Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
题目的意思是将k个有序链表合并成一个有序链表
思路:
利用归并排序,图解如下:
只不过在k链表合并中,图中的10 4 6 等元素变为了链表,需要 mergeTwoList(A,B),同理将K个链表看成是数组的K的元素,进行两两合并
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) {
if(lists.size()==0)
return NULL;
return merge(lists,0,lists.size()-1);
}
ListNode *merge(vector<ListNode *> &lists,int s,int t) //归并排序
{
ListNode *p,*q;
if(s==t) //如果指针指向同一lists,则返回
return lists[s];
else //归并核心代码
{
int m=(s+t)/2; // 找到中间点
p=merge(lists,s,m); //归并前半部分
q=merge(lists,m+1,t); //归并后半部分
return mergeTwoList(p,q); //将前后两部分合并
}
}
ListNode *mergeTwoList(ListNode *l1,ListNode *l2) //合并两个链表,这部分代码为上一个题中的源代码,直接拿来用的
{
if(l1==NULL)
return l2;
if(l2==NULL)
return l1;
ListNode *p,*q;
p=l1;
q=l2;
ListNode *result=new ListNode(0);
ListNode *temp =result;
while(p&&q)
{
if(p->val<q->val)
{
temp->next=p;
temp=p;
p=p->next;
}
else
{
temp->next=q;
temp=q;
q=q->next;
}
}
if(p)
{
temp->next=p;
}
if(q)
{
temp->next=q;
}
return result->next;
}
};时间复杂度分析: 下表为常见递推关系
| 算法 | 递推关系式 | 运算时间 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 折半搜索 |  | 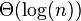 | 情形二(k = 0) |
| 二叉树遍历 | 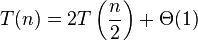 |  | 情形一 |
| 归并排序 |  | 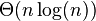 | 情形二(k = 0) |
这里有一个快速记忆方法:
T(n) = aT(n/b)+c(n^d) 这里的 n^d为合并的开销 在上面的K链表合并中 n^d 为 O(nK)
那么就可以得到问题的复杂度为:
- T(n) = O(n^d log(n)), if a = b^d
- T(n) = O(n^d ), if a < b^d
- T(n) = O(n^logb(a))), if a > b^d
所以时间复杂度为 nklogk
空间复杂度:
由于没进行一个合并 都创建了一个节点 为
k/2 + k/4 + k/8 +........
为 k























 1404
1404











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








