute_average_spacing<CGAL::Sequential_tag>
(points, 6, CGAL::parameters::point_map(CGAL::First_of_pair_property_map<Pwn>()));
if (CGAL::poisson_surface_reconstruction_delaunay
(points.begin(), points.end(),
CGAL::First_of_pair_property_map<Pwn>(),
CGAL::Second_of_pair_property_map<Pwn>(),
output_mesh, average_spacing))
{
std::ofstream out("kitten_poisson-20-30-0.375.off");
out << output_mesh;
}
else
return EXIT_FAILURE;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
5 重建类
类模板声明是template<class Gt> class Poisson_reconstruction_function,其中Gt是一个几何特征类。
5.1 例子
以下示例读取一个点集,创建一个泊松隐式函数并重建一个曲面。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_default_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/make_surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Implicit_surface_3.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/facets_in_complex_2_to_triangle_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Poisson_reconstruction_function.h>
#include <CGAL/property_map.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/read_points.h>
#include <CGAL/compute_average_spacing.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/distance.h>
#include <boost/iterator/transform_iterator.hpp>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
// Types
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
typedef Kernel::FT FT;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;
typedef Kernel::Vector_3 Vector;
typedef std::pair<Point, Vector> Point_with_normal;
typedef CGAL::First_of_pair_property_map<Point_with_normal> Point_map;
typedef CGAL::Second_of_pair_property_map<Point_with_normal> Normal_map;
typedef Kernel::Sphere_3 Sphere;
typedef std::vector<Point_with_normal> PointList;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<Kernel> Polyhedron;
typedef CGAL::Poisson_reconstruction_function<Kernel> Poisson_reconstruction_function;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh_default_triangulation_3 STr;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh_complex_2_in_triangulation_3<STr> C2t3;
typedef CGAL::Implicit_surface_3<Kernel, Poisson_reconstruction_function> Surface_3;
int main(void)
{
// Poisson options
FT sm_angle = 20.0; // Min triangle angle in degrees.
FT sm_radius = 30; // Max triangle size w.r.t. point set average spacing.
FT sm_distance = 0.375; // Surface Approximation error w.r.t. point set average spacing.
// Reads the point set file in points[].
// Note: read_points() requires an iterator over points
// + property maps to access each point's position and normal.
PointList points;
if(!CGAL::IO::read_points(CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/kitten.xyz"), std::back_inserter(points),
CGAL::parameters::point_map(Point_map())
.normal_map (Normal_map())))
{
std::cerr << "Error: cannot read file input file!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Creates implicit function from the read points using the default solver.
// Note: this method requires an iterator over points
// + property maps to access each point's position and normal.
Poisson_reconstruction_function function(points.begin(), points.end(), Point_map(), Normal_map());
// Computes the Poisson indicator function f()
// at each vertex of the triangulation.
if ( ! function.compute_implicit_function() )
return EXIT_FAILURE;
// Computes average spacing
FT average_spacing = CGAL::compute_average_spacing<CGAL::Sequential_tag>
(points, 6 /* knn = 1 ring */,
CGAL::parameters::point_map (Point_map()));
// Gets one point inside the implicit surface
// and computes implicit function bounding sphere radius.
Point inner_point = function.get_inner_point();
Sphere bsphere = function.bounding_sphere();
FT radius = std::sqrt(bsphere.squared_radius());
// Defines the implicit surface: requires defining a
// conservative bounding sphere centered at inner point.
