Logistic Regression
34.62365962451697,78.0246928153624,0
30.28671076822607,43.89499752400101,0
35.84740876993872,72.90219802708364,0
60.18259938620976,86.30855209546826,1
79.0327360507101,75.3443764369103,1
45.08327747668339,56.3163717815305,0
61.10666453684766,96.51142588489624,1
75.02474556738889,46.55401354116538,1
76.09878670226257,87.42056971926803,1
84.43281996120035,43.53339331072109,1
95.86155507093572,38.22527805795094,0
75.01365838958247,30.60326323428011,0
82.30705337399482,76.48196330235604,1
69.36458875970939,97.71869196188608,1
39.53833914367223,76.03681085115882,0
53.9710521485623,89.20735013750205,1
Visualization
现有一些数据,如上所示为部分数据。表示申请大学的学生的某两门课程的成绩,和申请的result。
我们先plot一下手上的数据获得一个直观的感觉
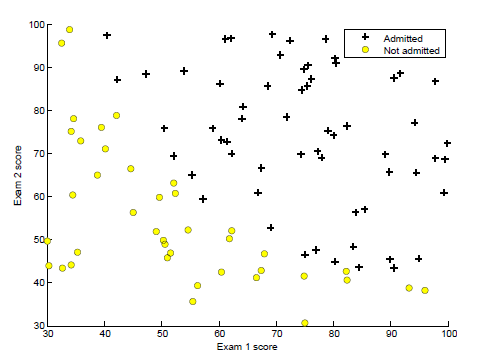
function plotData(X, y)
%PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure
% PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples
% and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix.
% Create New Figure
figure; hold on;
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a
% 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive
% examples and 'ko' for the negative examples.
%
% Find Indices of Positive and Negative Examples
pos = find(y==1); neg = find(y == 0);
% Plot Examples
plot(X(pos, 1), X(pos, 2), 'k+','LineWidth', 2, ...
'MarkerSize', 7);
plot(X(neg, 1), X(neg, 2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', ...
'MarkerSize', 7);% =========================================================================
hold off;
end
这里学习find函数的用法,它返回所有满足条件的元素的index
对于单行或者单列的矩阵find()直接返回对应的index组成的单行或单列的矩阵
对于多行多列矩阵[x,y]=find(),可以分别获得行号列号
对于plot画图,可以参考
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_3eb5b46a0100flq4.html
sigmoid function

function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid functoon
% J = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z.
% You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).
g = (1 + e.^(-1 *z)).^(-1);
% =============================================================
end
Cost Function & Gradient
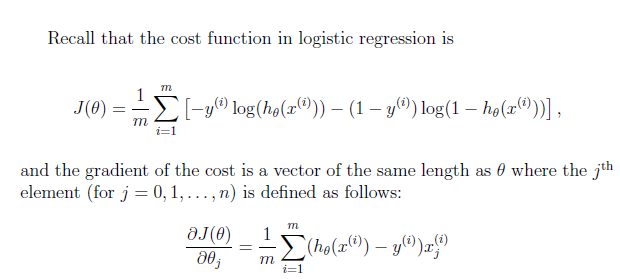
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%
h = sigmoid(X*theta);
J = m^-1 * sum(((-1) * y.*log(h)).-((1- y).*log(1 - h)));
grad = m^-1 * ((h.-y)'*X)';
% =============================================================
end
X每行代表一个example,每列表示一个feature,第一列是增广列常数1,而y只有一列,theta有一列,这就是矩阵的格式套进公式即可。
由于后文要使用系统内置的函数所以这里有标准输出cost function 和 gradient
Learning Parameters using fminunc
Octave’s fminunc is an optimization solver that finds the minimum of an unconstrained function. For logistic regression, you want to optimize the cost function J() with parameters .Concretely, you are going to use fminunc to find the best parameters for the logistic regression cost function, given a fixed dataset (of X and y values). You will pass to fminunc the following inputs:
The initial values of the parameters we are trying to optimize.
A function that, when given the training set and a particular , computes the logistic regression cost and gradient with respect to for the dataset(X, y)
下面是部分ex2.m 的code,由于标准的fminunc只会给costfunction传递一个参数就是theta,所以这里有一点特殊处理。
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial theta, options);
下面看一下计算得到的theta画出来的decision boundary

function plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y)
%PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY Plots the data points X and y into a new figure with
%the decision boundary defined by theta
% PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY(theta, X,y) plots the data points with + for the
% positive examples and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be
% a either
% 1) Mx3 matrix, where the first column is an all-ones column for the
% intercept.
% 2) MxN, N>3 matrix, where the first column is all-ones
% Plot Data
plotData(X(:,2:3), y);
hold on
if size(X, 2) <= 3
% Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints
plot_x = [min(X(:,2))-2, max(X(:,2))+2];
% Calculate the decision boundary line
plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
% Plot, and adjust axes for better viewing
plot(plot_x, plot_y)
% Legend, specific for the exercise
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary')
axis([30, 100, 30, 100])
else
% Here is the grid range
u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50);
v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50);
z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = 1:length(u)
for j = 1:length(v)
z(i,j) = mapFeature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
end
end
z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour
% Plot z = 0
% Notice you need to specify the range [0, 0]
contour(u, v, z, [0, 0], 'LineWidth', 2)
end
hold off
end
到目前为止,只用了plot decision boundary的一半,另一半是给后面画椭圆形decision boundary的时候用的,采用等高线的画法。
Predict
预测给定数据,既分类。
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1)
m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%
p_medium = sigmoid(X*theta);
pos = find(p_medium >= 0.5);
p(pos,1)=1;
% =========================================================================
end
Regularized logistic regression
Visualization
这里使用的数据是一个工厂对生产的芯片进行的质量检查相关数据,包含2次不同测试的结果和是否合格产品的结果
0.051267,0.69956,1
-0.092742,0.68494,1
-0.21371,0.69225,1
-0.375,0.50219,1
-0.51325,0.46564,1
-0.52477,0.2098,1
-0.39804,0.034357,1
-0.30588,-0.19225,1
0.016705,-0.40424,1
0.13191,-0.51389,1
0.38537,-0.56506,1
0.52938,-0.5212,1
0.63882,-0.24342,1
0.73675,-0.18494,1
0.54666,0.48757,1
0.322,0.5826,1
0.16647,0.53874,1
-0.046659,0.81652,1
-0.17339,0.69956,1
-0.47869,0.63377,1
-0.60541,0.59722,1
-0.62846,0.33406,1
-0.59389,0.005117,1
-0.42108,-0.27266,1
-0.11578,-0.39693,1
0.20104,-0.60161,1
0.46601,-0.53582,1
0.67339,-0.53582,1
Feature mapping
这里非常重要的一步,直接决定了最终是否可以得到一个比较吻合的model

