Summary: Proxies ProxySelector InetAddress RIM
-Some firewalls not only prevent outsiders from getting in, but by default, prevent applications inside the firewall from opening direct socket-level connections to the outside network.
-Instead, firewalls that do this often provide a service called SOCKS (named for sockets) that acts as a proxy server for socket connections, giving the administrators more control over what connections are allowed.
-Java has built-in support for SOCKS as well as HTTP and FTP protocol proxies. set the following system properties:
| socksProxyHost | The SOCKS proxy server name. |
| socksProxyPort | The SOCKS proxy port number |
| http.proxyHost ftp.proxyHost | The proxy server name |
| http.proxyPort | The proxy port number |
-Java also has an API to allow programmatic control of Java’s use of proxies. The java.net.ProxySelector class has a method that takes a uniform resource identifier (URI) object and returns a list of java.net.Proxy objects representing the proxies.
ProxySelector ps = java.net.ProxySelector.getDefault();
List list = ps.select( new URI("http://java.sun.com/") );
System.out.println( list.get(0) );//e.g. HTTP@myserver:1234-Java utilized the static InetAddress.getByName() method to map the name to a physical IP address.
-A useful feature of InetAddress is the method isReachable() , which attempts to use the ICMP ping protocol to determine whether a remote address can be reached over the network.
InetAddress server = InetAddress.getByName("myserver");
If ( !server.isReachable( timeout ) ) // milliseconds
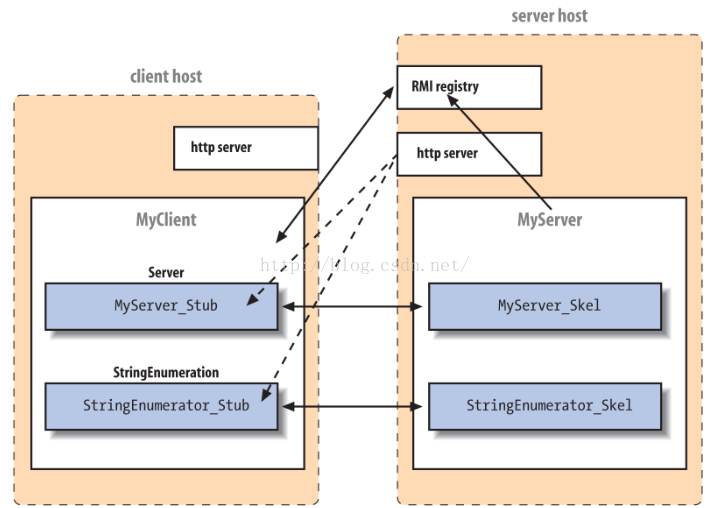
pageSomeone();-Java’s RMI mechanism does just that. It lets us get a reference to an object on a remote host and use it almost as if it were in our own virtual machine. RMI lets us invoke methods on remote objects, passing real Java objects as arguments and getting real Java objects as returned values.
-Here’s a simple example of the remote interface that defines the behavior of RemoteObject ; we give it two methods that can be invoked remotely, both of which return some kind of Value object:
import java.rmi.*;
public interface RemoteObject extends Remote {
public Value doSomething() throws RemoteException;
public Value doSomethingElse() throws RemoteException;
}-First, we need to tell RMI where to find any other classes it needs. We can use the system property java.rmi.server.codebase to specify a URL on a web server (or FTP server) when we run our client or server. we can let the client download class files as necessary.
-Next, we have to set up security. Since we are loading class files over the network and executing their methods, we must have a security manager in place to restrict the kinds of things those classes may do, at least when they are not coming from a trusted code source.
























 1545
1545

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