FT sm_sphere_radius = 5.0 * radius;
FT sm_dichotomy_error = sm_distance*average_spacing/1000.0; // Dichotomy error must be << sm_distance
Surface_3 surface(function,
Sphere(inner_point,sm_sphere_radius*sm_sphere_radius),
sm_dichotomy_error/sm_sphere_radius);
// Defines surface mesh generation criteria
CGAL::Surface_mesh_default_criteria_3<STr> criteria(sm_angle, // Min triangle angle (degrees)
sm_radius*average_spacing, // Max triangle size
sm_distance*average_spacing); // Approximation error
// Generates surface mesh with manifold option
STr tr; // 3D Delaunay triangulation for surface mesh generation
C2t3 c2t3(tr); // 2D complex in 3D Delaunay triangulation
CGAL::make_surface_mesh(c2t3, // reconstructed mesh
surface, // implicit surface
criteria, // meshing criteria
CGAL::Manifold_with_boundary_tag()); // require manifold mesh
if(tr.number_of_vertices() == 0)
return EXIT_FAILURE;
// saves reconstructed surface mesh
std::ofstream out("kitten_poisson-20-30-0.375.off");
Polyhedron output_mesh;
CGAL::facets_in_complex_2_to_triangle_mesh(c2t3, output_mesh);
out << output_mesh;
// computes the approximation error of the reconstruction
double max_dist =
CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing::approximate_max_distance_to_point_set
(output_mesh,
CGAL::make_range (boost::make_transform_iterator