Cost function and gradient
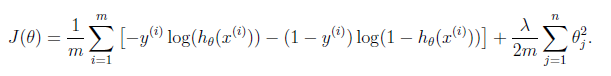

function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
h = sigmoid(X*theta);
t = theta(2:length(theta),1);
J = m^-1 * sum(((-1) * y.*log(h)).-((1- y).*log(1 - h))) + 0.5*(lambda/m) * sum(t.^2);
grad = m^-1 * ((h.-y)'*X)';
tmp = grad;
tmp = tmp + (lambda/m)*theta;
grad = [grad(1,1);tmp(2:length(theta),1)];
% =============================================================
end
注意第一个theta不需要进行regularization就好,cost function中不要加上theta0,计算gradient的时候也要保持theta0和没有regularization的时候update是一样的。
Ploting the decision boundary
这里就使用的是上面函数的第二部分了。另外就是lamda取不同的值,可以从下面开得到对于fitting的影响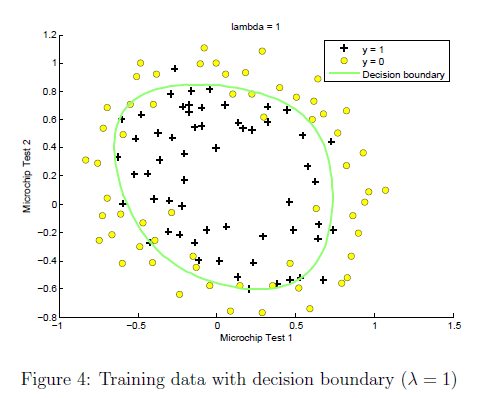
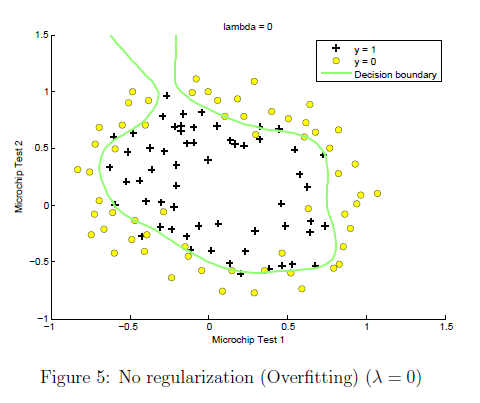
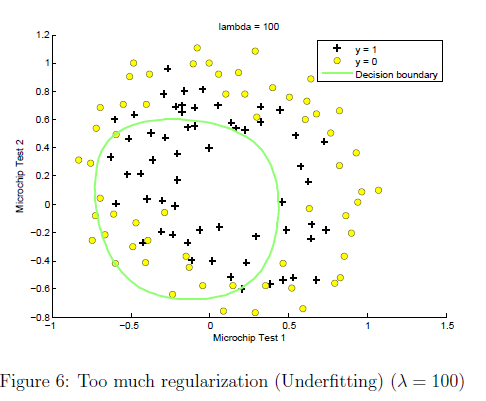
% =============================================================
ex2.m 第一部分的主函数
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 2: Logistic Regression
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the logistic
% regression exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% sigmoid.m
% costFunction.m
% predict.m
% costFunctionReg.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Load Data
% The first two columns contains the exam scores and the third column
% contains the label.
data = load('ex2data1.txt');
X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = data(:, 3);
%% ==================== Part 1: Plotting ====================
% We start the exercise by first plotting the data to understand the
% the problem we are working with.
fprintf(['Plotting data with + indicating (y = 1) examples and o ' ...
'indicating (y = 0) examples.\n']);
plotData(X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Exam 1 score')
ylabel('Exam 2 score')
% Specified in plot order
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted')
hold off;
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============ Part 2: Compute Cost and Gradient ============
% In this part of the exercise, you will implement the cost and gradient
% for logistic regression. You neeed to complete the code in
% costFunction.m
% Setup the data matrix appropriately, and add ones for the intercept term
[m, n] = size(X);
% Add intercept term to x and X_test
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
% Compute and display initial cost and gradient
[cost, grad] = costFunction(initial_theta, X, y);
fprintf('Cost at initial theta (zeros): %f\n', cost);
fprintf('Gradient at initial theta (zeros): \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', grad);
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============= Part 3: Optimizing using fminunc =============
% In this exercise, you will use a built-in function (fminunc) to find the
% optimal parameters theta.
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
% Print theta to screen
fprintf('Cost at theta found by fminunc: %f\n', cost);
fprintf('theta: \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', theta);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Exam 1 score')
ylabel('Exam 2 score')
% Specified in plot order
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted')
hold off;
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============== Part 4: Predict and Accuracies ==============
% After learning the parameters, you'll like to use it to predict the outcomes
% on unseen data. In this part, you will use the logistic regression model
% to predict the probability that a student with score 45 on exam 1 and
% score 85 on exam 2 will be admitted.
%
% Furthermore, you will compute the training and test set accuracies of
% our model.
%
% Your task is to complete the code in predict.m
% Predict probability for a student with score 45 on exam 1
% and score 85 on exam 2
prob = sigmoid([1 45 85] * theta);
fprintf(['For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict an admission ' ...
'probability of %f\n\n'], prob);
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
ex2_reg.m 第二部分的主函数
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 2: Logistic Regression
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the second part
% of the exercise which covers regularization with logistic regression.
%
% You will need to complete the following functions in this exericse:
%
% sigmoid.m
% costFunction.m
% predict.m
% costFunctionReg.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Load Data
% The first two columns contains the X values and the third column
% contains the label (y).
data = load('ex2data2.txt');
X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = data(:, 3);
plotData(X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
% Specified in plot order
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0')
hold off;
%% =========== Part 1: Regularized Logistic Regression ============
% In this part, you are given a dataset with data points that are not
% linearly separable. However, you would still like to use logistic
% regression to classify the data points.
%
% To do so, you introduce more features to use -- in particular, you add
% polynomial features to our data matrix (similar to polynomial
% regression).
%
% Add Polynomial Features
% Note that mapFeature also adds a column of ones for us, so the intercept
% term is handled
X = mapFeature(X(:,1), X(:,2));
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1
lambda = 1;
% Compute and display initial cost and gradient for regularized logistic
% regression
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);
fprintf('Cost at initial theta (zeros): %f\n', cost);
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============= Part 2: Regularization and Accuracies =============
% Optional Exercise:
% In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and
% see how regularization affects the decision coundart
%
% Try the following values of lambda (0, 1, 10, 100).
%
% How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does
% the training set accuracy vary?
%
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this)
lambda = 1;
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
这里map feature的程序,要看一看
function out = mapFeature(X1, X2)
% MAPFEATURE Feature mapping function to polynomial features
%
% MAPFEATURE(X1, X2) maps the two input features
% to quadratic features used in the regularization exercise.
%
% Returns a new feature array with more features, comprising of
% X1, X2, X1.^2, X2.^2, X1*X2, X1*X2.^2, etc..
%
% Inputs X1, X2 must be the same size
%
degree = 6;
out = ones(size(X1(:,1)));
for i = 1:degree
for j = 0:i
out(:, end+1) = (X1.^(i-j)).*(X2.^j);
end
end
end% =========================================================================
end
================================================================
等高线与decision boundary





















 537
537

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