(points.begin(), CGAL::Property_map_to_unary_function<Point_map>()),
boost::make_transform_iterator
(points.end(), CGAL::Property_map_to_unary_function<Point_map>())),
4000);
std::cout << "Max distance to point_set: " << max_dist << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
5.2 等值线
可以使用 CGAL 表面网格生成器对计算出的隐式函数进行等值线重建以重建表面:make_surface_mesh()
该参数Tag影响以下行为make_surface_mesh():
Manifold_tag:输出网格保证是无边界的流形表面。Manifold_with_boundary_tag:输出网格保证是流形的并且可能有边界。Non_manifold_tag:输出网格没有保证,因此输出为多边形。
5.3 输出
重建的表面make_surface_mesh()需要是概念的模型SurfaceMeshComplex_2InTriangulation_3,这是一种数据结构,旨在表示嵌入到三维三角剖分中的二维复合体。
SurfaceMeshComplex_2InTriangulation_3定义遍历重建表面的方法,例如将其转换为三角形汤。
其他 CGAL 组件提供将重建的表面网格写入对象文件格式 (OFF)并将其转换为多面体(当它是流形时)的功能:
output_surface_facets_to_off()output_surface_facets_to_polyhedron()
6 实例探究
表面重建问题本质上是病态的,所提出的算法不会假装以任意采样条件重建各种表面。本节为用户提供了一些关于理想采样和等高线条件的提示,并描述了这些条件不匹配时的一些失败案例。
6.1 理想条件
用户必须记住,泊松曲面重建算法包括两个阶段(从输入点集计算隐式函数和绘制该函数的等值面)。两者都需要注意采样条件和参数调整。
6.2 点集
理想情况下,泊松表面重建方法的当前实现需要密集的 3D 定向点集(通常匹配 epsilon 采样条件)并在封闭的光滑表面上采样。此处定向意味着所有 3D 点必须具有与推断表面一致的定向法线。下图说明了满足这些理想条件的情况。左图:在雕像上采样的 120K 个点(美能达激光扫描仪)。右:重建的表面网格。
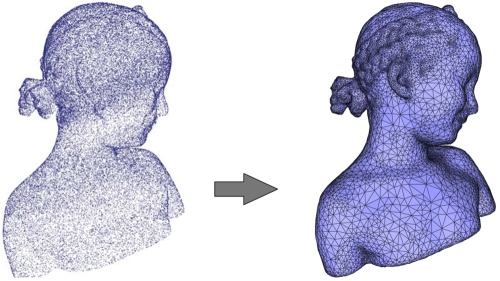
左:在雕像上采样的 120K 个点(美能达激光扫描仪)。右:重建的表面网格。
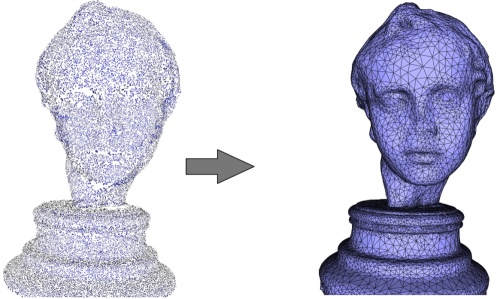
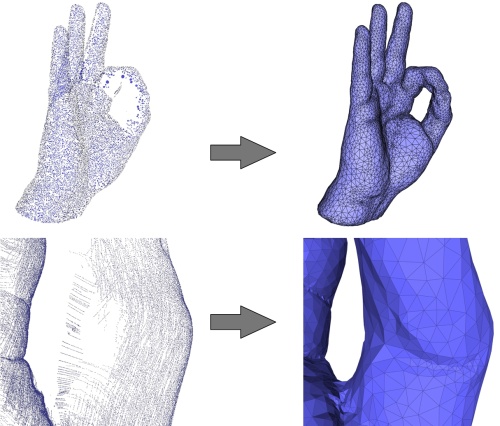
该算法对各向异性采样和噪声相当稳健。由于该算法旨在重建推断实体的指示函数,因此它还可以通过填充相应的孔对缺失数据具有鲁棒性。左上角:在手上采样的 65K 个点(Kreon 激光扫描仪)。左下:由于扫描技术,点集具有高度各向异性。右图:重建的表面网格和特写。孔已正确关闭。
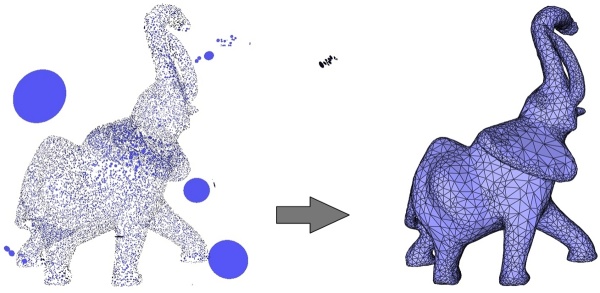
该算法通常对离群值不稳健,尽管一些离群值并不总是会导致失败。
即使推断的表面由多个连接的分量组成,该算法也能很好地工作,前提是所有法线都被正确估计和定向(当前的 CGAL 法线定向器算法在某些情况下可能会失败,请参阅参考资料),并且最终轮廓算法是正确mst_orient_normals()的为每个组件播种。当推断表面由多个嵌套连接的组件组成时,应注意交替(向内/向外)定向每个组件的法线,以便最终轮廓阶段选择适当的轮廓值。
6.3 轮廓参数
我们的泊松曲面重建算法的实现计算一个隐函数,表示为 3D Delaunay 三角剖分的四面体上的分段线性函数,该三角剖分由输入点构建,然后通过 Delaunay 细化进行细化。因此,任何等值面也是分段线性的,因此可能包含尖锐的折痕。由于等高线算法make_surface_mesh()需要一个平滑的隐式函数,因此当设置一个小的网格大小或表面近似误差参数时,这些尖锐的折痕可能会在最终重建的表面网格中产生虚假的顶点簇。
避免这些虚假簇的一种方法包括将网格大小和表面近似参数调整到与平均采样密度(通过获得compute_average_spacing())相比足够大,以便轮廓算法感知平滑的等值面。我们建议使用以下轮廓参数:
- 最大三角形半径:至少为平均间距的100倍。
- 近似距离:至少为平均间距的0.25倍。
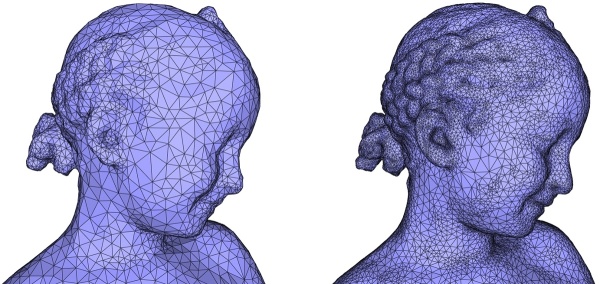
左:使用近似距离 = 0.25 * 平均间距重建的表面。右图:使用近似距离 = 0.15 * 平均间距重建的表面。注意脸颊上的虚假簇。
6.4 退化条件
上面列出的条件相当严格,实际上并不是所有的条件都在申请中得到满足。我们现在说明在采样、错误定向的法线、噪声和尖锐折痕方面不满足条件时算法的行为。
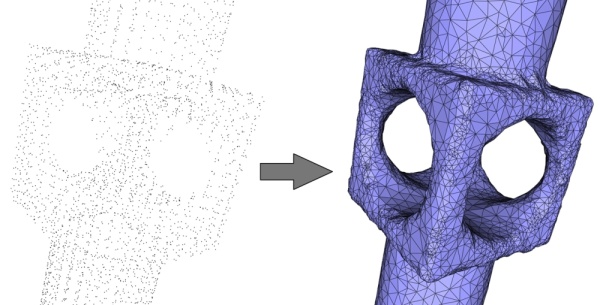
6.5 稀疏采样
重建算法需要足够密集的点集。尽管由于算法的变化性质,在某些密度条件下没有正式证明该算法的正确性,但我们的实验表明,当局部间距最多为局部特征尺寸的十分之一(距离到中轴,它捕获了曲率、厚度和分离)。当不满足此条件时,重建不会重建薄的欠采样特征。
左:在 Neptune 三叉戟上采样的 50K 个点。在这种情况下,重建(未显示)是成功的。右图:点集简化为 1K 个点然后重建(所有输入点都用法线描绘)。不重建薄特征。
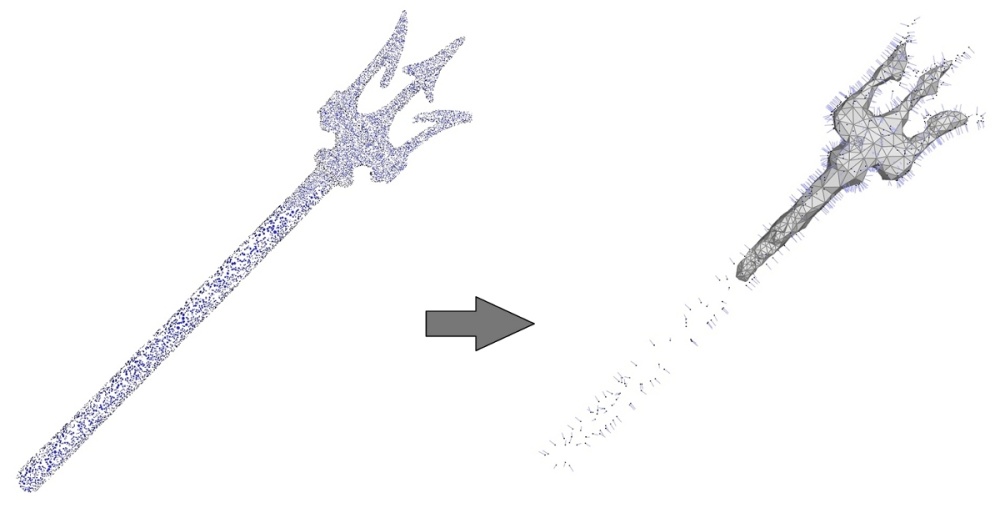

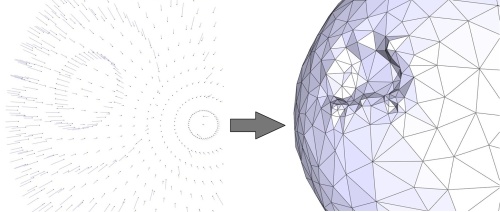
6.6 大孔
设计重构以求解隐函数,该隐函数是推断实体的近似指示函数。出于这个原因,等高线算法总是提取一个封闭的表面网格,因此能够填充数据丢失的小孔,例如,由于采集期间的遮挡。左:在手上采样了 65K 个点,在手腕底部没有捕获数据。右:重建的表面网格。该表面在手指上正确闭合,在手腕处也闭合,但以不太合理的方式闭合。
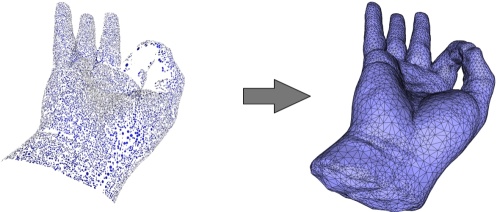
在大孔的情况下,该算法仍将它们全部关闭,但生成的分段线性隐式函数可能会出现大的三角形补丁和尖锐的折痕,因为用于求解的 3D Delaunay 三角剖分在孔被填充的地方非常粗糙。这可以通过两次通过的方法来避免。点的子集的第一遍用于获得孔处表面的近似值。然后,该表面用于计算更平滑的 3D Delaunay 三角剖分,以便使用完整的点集进行第二次传递。
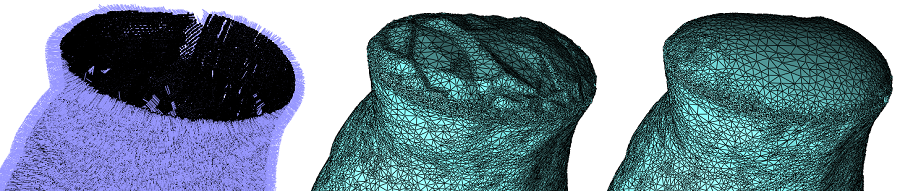
6.7 方向错误的法线
泊松曲面重建方法求解其梯度与一组输入法线最匹配的隐式函数。因为它在最小二乘意义上解决了这个问题,所以它对少数孤立的错误定向(翻转)法线具有鲁棒性。尽管如此,一簇方向错误的法线会导致不正确的隐函数,从而导致虚假的几何甚至拓扑失真。
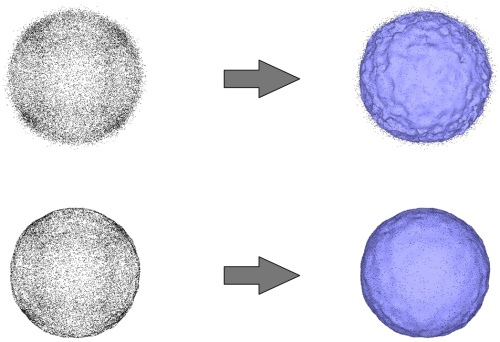
6.8 噪声和异常值
大量噪声不可避免地影响重建并且当前的实现不提供任何手段来交换数据拟合以换取平滑度。然而,如果信噪比足够高和/或为等值面轮廓设置的表面近似和大小调整参数相对于噪声水平很大,则输出表面网格将显得平滑(未显示)。如果用户想要生成平滑且详细的输出表面网格,我们建议应用平滑jet_smooth_point_set()。
左上角:在球体上采样并被大量噪声损坏的点。右上角:重建的表面网格。左下角:平滑点集。右下:重建的表面网格。
对于大量异常值,故障案例(未显示)转化为虚假的小连接组件和推断表面附近的大量失真。在这种情况下,必须通过remove_outliers() 移除异常值。
6.9 尖锐的折痕
当前的重建算法无法恢复推断表面中存在的尖锐折痕和拐角。这转化为平滑的尖锐折痕。
左:在具有尖锐特征(折痕、飞镖和角)的机械零件上采样的 5K 个点。右图:具有平滑折痕的重建表面网格。








 该文介绍了CGAL库中的泊松表面重建方法,该方法用于将带有法线的3D点集转换为隐函数,并通过等值线提取表面网格。文章详细阐述了重建过程,包括点预处理、泊松方程求解和表面提取,并讨论了理想条件、采样问题、噪声、异常值和尖锐折痕对结果的影响。
该文介绍了CGAL库中的泊松表面重建方法,该方法用于将带有法线的3D点集转换为隐函数,并通过等值线提取表面网格。文章详细阐述了重建过程,包括点预处理、泊松方程求解和表面提取,并讨论了理想条件、采样问题、噪声、异常值和尖锐折痕对结果的影响。

















 518
518

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








